Recent Articles
-
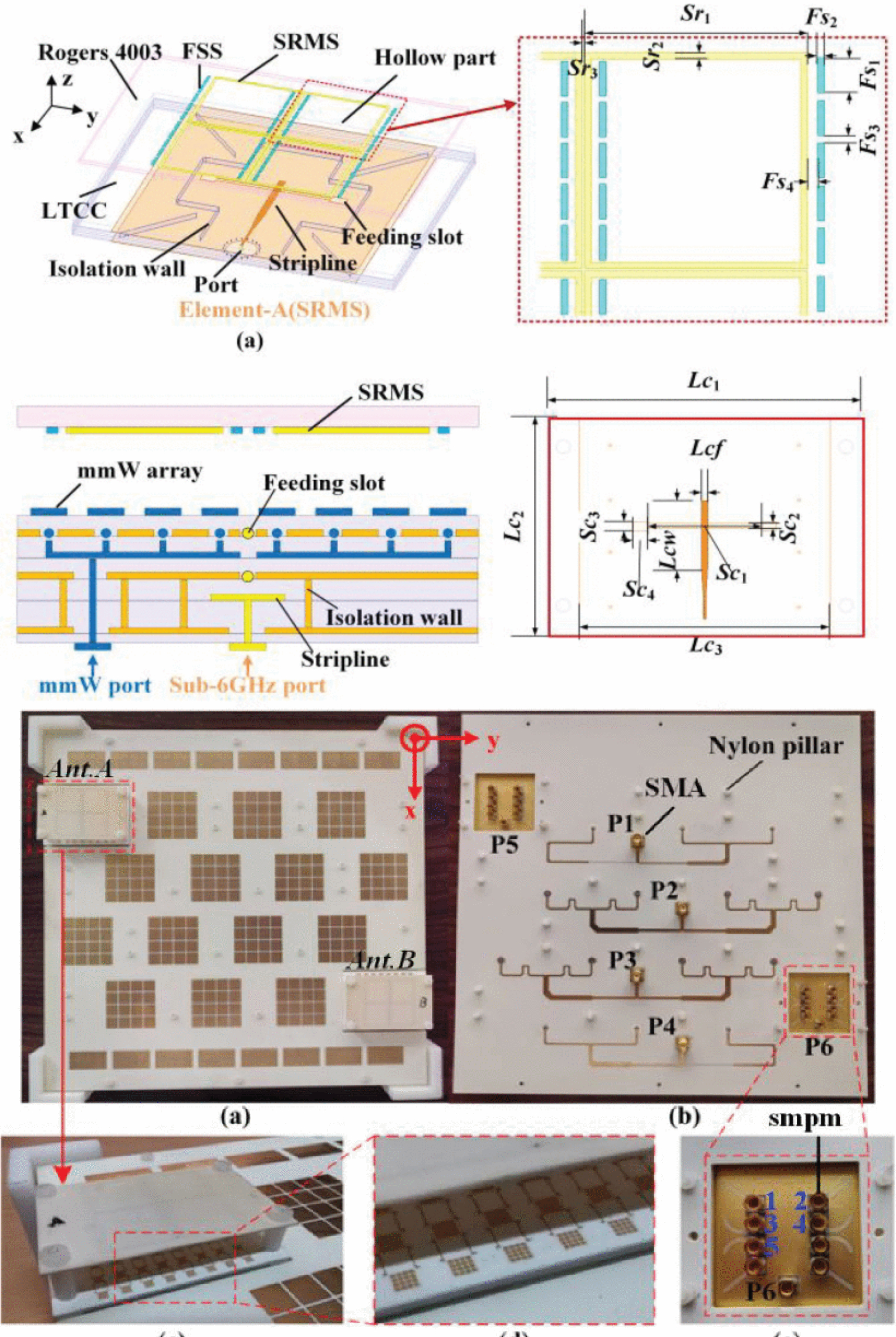
Dual-Band and Dual Wide-Angle Scanning Heterogeneous Metasurface-Based Antenna Array in Large Frequency Ratio Integrating With Millimeter-Wave Phased Arrays in Same Aperture
22 September 2025 Li Wei, Wanchen Yang, Guoping Tan, Chujun Liang, Zhongying Wang and Wenquan Che present a 4×4 Sub-6GHz heterogeneous metasurface-based array integrated with 8×8 millimeter-wave (mmW) phased array within same aperture. Firstly, two heterogeneous Sub-6GHz antenna elements are designed based on a square ring metasurface (SRMS) and an overlapped metasurface (OLMS), respectively. The SRMS-based antenna is stacked above the 8×8 mmW array without occupying additional space, while the feeding networks of the Sub-6GHz and mmW antennas are also integrated together in one package using the low-temperature-cofired ceramic (LTCC) technology.
-
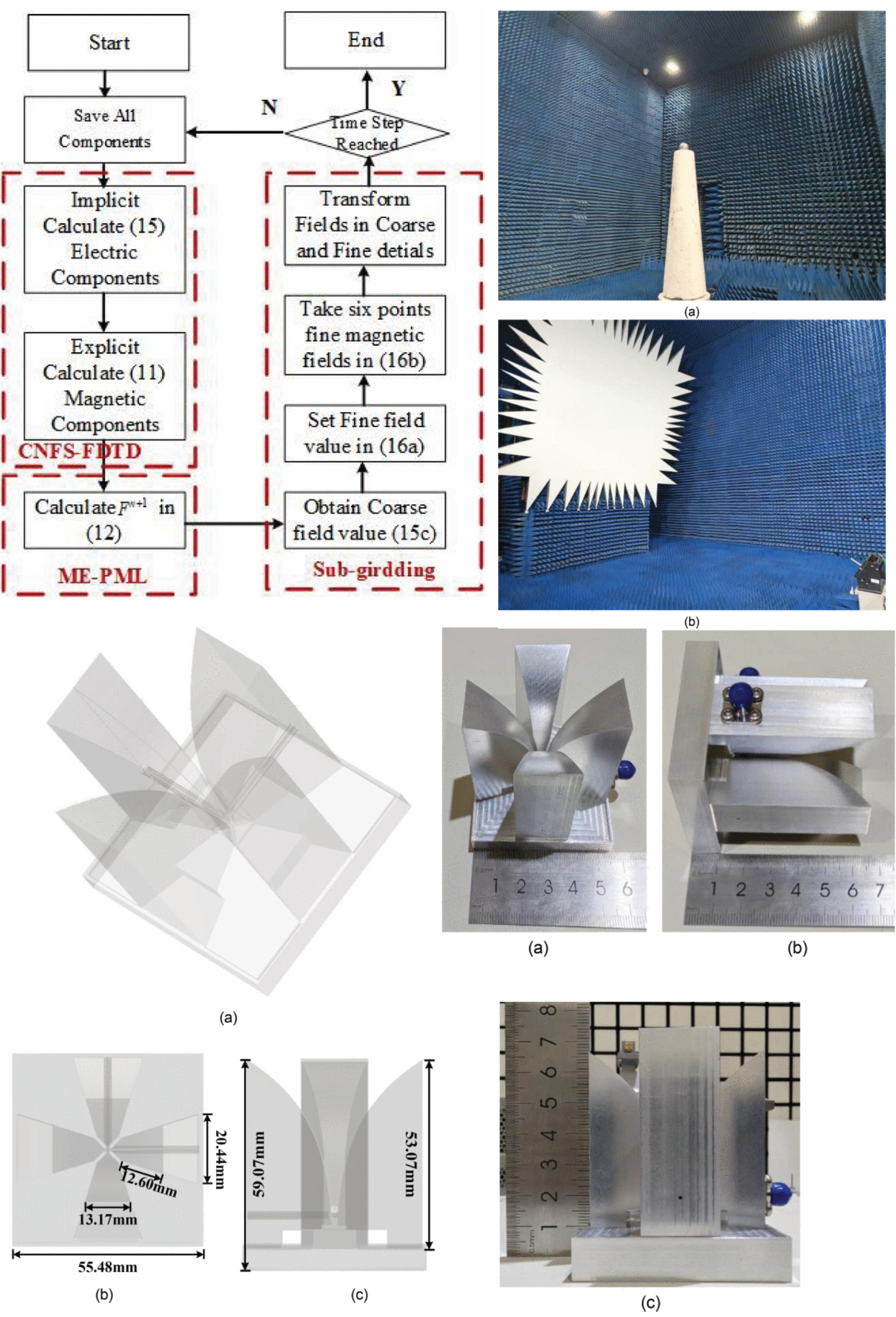
Higher-Order Matrix Exponential Perfectly Matched Layer Scheme With Sub-Gridding Technique Based on the Factorization Approximate Crank–Nicolson Algorithm
18 September 2025 Weikang Si, Hao Lei, Haolin Jiang, Yongjun Xie, Weilong Wang and Peiyu Wu develops an unconditionally stable Crank–Nicolson factorization-splitting (CNFS) algorithm with a higher-order perfectly matched layer (PML) scheme. The higher-order PML is formulated through the matrix exponential (ME) method, which requires fewer operators and less manipulation than the existing implementation. To analyze the fine details and curves, the sub-gridding technique is modified through the unconditionally stable CNFS algorithm. Introducing nonuniform mesh sizes inside the computational domains improves the efficiency without degrading the computational accuracy.
-
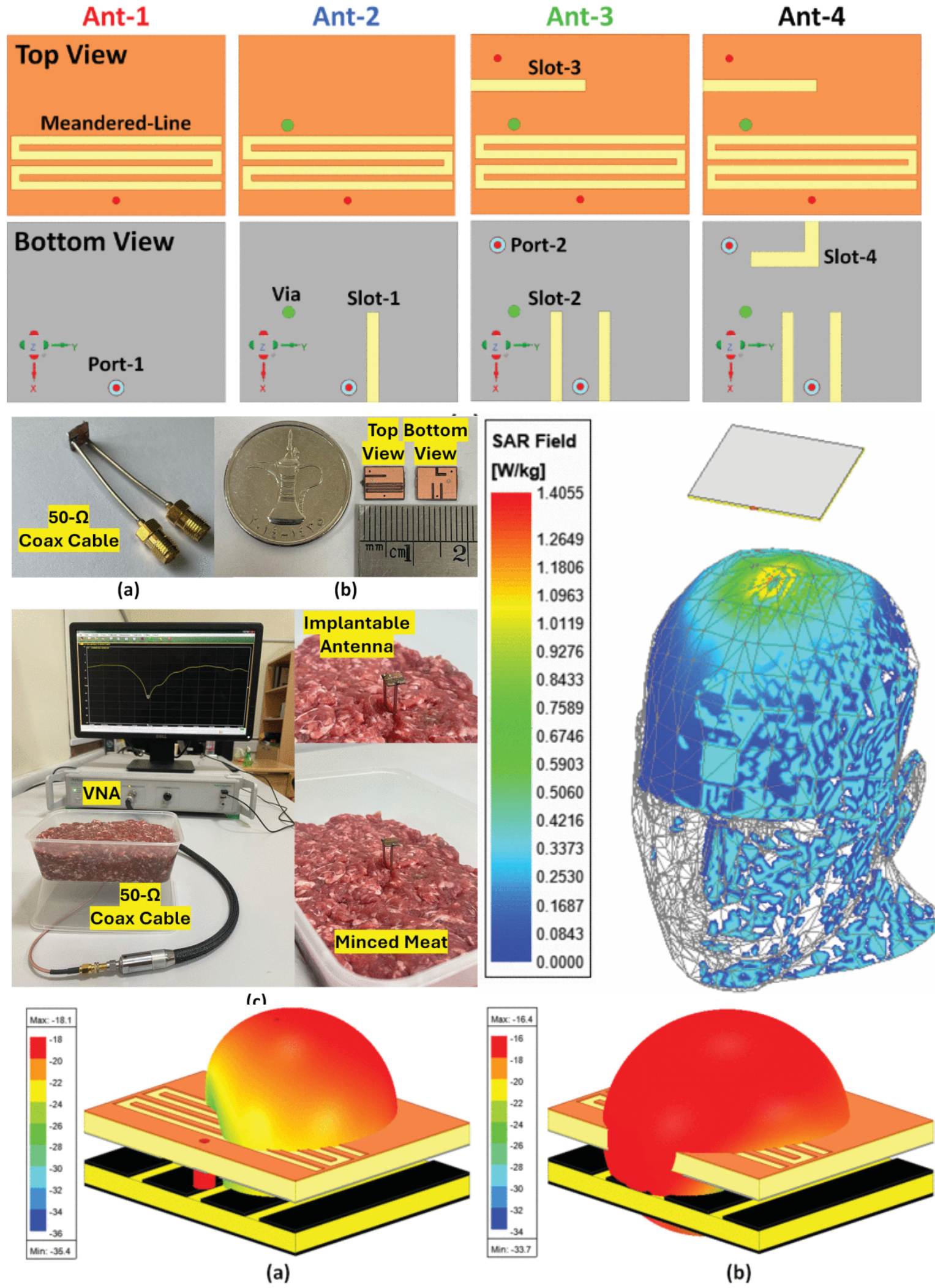
A Compact Tissue-Insensitive Ultra-Wideband Implantable Antenna for Wireless Power Transfer in Implantable Medical Devices
18 September 2025 Amine Essa, Eqab Almajali, Feras Barneih, Jawad Yousaf, Rony E. Amaya and Soliman Mahmoud present the development of a new, compact, two-port ultra-wideband implantable antenna with low sensitivity to implanting tissue and depth for energy harvesting applications in implantable medical devices (IMD). The proposed antenna features two compact radiating elements, operating at a center frequency of 2.45 GHz and occupying a very compact volume of 22.1 mm3 ( 7.25×6×0.508 mm3). Miniaturization techniques such as meandered line slots, Defected Ground Structure (DGS), and shorting via were utilized to achieve this compactness.
-
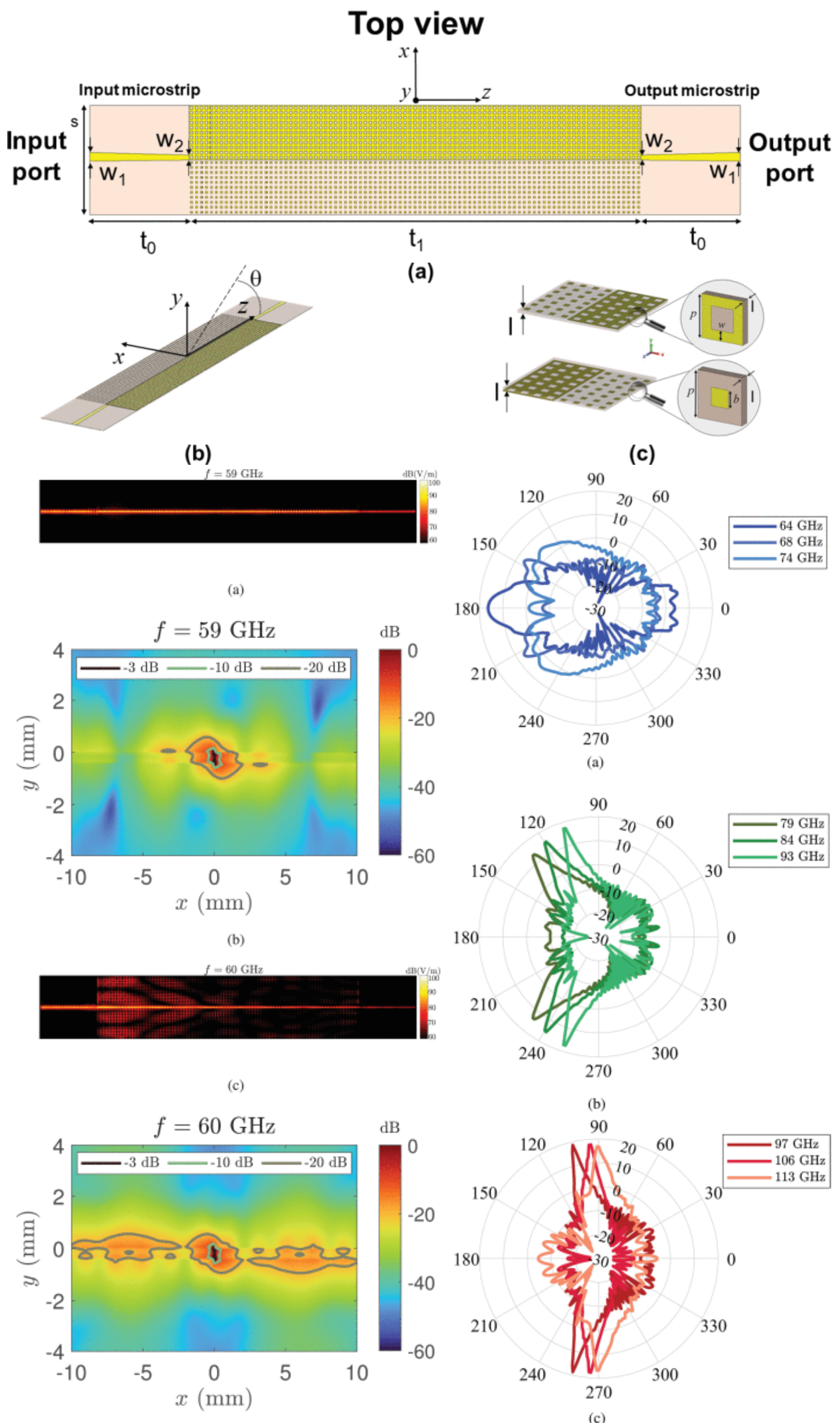
Wideband Modal Analysis of a Double-Layer Line-Wave Waveguide: Dispersive Properties and Radiative Effects
16 September 2025 Mikhail Madji, Paolo Baccarelli, Alessio Monti, Alessandro Toscano, Filiberto Bilotti and Paolo Burghignoli present a broadband modal analysis of a double-layer line-wave waveguide constituted by two center-symmetric pairs of inductive and capacitive metasurfaces with the aim of characterizing the dispersive and radiative properties of the relevant line-wave mode both inside and outside the metasurface homogenization limit. To this aim, a finite length of the waveguide, excited at both ports through suitable microstrip transitions, is first simulated with a commercial solver. Then, a numerical fitting of the field along the waveguide axis is performed using exponential functions, in order to retrieve the wavenumbers and excitation coefficients of the modal line wave and of its higher order space harmonics.
-
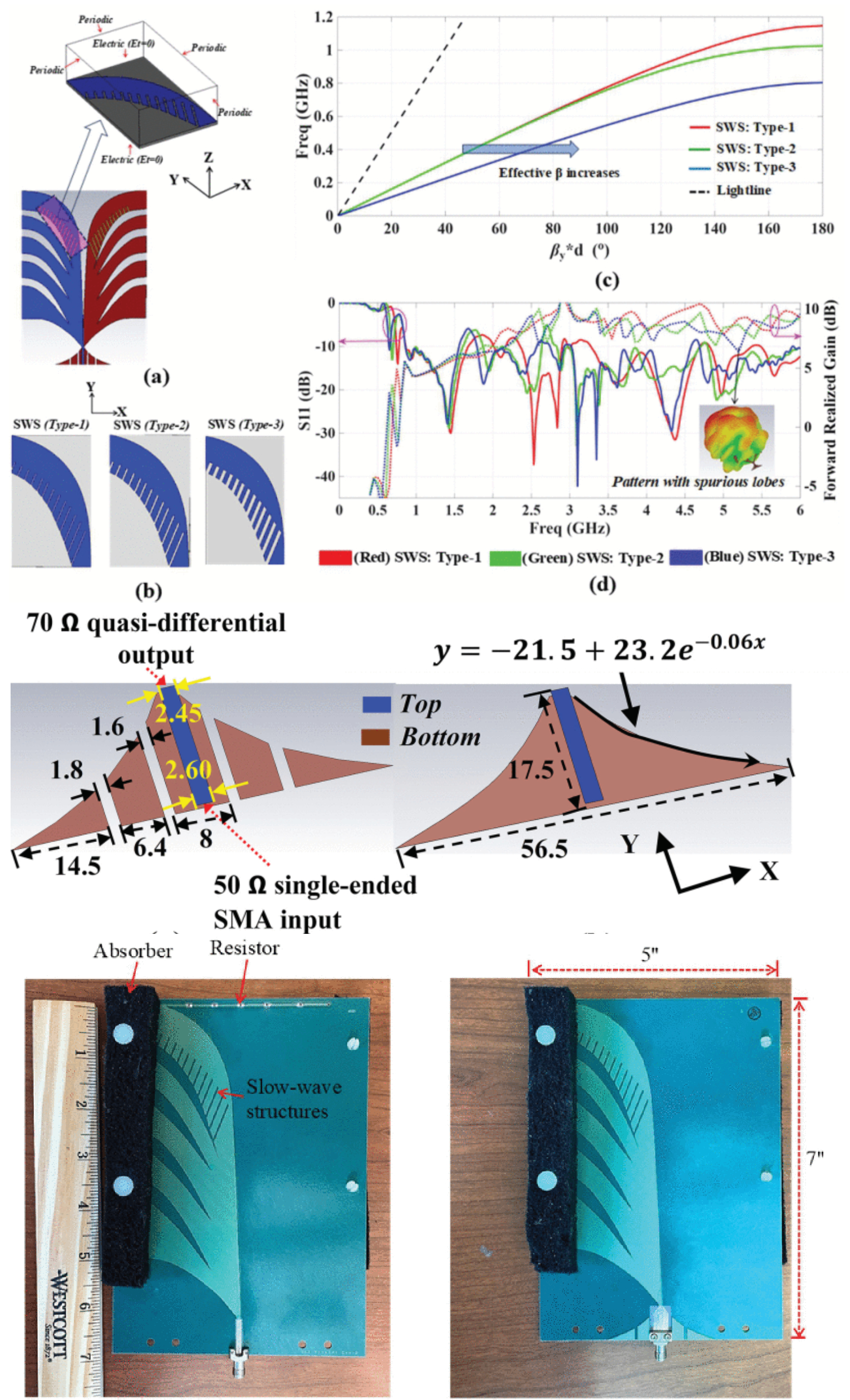
An Electrically Highly Compact Ultra-Wideband Vivaldi Antenna With Substantial Gain Performance
11 September 2025 Ababil Hossain, Samuel Wagner, Stephen Pancrazio and Anh-Vu Pham present the design, analysis, fabrication, and measurement of an electrically highly compact ultrawideband Vivaldi antenna. The overall dimensions of the antenna are 0.21λ0×0.15λ0×0.002λ0 , where λ0 refers to the free space wavelength corresponding to the lowest operating frequency. The antenna has been designed and optimized with full-wave electromagnetic simulation and fabricated on a low-loss RT/duroid5880 substrate. They apply a novel aperture modification that embeds slow-wave structures in traditional tapered slots to achieve enhanced miniaturization in a Vivaldi antenna.
-
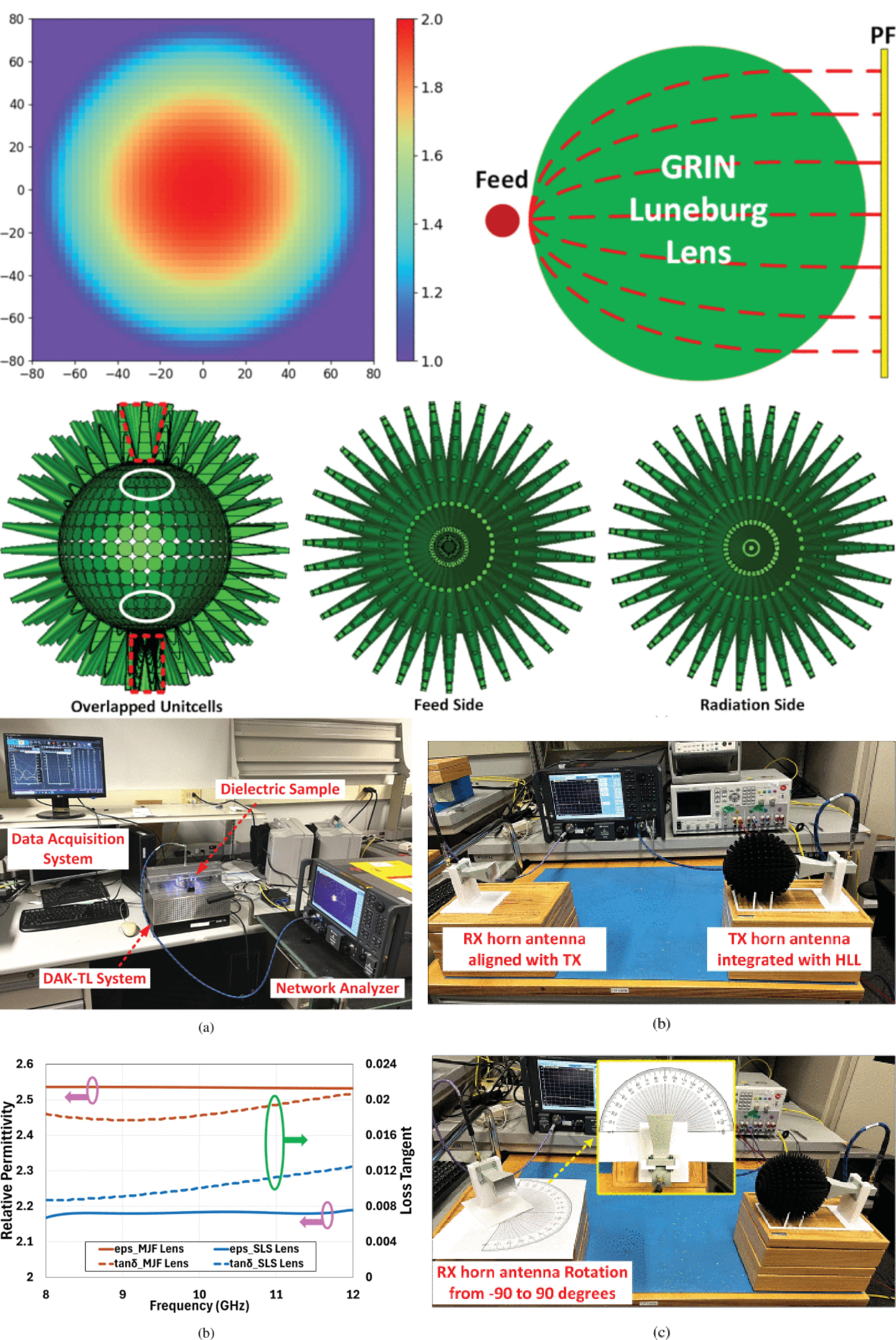
Uniformly 3-D-Printed Low-Cost Hedgehog Spherical Lens Antenna
10 September 2025 Mohammad Omid Bagheri, Erik Yann Harmgarth, Omar M. Ramahi, Yahia M. M. Antar and George Shaker present a design strategy for a low-profile, low-cost, uniformly 3D-printed dielectric spherical lens antenna, tailored for high-gain communication applications. The proposed approach employs a cost-effective and modified fabrication process inspired by the Hedgehog form to simplify the traditional gradient-index (GRIN) permittivity distribution. This simplification is achieved through a spherical array of tapered dielectric rods with constant relative permittivity exposed to air, utilizing the concept of effective permittivity equivalence over conventional GRIN techniques.
-
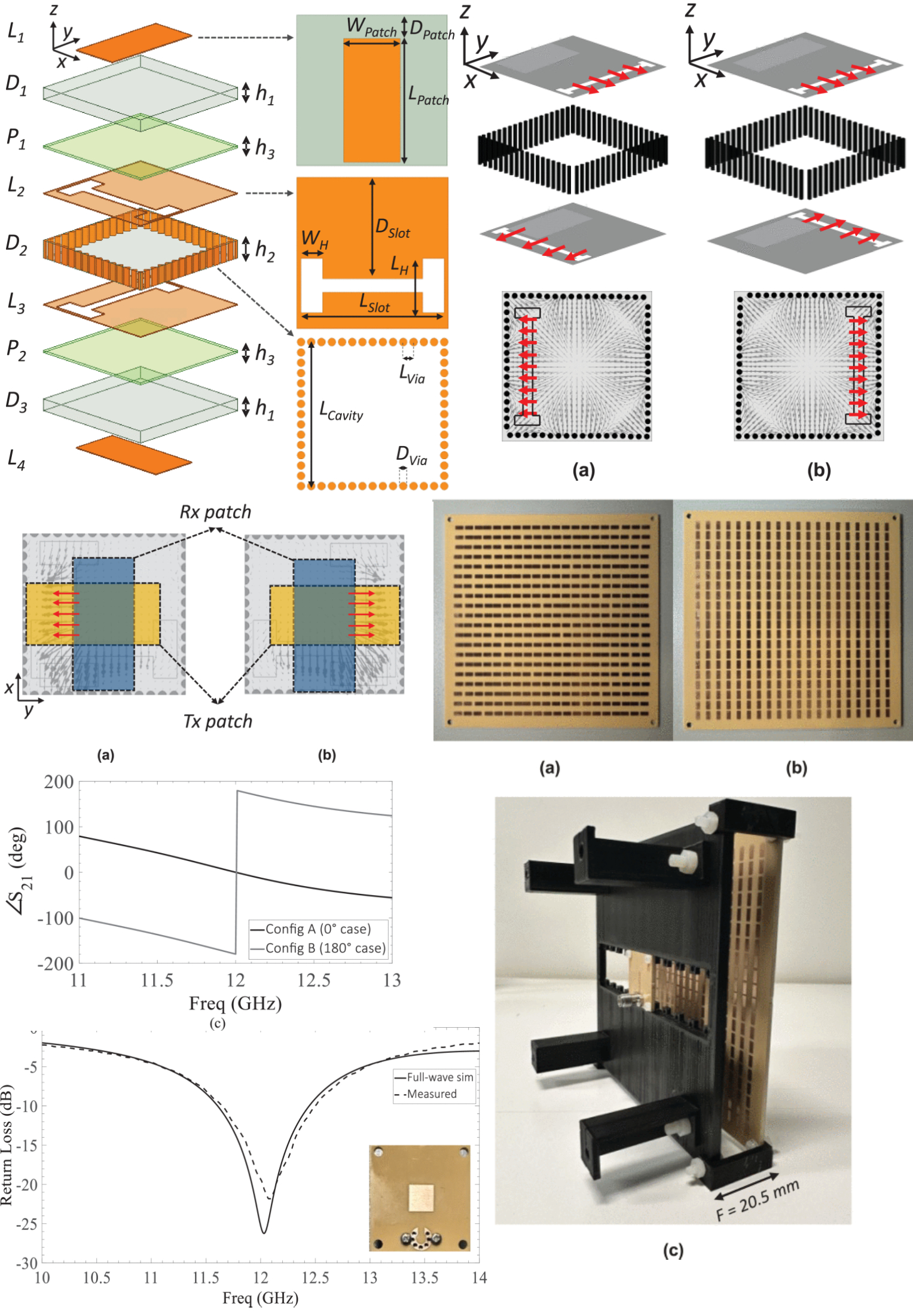
Sub-Wavelength Unit-Cell for Ultra-Low F/D Ratio Transmitarray Antenna
10 September 2025 R. de Marco, A. Bordbar, M. Gokdemir, Emilio Arnieri, Giandomenico Amendola and Luigi Boccia propose a novel sub-wavelength transmitarray antenna (TA) unit-cell based on Substrate Integrated Waveguide (SIW) cavity integrated frequency selective surface. The unit-cell is implemented with a single Printed Circuit Board (PCB) featuring four metal layers. Two patch antennas are used as receiving and transmitting elements and they are coupled through a SIW cavity placed between them. The unit-cell operates at 12 GHz and its periodicity is 0.22λ o ×0.22λ o. The high miniaturization results from the combination of the SIW cavity features and the Frequency Selecting Surface (FSS) formed by aperture coupled resonators. Specifically, the SIW cavity is used to achieve a dual-configuration unit-cell, each one with 180 degrees phase range.
-
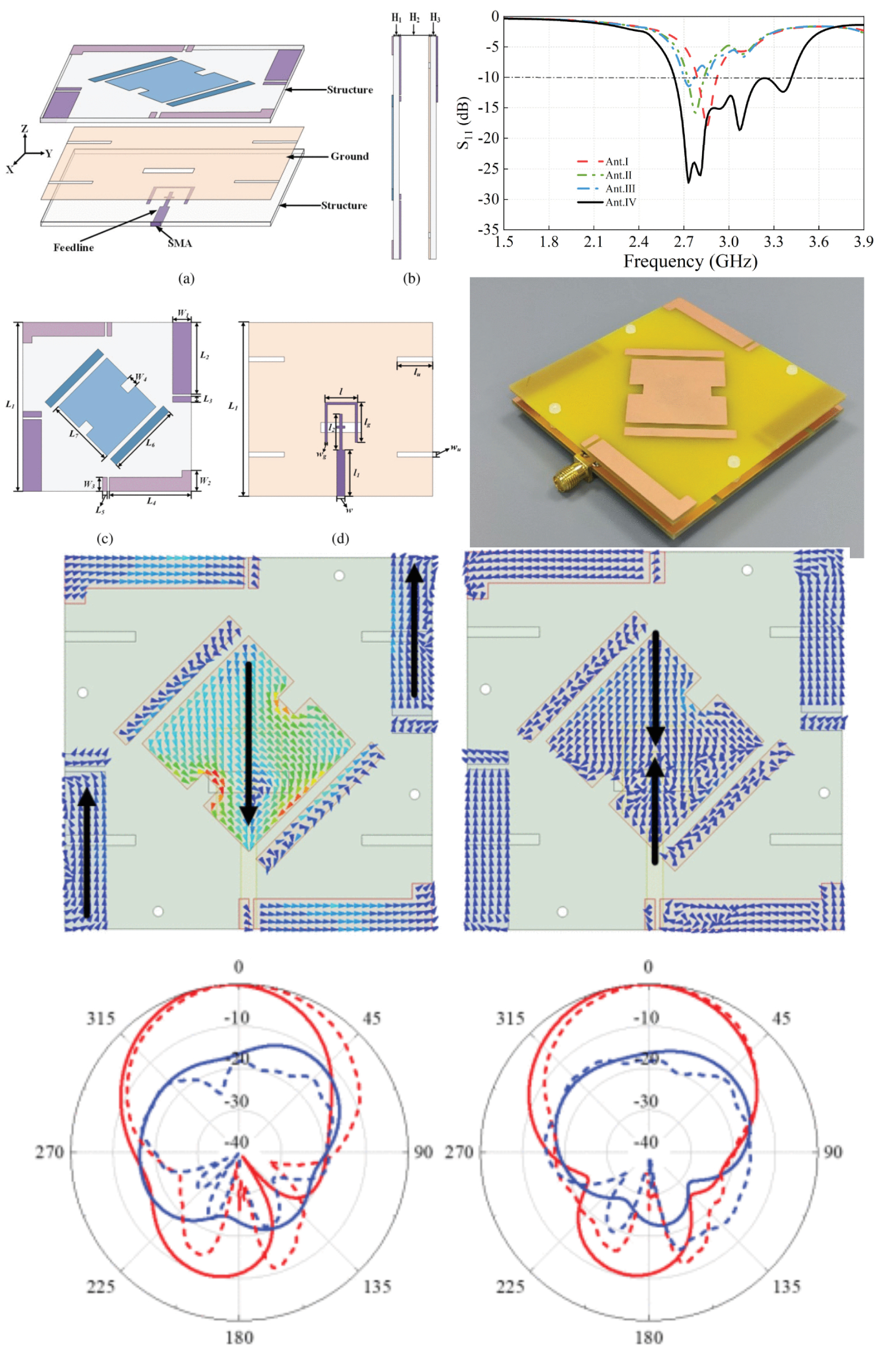
Broadband Filtering Circularly Polarized Patch Antenna Based on Ground Slot and Coupling Stub
08 September 2025 Xianjing Lin, Wenyong Liu, Zuhao Jiang and Weichao Kuang presents a broadband filtering circularly polarized (CP) patch antenna based on a ground slot and coupling stub. The antenna achieves three CP radiation modes by employing a + 45° rotated slotted main radiating patch printed on the upper dielectric substrate, along with a pair of + 45° aligned rectangular parasitic patches and surrounding microstrip patches. Without requiring additional filtering circuits, the antenna introduces a controllable radiation null at the lower band through four rectangular slots etched at the edges of the ground plane on the lower substrate.
-
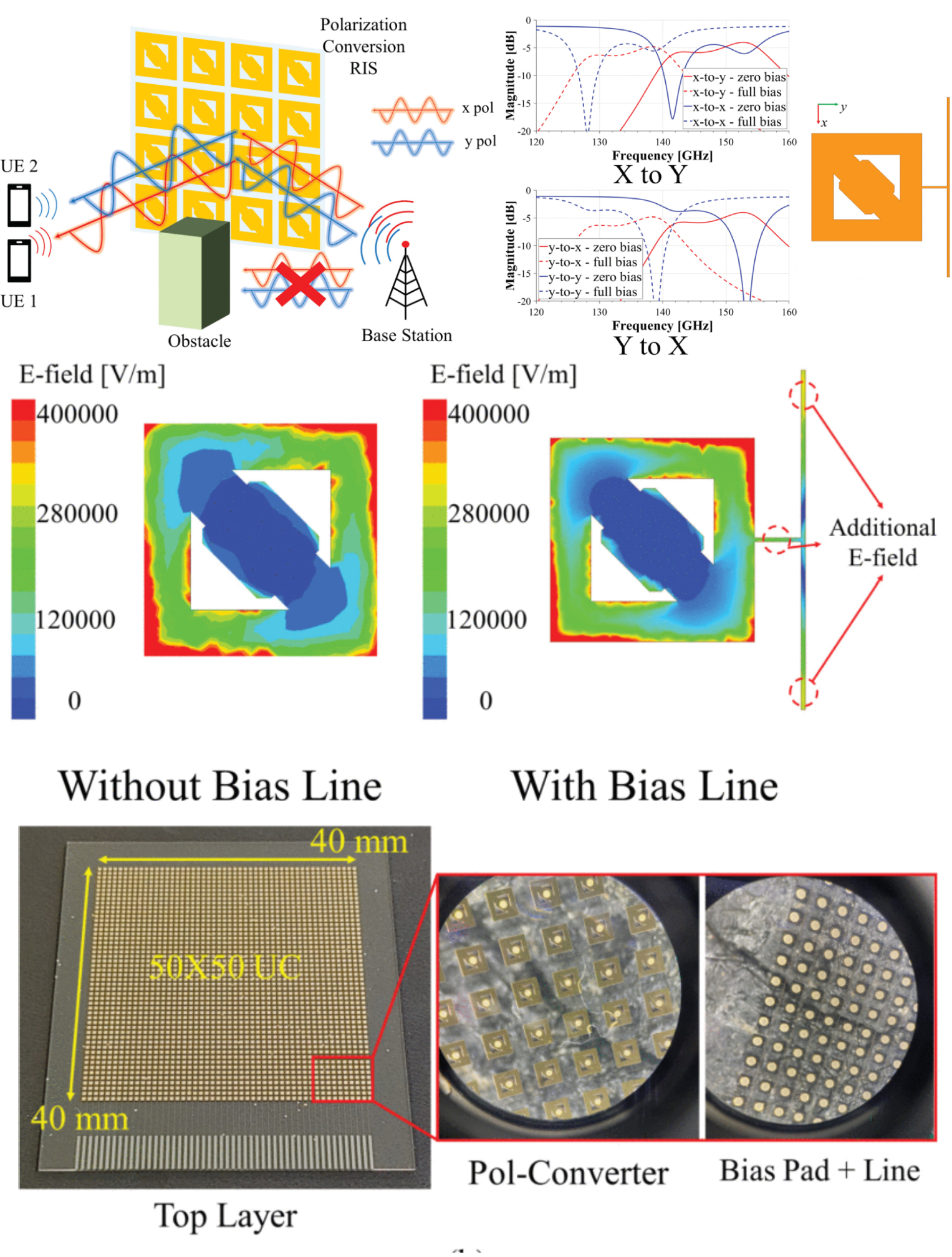
Design and Experimental Validation of a Through-Quartz Via-Based LC RIS for Dual-Polarization Beam Steering in Sub-Terahertz Bands
08 September 2025 Byeongju Moon, Seungwoo Bang, Seongwoog Oh and Jungsuek Oh present a liquid crystal (LC)-based reconfigurable intelligent surface (RIS) capable of simultaneously achieving dual-polarization conversion and beam steering, enabled by through-quartz vias (TQVs). The proposed RIS offers two primary functionalities-dynamic beam steering and polarization conversion-both of which are validated through full-wave simulations and experimental measurements. A tunable LC layer is employed as the dielectric substrate for each unit cell to facilitate beam steering, while bias lines are used to apply external electric fields to the LC medium. To prevent degradation in polarization conversion performance, the bias lines are connected to the patterned copper structures via TQVs embedded within the quartz substrate.
-
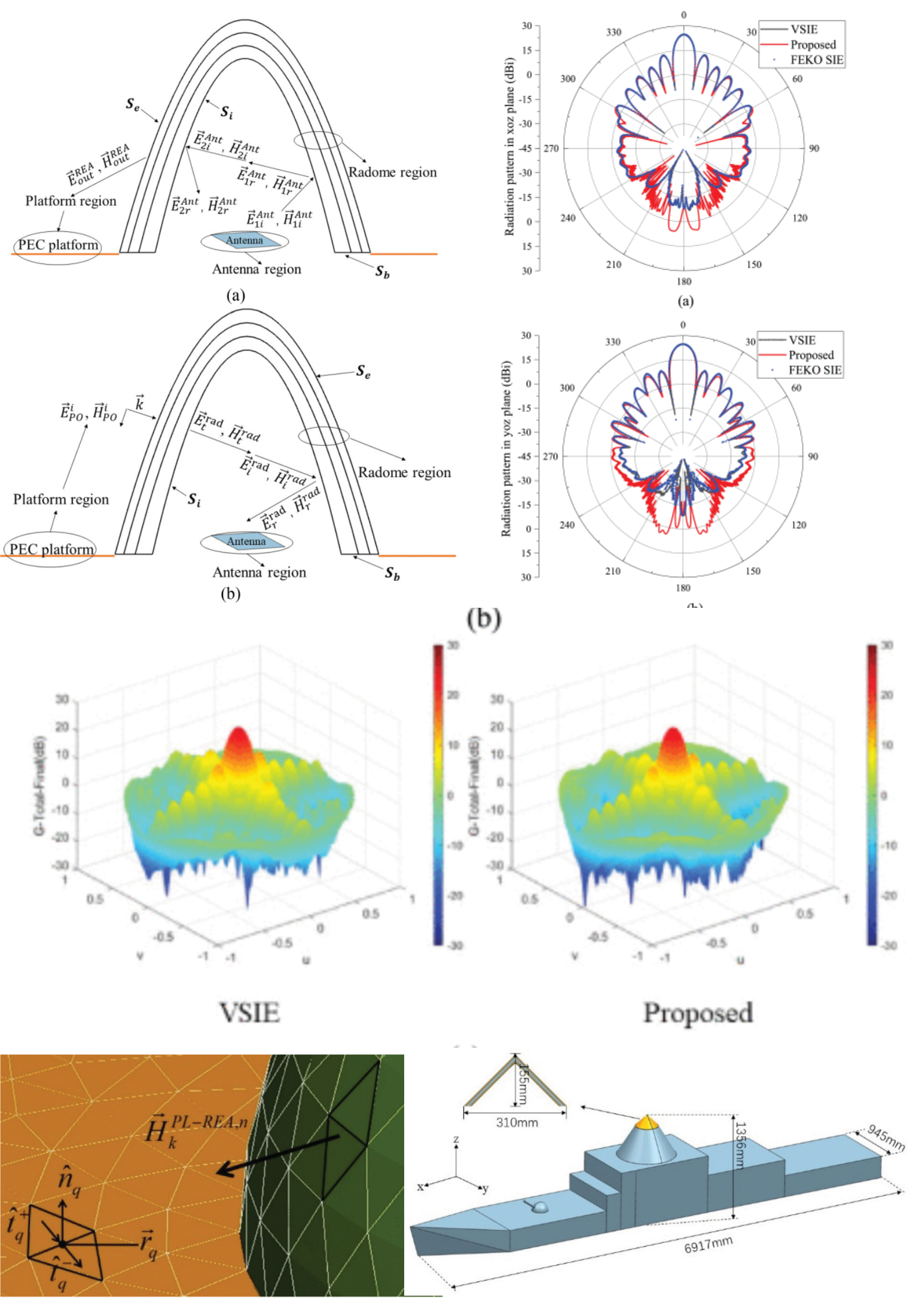
Modeling of Complex Radome-Enclosed Antennas Mounted on Large-Size Platform Using Double-Nested Iterative VSIE-MSI-PO Method
05 September 2025 Haiwen Ke, Pengyuan Wang, Jintong Liu, Weidong Hu and Mang He present a novel double-nested iterative hybrid method that combines the volume-surface integral equation (VSIE), the modified surface integration (MSI) method, and the physical optics (PO) to analyze electromagnetic (EM) radiation of radome-enclosed antennas (REA) installed on large-size perfect electric conductor (PEC) platforms. The entire target is firstly decomposed into the antenna, radome, and platform regions according to the structural characteristics of respective parts. The full-wave VSIE is used to analyze the complex antenna, and the MSI is applied to model the multilayer dielectric radome of arbitrary shape.