-
Guest Editorial: Introduction to the Special Section on Modeling, Analysis, and Design Methods for Embedded Antennas in IoT Wireless Devices
06 November 2025Jaume Anguera, Martijn Van Beurden and Miloslav Capek present the continuous evolution of wireless communication systems, particularly within the domains of the Internet of Things (IoT) and advanced aerospace platforms, has intensified the demand for compact, efficient, and versatile antenna solutions. Conventional full-wave electromagnetic simulations, though precise, are often computationally expensive and time-consuming, posing limitations in scenarios requiring rapid prototyping and integration into constrained form factors. To overcome these challenges, recent research has advanced a variety of innovative methodologies, including machine learning–assisted antenna performance prediction, automated and synthesis-based design of matching networks, antenna booster technologies, and reconfigurable architectures. Furthermore, novel strategies for polarization and bandwidth enhancement have been proposed to ensure robust performance under diverse operational conditions. Collectively, these contributions highlight a paradigm shift in antenna engineering, where efficiency, adaptability, and design automation are prioritized alongside traditional performance metrics. The papers included in this special section reflect this transition, presenting state-of-the-art approaches that significantly reduce design complexity while achieving high performance across a wide range of wireless applications.
-
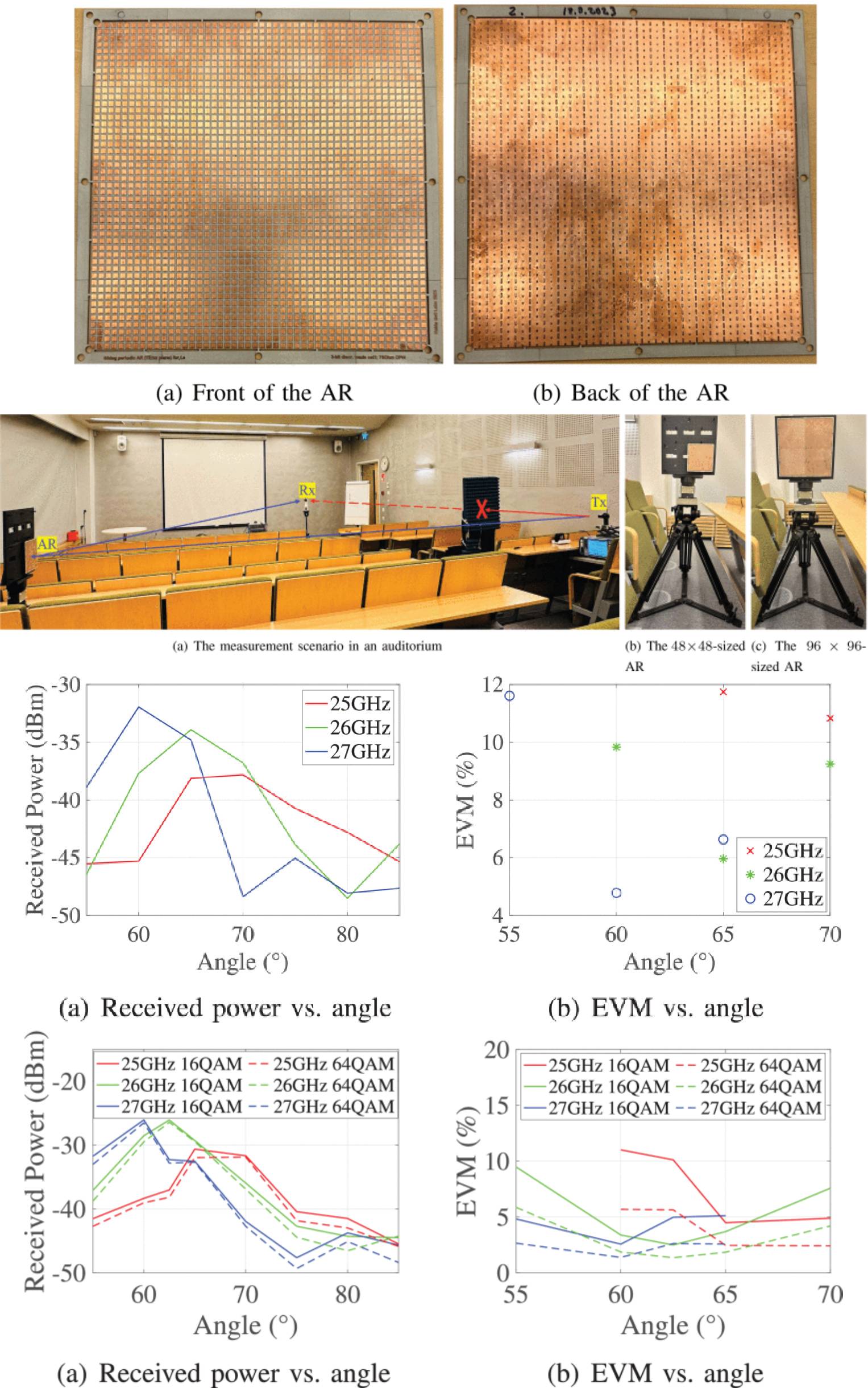
Analysis of Scalable Electromagnetically-Modeled Anomalous Reflectors Through Ray Tracing and Measurements
11 August 2025Le Hao, Sravan Kumar Reddy Vuyyuru, Sergei A. Tretyakov, Markus Rupp and Risto Valkonen elaborate on the concept of a scalable anomalous reflector to analyze the angular response, frequency response, and spatial scalability of a designed anomalous reflector across a broad range of angles and frequencies. We utilize theoretical models and ray tracing simulations to investigate the communication performance of two different-sized scalable finite anomalous reflectors, one smaller configuration with 48×48 array of unit cells and the other constructed by combining four smaller anomalous reflectors to form a larger array with 96×96 unit cells. To validate the theoretical approach developed, we conducted measurements in an auditorium to evaluate the received power through an anomalous reflector link at different angles and frequencies.
-
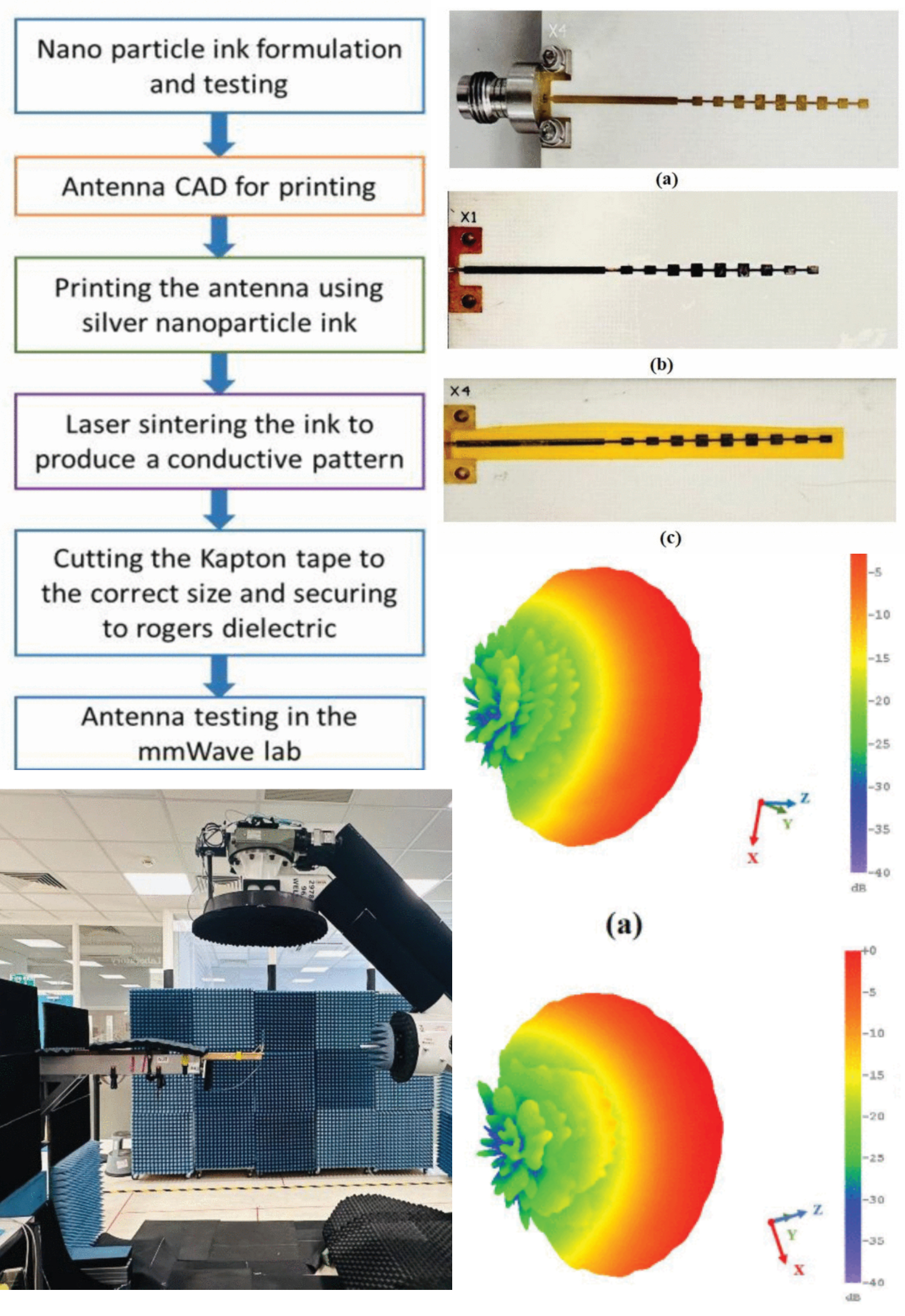
Additive Manufacturing on Kapton Substrate for Rapid Prototyping of Low-Cost mmWave Antennas
31 July 2025 Sumin David Joseph, Benedict Davies, Matthew Davies, Edward A. Ball and Jon. R. Willmott investigate the potential of aerosol jet printing for rapid prototyping of millimeter-wave antennas. Traditionally, antenna design and production require extensive simulation and multiple prototyping stages to achieve the desired radiation pattern and bandwidth performance, with each iteration incurring material costs. In this work, a commercial aerosol jet printer, as a direct write additive manufacturing tool, was used to create antenna arrays on Rogers substrate and Kapton tape. A 9-element series-fed patch array with amplitude tapering based on the Dolph-Chebyshev method was designed.
-
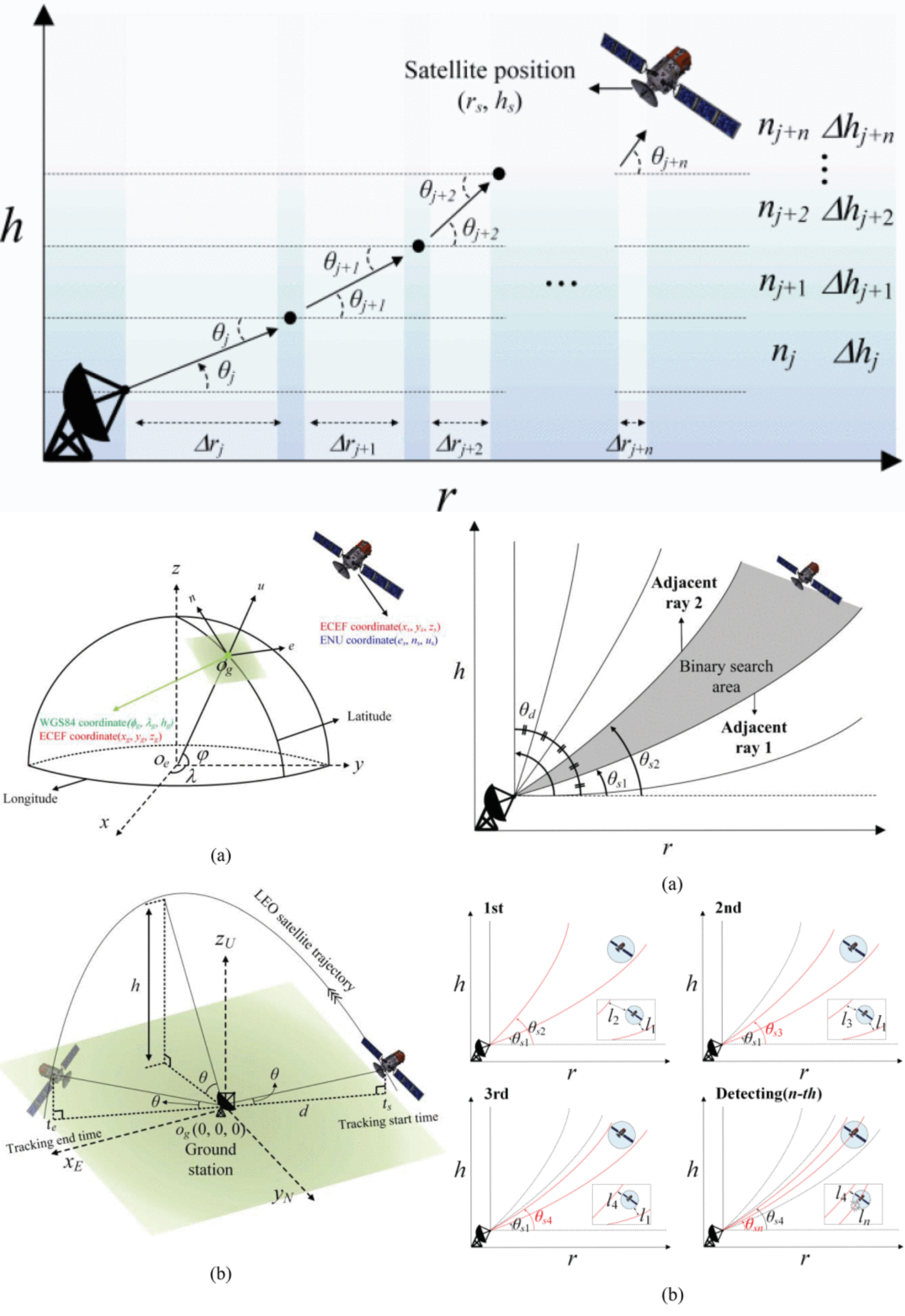
Analysis of LEO Satellite Detection Errors Considering Atmospheric Environment
30 July 2025 Jongho Keun, Doyoung Jang and Hosung Choo propose a ray-tracing method to estimate a propagation path between a ground station and low-Earth-orbit (LEO) satellites. To accurately predict a propagation path and detection error, the proposed ray-tracing method adopts an atmospheric refractivity model that includes not only the troposphere but also the ionosphere. Herein, atmospheric refractivity in the troposphere is the measurement data obtained from weather observatories in Korea. In addition, atmospheric refractivity in the ionosphere is obtained from the simplified Appleton-Hartree equation. The detection angle errors are examined by changing various conditions, such as the locations of ground stations, satellite trajectories, and observation date.
-
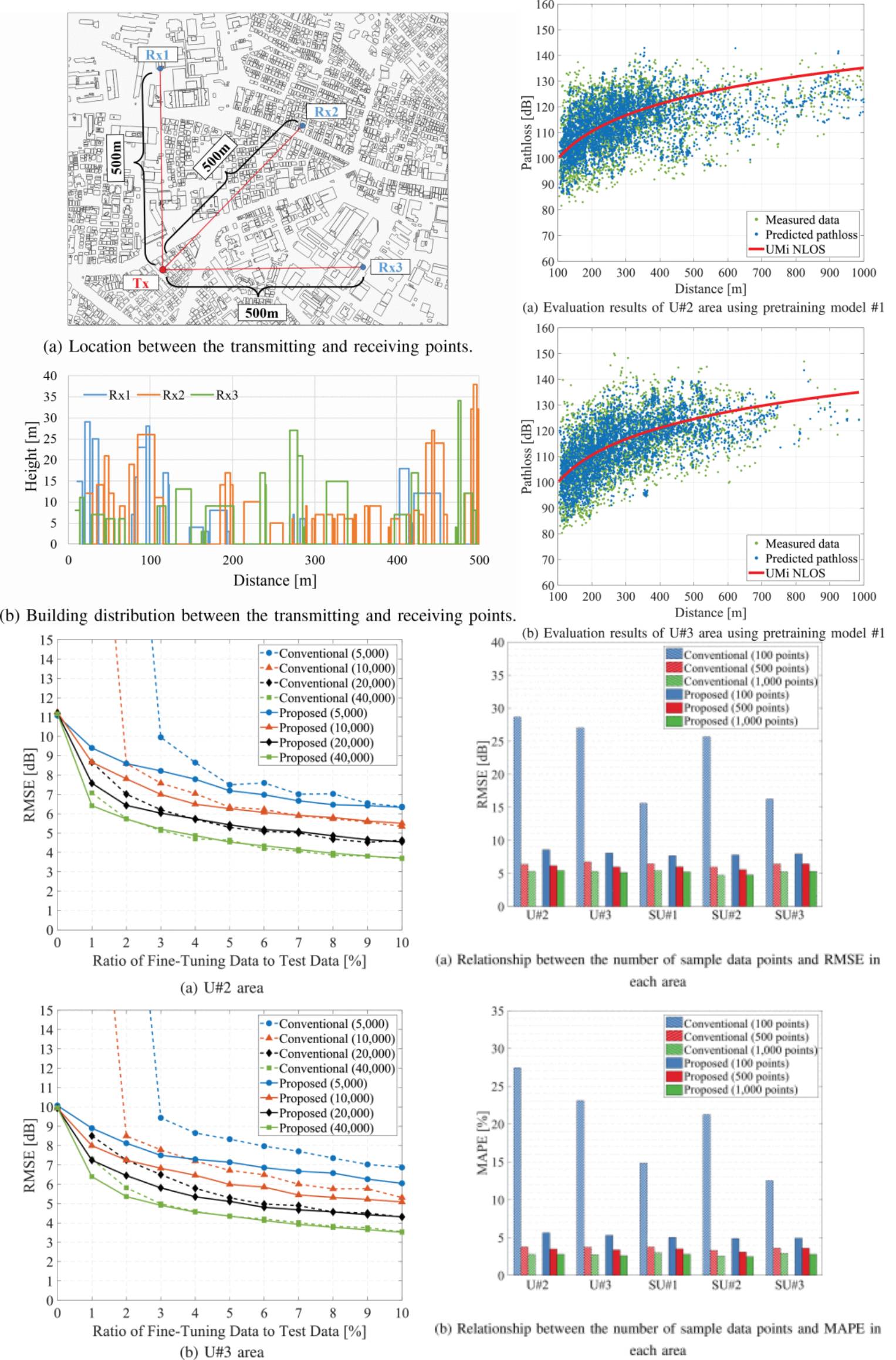
Fine-Tuning Approach to Configuration and Data Selection for Path Loss Prediction in Different Geographical Environments
28 July 2025 Takahiro Hayashi and Koichi Ichige developed a site-specific path loss model by using machine learning in conjunction with spatial information data and environmental parameters related to propagation characteristics. They proposed a fine-tuning method that transfers a machine learning model constructed in a specific environment to a new environment and refines it through an effective data selection technique. Evaluating the measurement data at 2 GHz revealed that the proposed method achieves higher estimation accuracy than does the conventional method when a model pretrained in a specific environment in an urban area is applied to other urban and suburban areas, with only 1% of the test data required as additional training data.
-
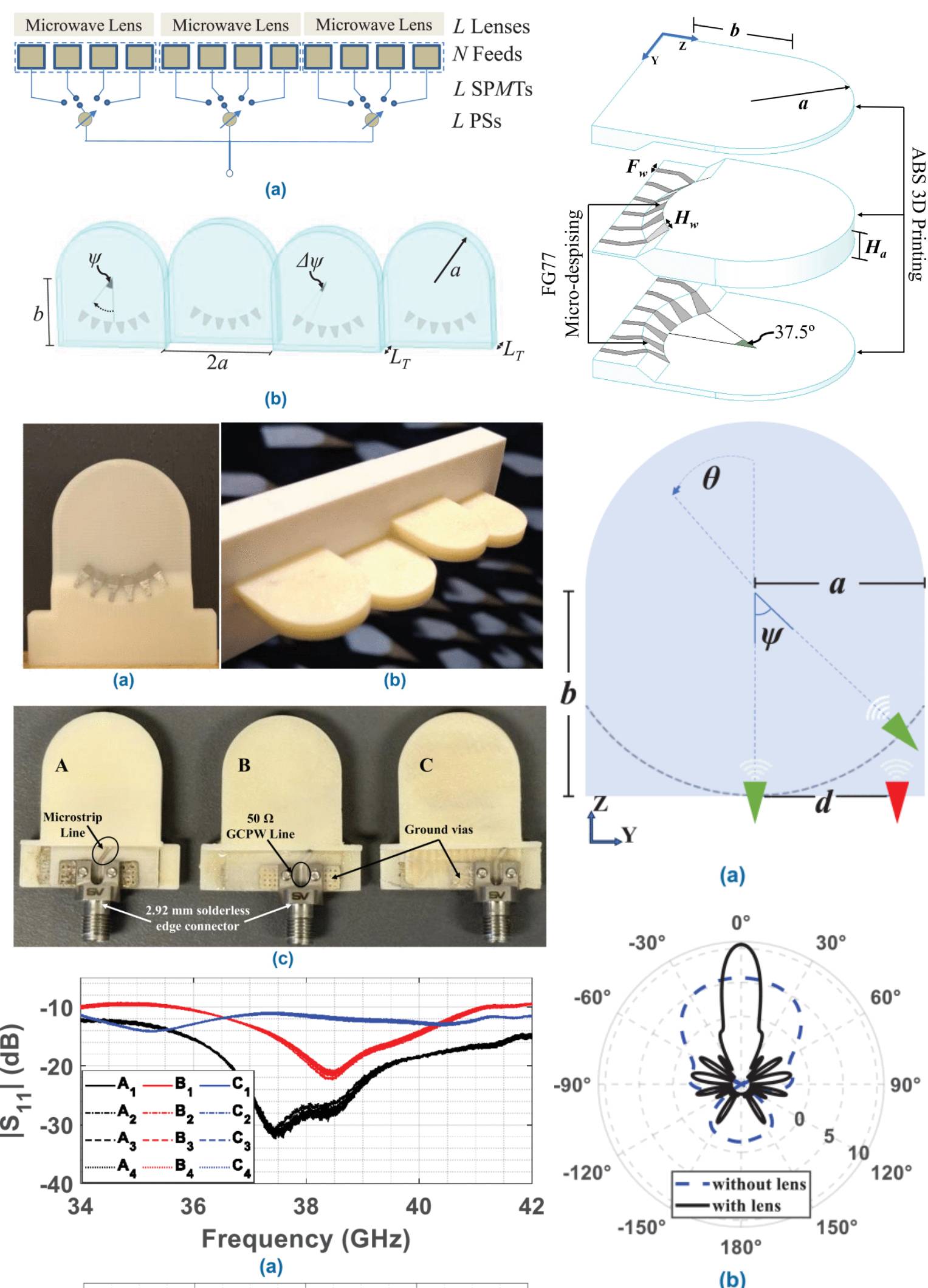
Fully 3D-Printed mm-Wave Wide-Angle 1D Beam-Steering Antenna Using Zigzagged Lens Antenna Subarrays With Curved Focal Surfaces
28 July 2025 Omar Jebreil, Ruoke Liu and Gökhan Mumcu resents a fully 3D-printed wideband mm-wave beam-steering antenna concept capable of performing wide-angle electronic beam-steering by making use of zigzagged lens antenna subarrays (LASs) with curved focal surfaces. The concept is demonstrated through the design and realization of a 38 GHz antenna consisting of L=4 dielectric slab waveguide (DSW) lenses each fed with structurally embedded M=6 TEM horn antennas, which can effectively reduce the required number of phase shifters (PSs) from N=M×L=24 to L=4. It is demonstrated that the joint utilization of zigzagged LAS and curved focal surfaces with structurally integrated TEM horn antennas, all enabled through the design flexibilities offered by the emerging additive manufacturing (AM) technology, improves the realized gain, side lobe level (SLL), and beam-steering range in comparison to the earlier versions realized with planar focal surfaces.
-

A Topology-Based Array Compensation Empowered by Equivalent Current Modeling of TM₁₀ Patch Antennas for Cross-Polarization Reduction
24 July 2025 Taeyeong Yoon, Uichan Park, Minje Kim, Sanghun Lee, Young-Seok Lee, Sangwook Nam and Jungsuek Oh introduce a comprehensive analysis of cross-polarization effects originating from current imbalances in patch antennas and array configurations. A simplified yet broadly applicable mitigation strategy is proposed, offering a generalized approach to improve cross-polarization performance for antenna arrays operating in the TM10 mode. In contrast to earlier works that predominantly employed heuristic array rotation techniques, the present work adopts a systematic modeling approach to elucidate and regulate cross-polarization across a wide range of array scales and topologies. By utilizing electric current modeling at both the single-element and array levels, and analyzing radiation behavior in multiple planes, the beam pattern characteristics are thoroughly examined.
-
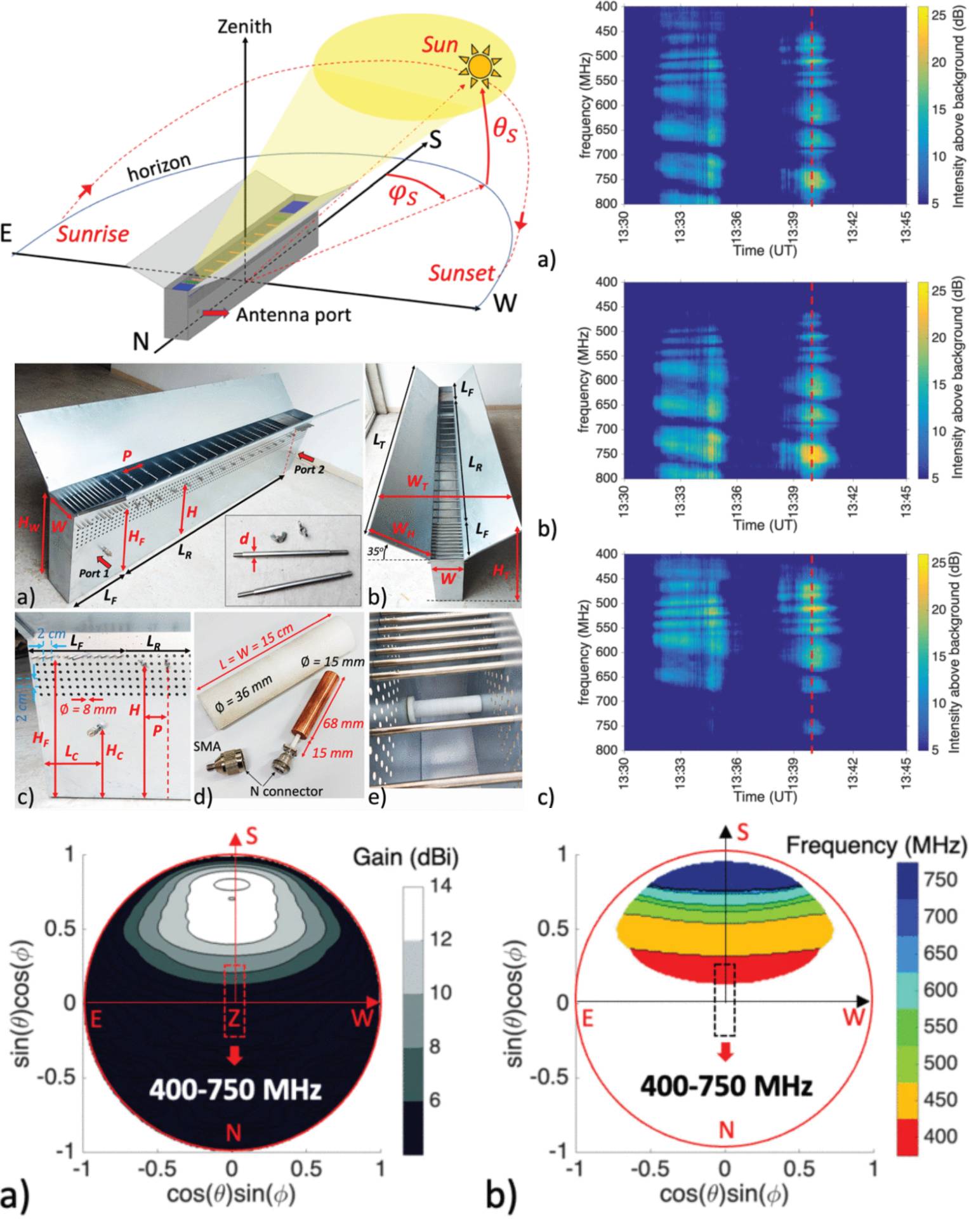
Frequency-Scanning Waveguide Antenna for Solar Radio Bursts Detection in the UHF Band
15 July 2025 José Luis Gómez-Tornero, Alejandro Rabadán-Parra, Alejandro Gil-Martínez, David Cañete-Rebenaque, Javier Bussons-Gordo, Christian Monstein and Manuel Prieto-Mateo proposes a frequency-scanning antenna designed to operate in the 400 MHz to 800 MHz band for solar radio astronomy applications. It is constructed with perforated metallic walls and cylinders, that form a rectangular leaky waveguide. By adjusting the metallic cylinders in the appropriate subwavelength holes, the scanning angle of the directive beams and directivity can be effectively controlled while assuring high radiation efficiency and gain.
-
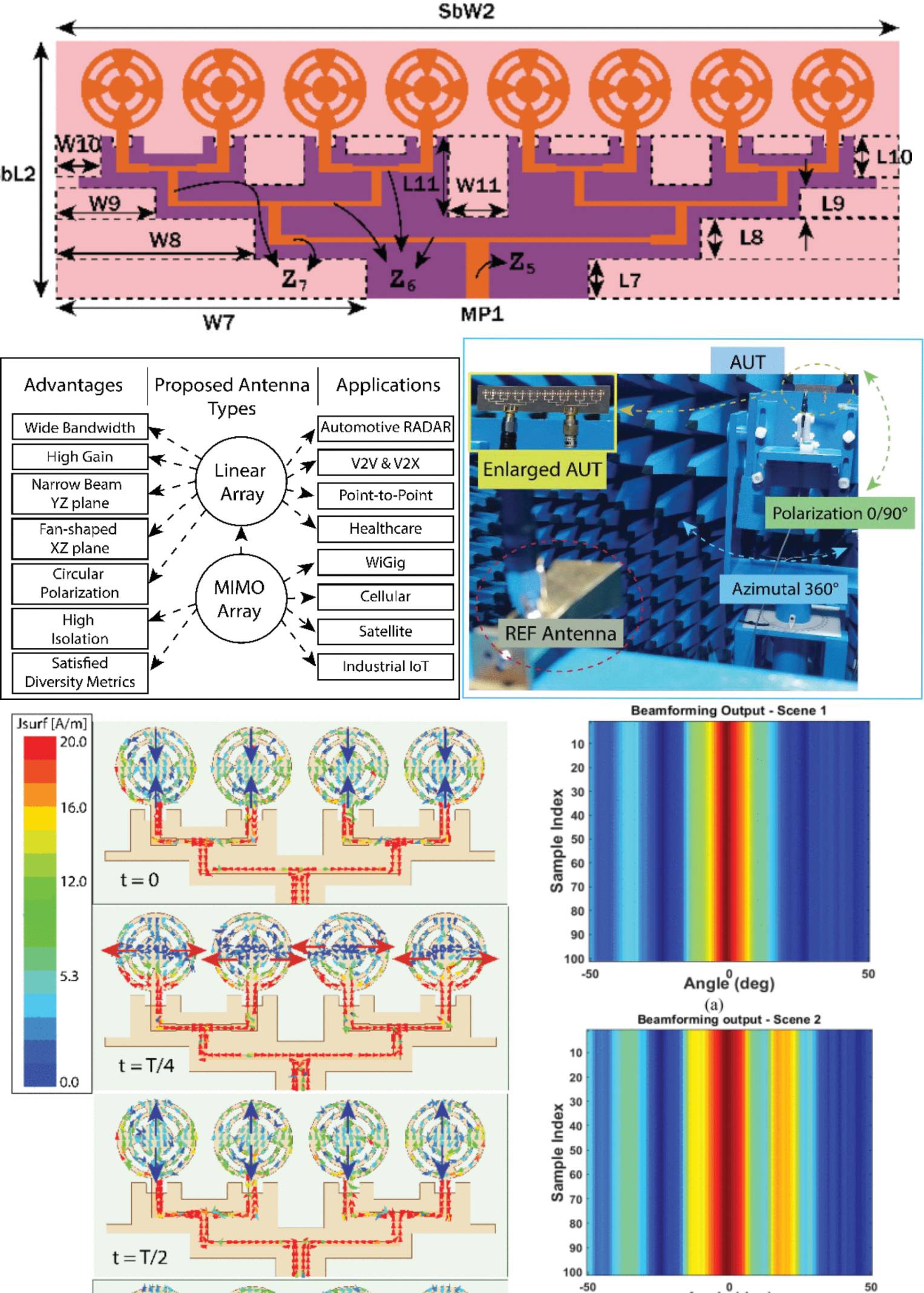
Wideband Narrow-Beam 16-Element Two-Port MIMO Array Antenna With High Isolation for Automotive Radar and 5G Millimeter Wave Applications
11 July 2025 B. G. Parveez Shariff, Tanweer Ali, Pallavi R. Mane, Sameena Pathan, Qammer H. Abbasi, Masood Ur-Rehman, Yahia M. M. Antar, Satish Kumar Sharma and Ahmed A. Kishk design an eight-element linear array antenna to provide a narrow beam, wide bandwidth, and high gain for compact electronic devices while mitigating propagation losses. The design is extended to a two-port MIMO array to enhance channel capacity and reduce RF chain complexity, and can be further scaled to an N-port configuration. A parallel feeding network ensures uniform power distribution. Wideband impedance matching and self-decoupling are achieved by optimizing the ground plane using characteristic mode theory (CMT).
-
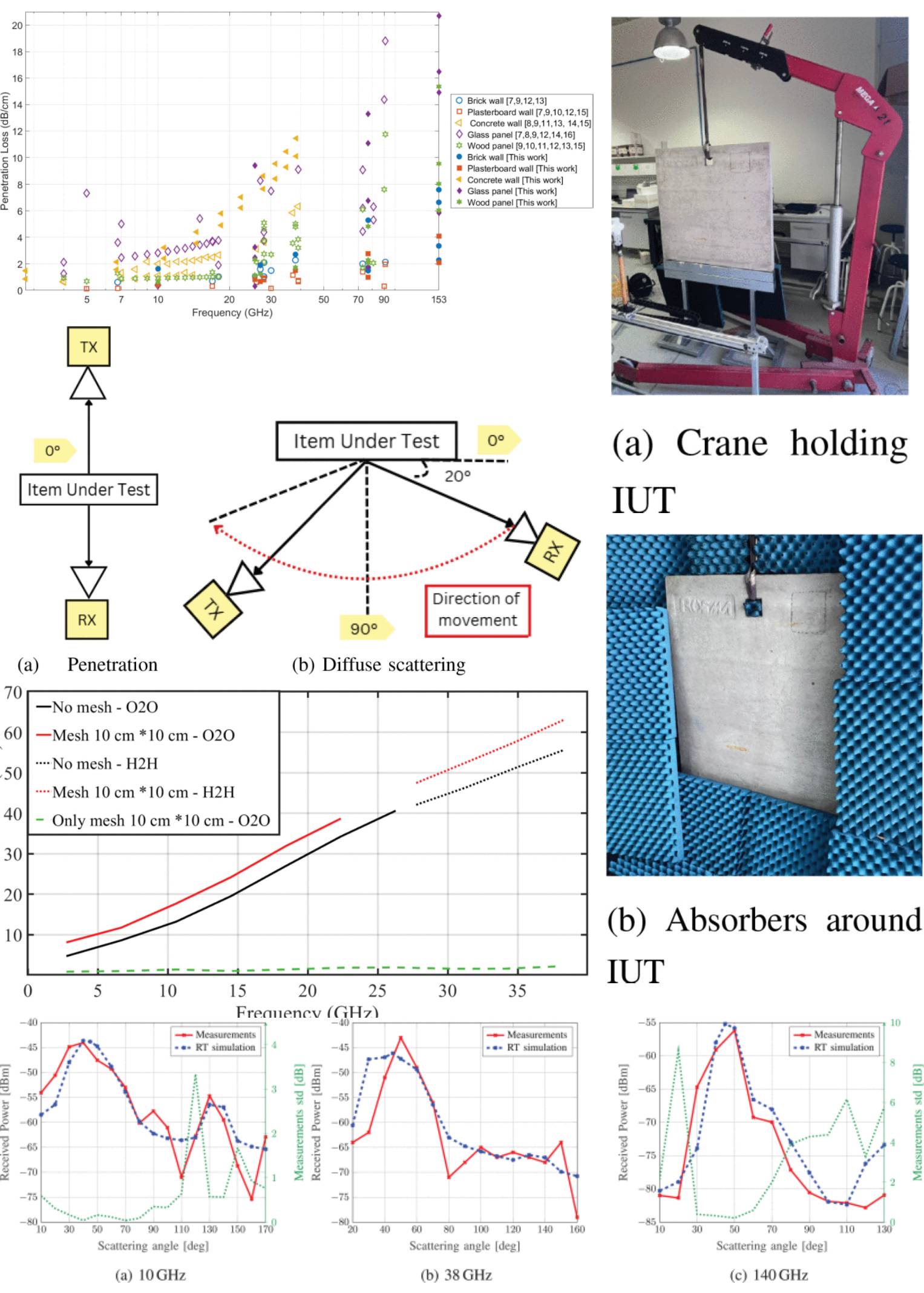
Multiband Measurement-Based Characterization of Building Materials
10 July 2025 Silvi Kodra, Elena Bernardi, Nicolò Cenni, Jiahao Hu, Marina Barbiroli, Franco Fuschini, Enrico Maria Vitucci, Jose-Maria Molina Garcia-Pardo, María-Teresa Martínez-Inglés, Sana Salous and Vittorio Degli-Esposti investigate the attenuation and scattering behaviors of some of the most common construction materials at frequencies ranging from 10 to 153 GHz, using proper measurement setups and post-processing procedures. Our findings can contribute to the design of future communication systems and to the calibration of propagation simulators that are necessary for their optimization and deployment in real-life scenarios.
-
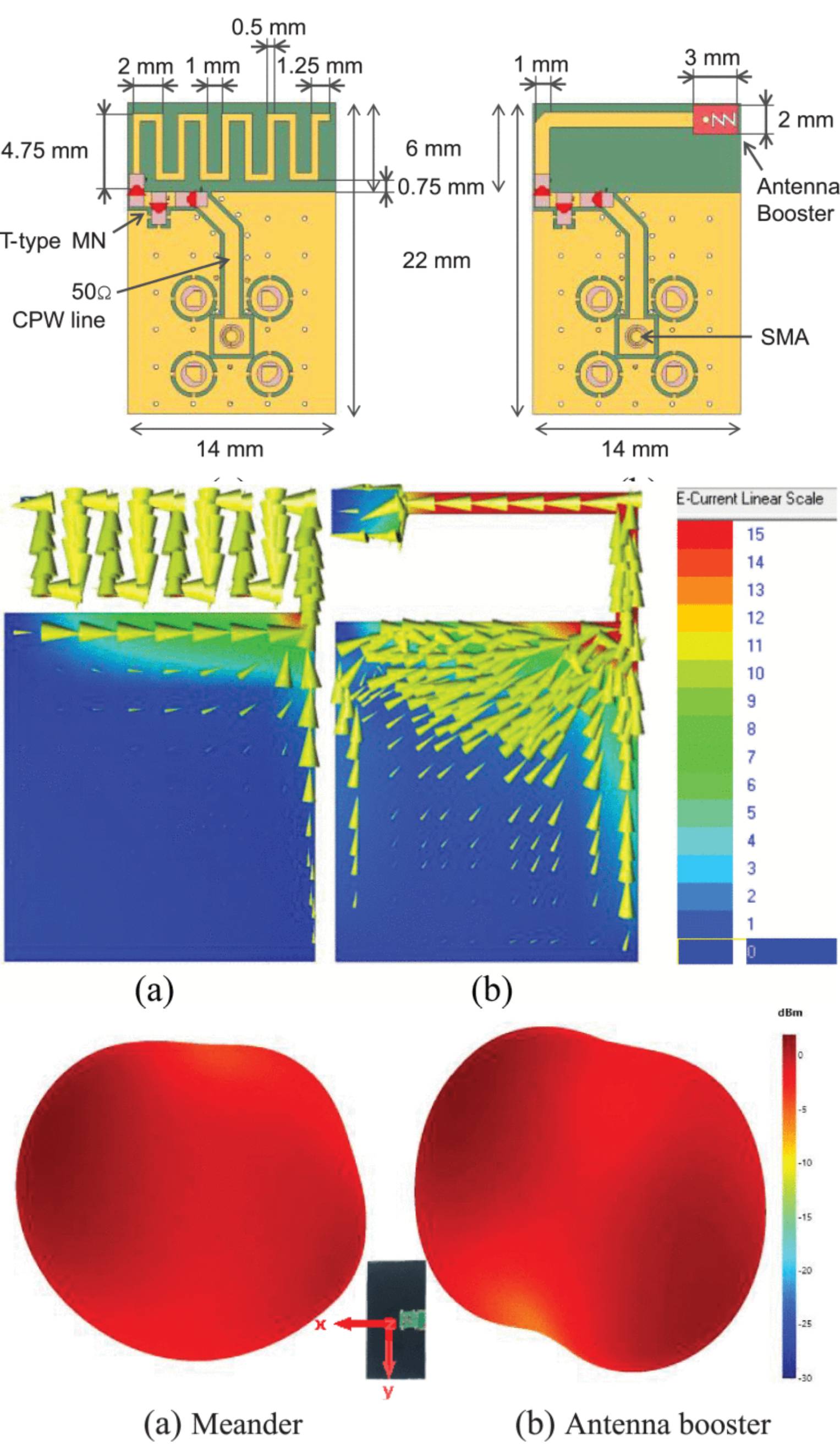
Antenna Boosters Versus Meander Antennas for Bluetooth Module Integration
21 May 2025 Alejandro Fernández, Mireia Vera, Jose Luis Pina, Aurora Andújar and Jaume Anguera compare a common meander-type antenna to an antenna booster in a 21×14 mm2 module. Furthermore, as the final placement of the module on the device and its dimensions remain undetermined, both modules have been evaluated in four different positions of the device (left corner, short-edge center, right corner, long-edge center) for three different Printed Circuit Board (PCB) sizes of 50×50 mm2,75×50 mm2 , and 100×50 mm2 . A module antenna system should be robust enough to cover 2.4−2.484GHz for all 12 setups without the need to change either the antenna geometry and/or the matching network, as you cannot change the Bill of Materials (BoM) of the module once you have passed certification.
-
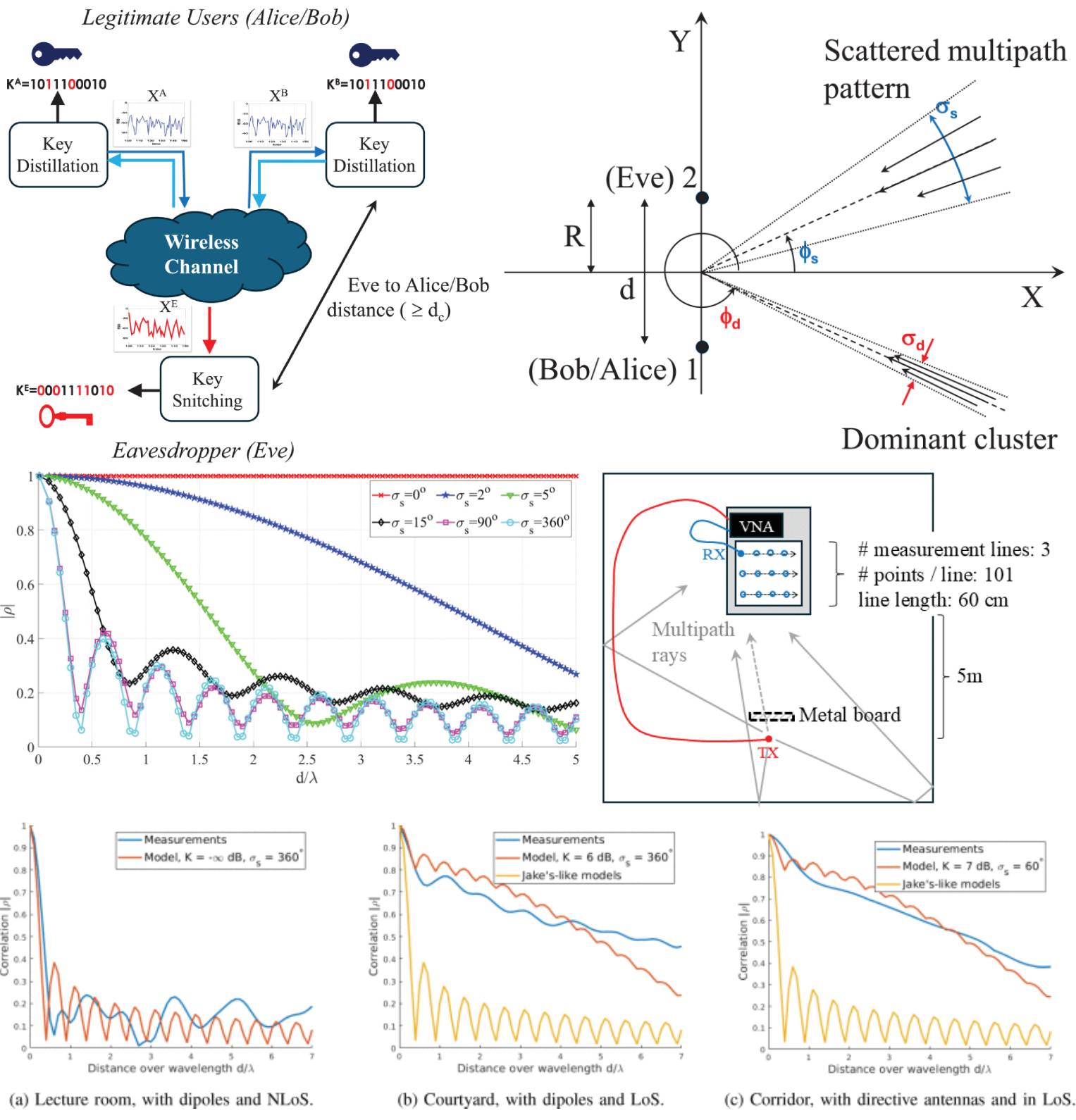
On Spatial Correlation Properties in Rice Wireless Channels for Physical Layer Security
19 May 2025 Simone Del Prete, Marina Barbiroli, Mohammad Hossein Zadeh and Franco Fuschini presents a general, analytical spatial correlation model tailored to Rice fading channels, whereas most of the existing studies are basically limited to the Rayleigh fading case. Results show that the spatial correlation distance is clearly affected by both the power angle profile at the receiver side and the channel Rice factor. Depending on the propagation conditions, the correlation distance can be significantly larger than the value commonly and hurriedly assumed in many previous works on physical layer security, even several times the commonly assumed half-wavelength correlation distance.
-
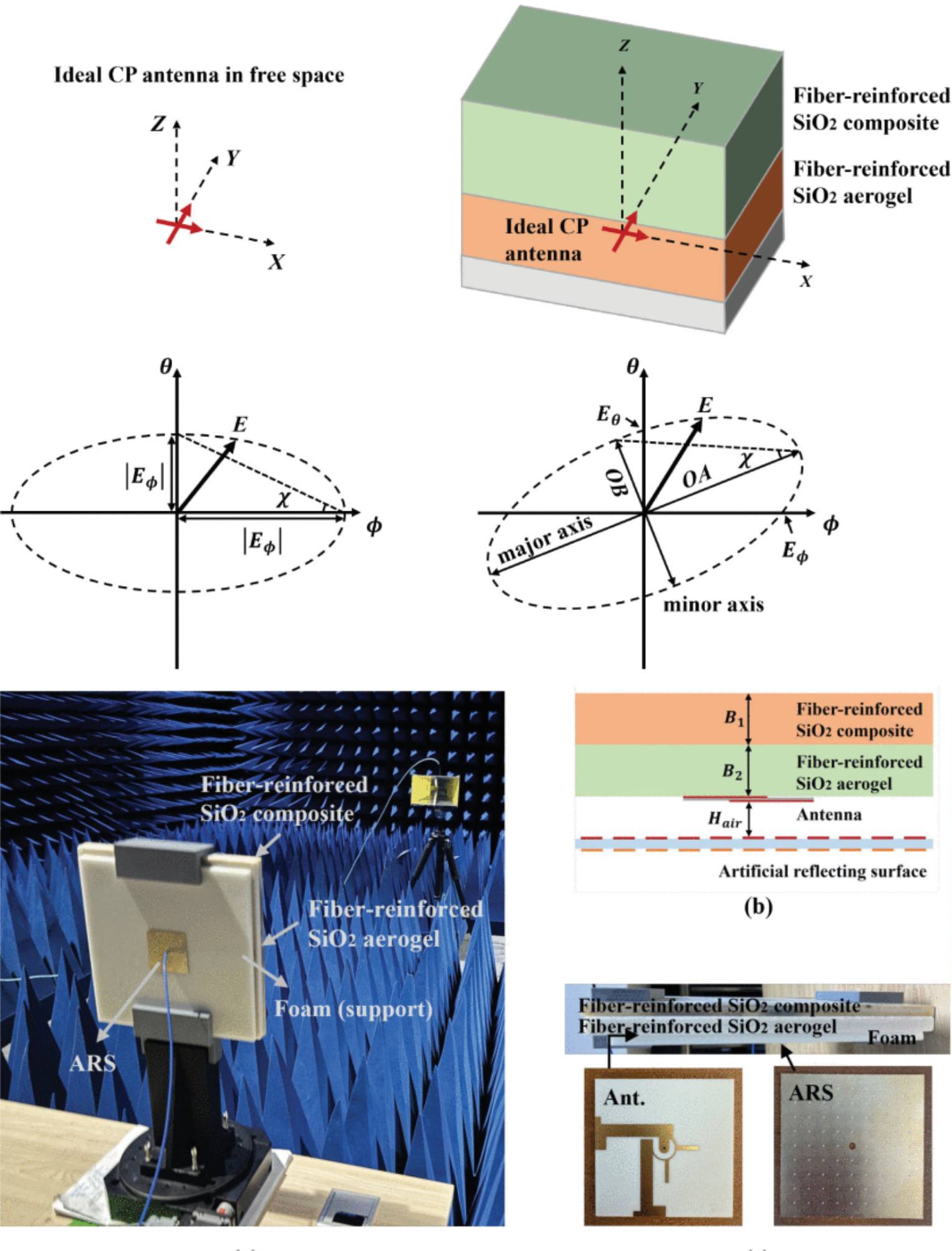
Dual-Band, Wide-AR Beamwidth, CP Antenna With Artificial Reflecting Surface for Hypersonic Vehicles
12 May 2025 Haoqing Wen and Qi Wu analyze electromagnetic interactions between circularly polarized (CP) antennas and a thermal protection system (TPS) through the reciprocal and transmission line (TL) theories. A method is proposed to design an artificial reflecting surface (ARS) by calculating its optimal equivalent circuit. The designed ARS restores the CP properties of an embedded antenna by substituting its perfect electric conductor (PEC) ground. A dual-band 3/7 GHz CP antenna is designed and fabricated to verify the proposed theoretical method.
-
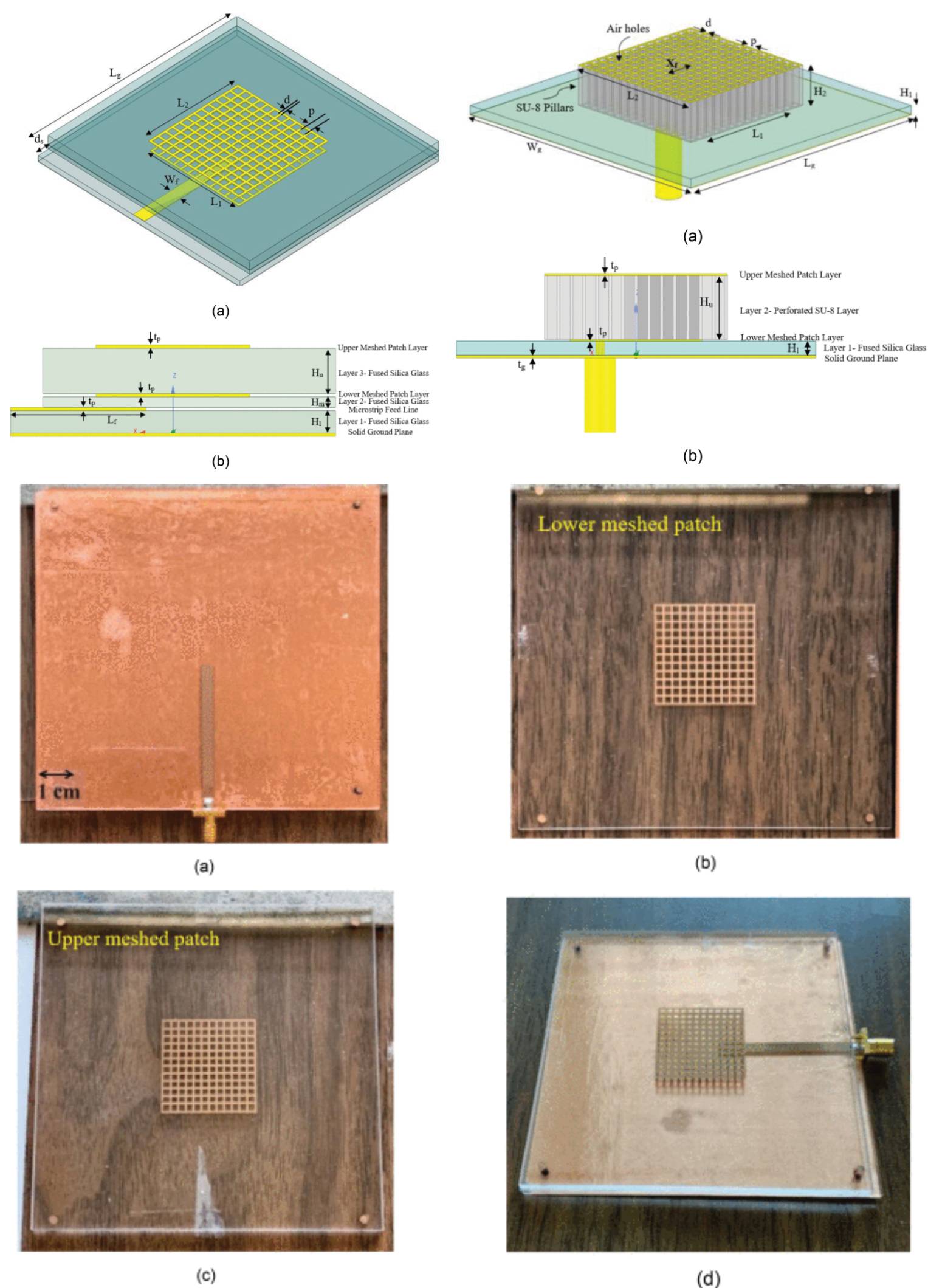
Low Profile Enhanced Bandwidth Optically Transparent and Semi-Transparent Meshed Patch Antennas for Integration With Solar Cells
12 May 2025 Shirin Ramezanzadehyazdi, Dustin Isleifson, Philip Ferguson, Lot Shafai and Cyrus Shafai present three novel low-profile optically transparent meshed patch antennas with enhanced bandwidth that can be fully integrated into a solar cell. The bandwidth enhancement was achieved by applying a stacking technique to two square meshed patches with close resonance frequencies. The first antenna used fused silica glass substrates for both lower and upper dielectric layers to maintain transparency and high integrability with the solar cells. In the second design, a polymer layer replaced the upper glass substrate and was partially removed to reduce the antenna mass. To further reduce the mass, the polymer layer was perforated in the third design.
-
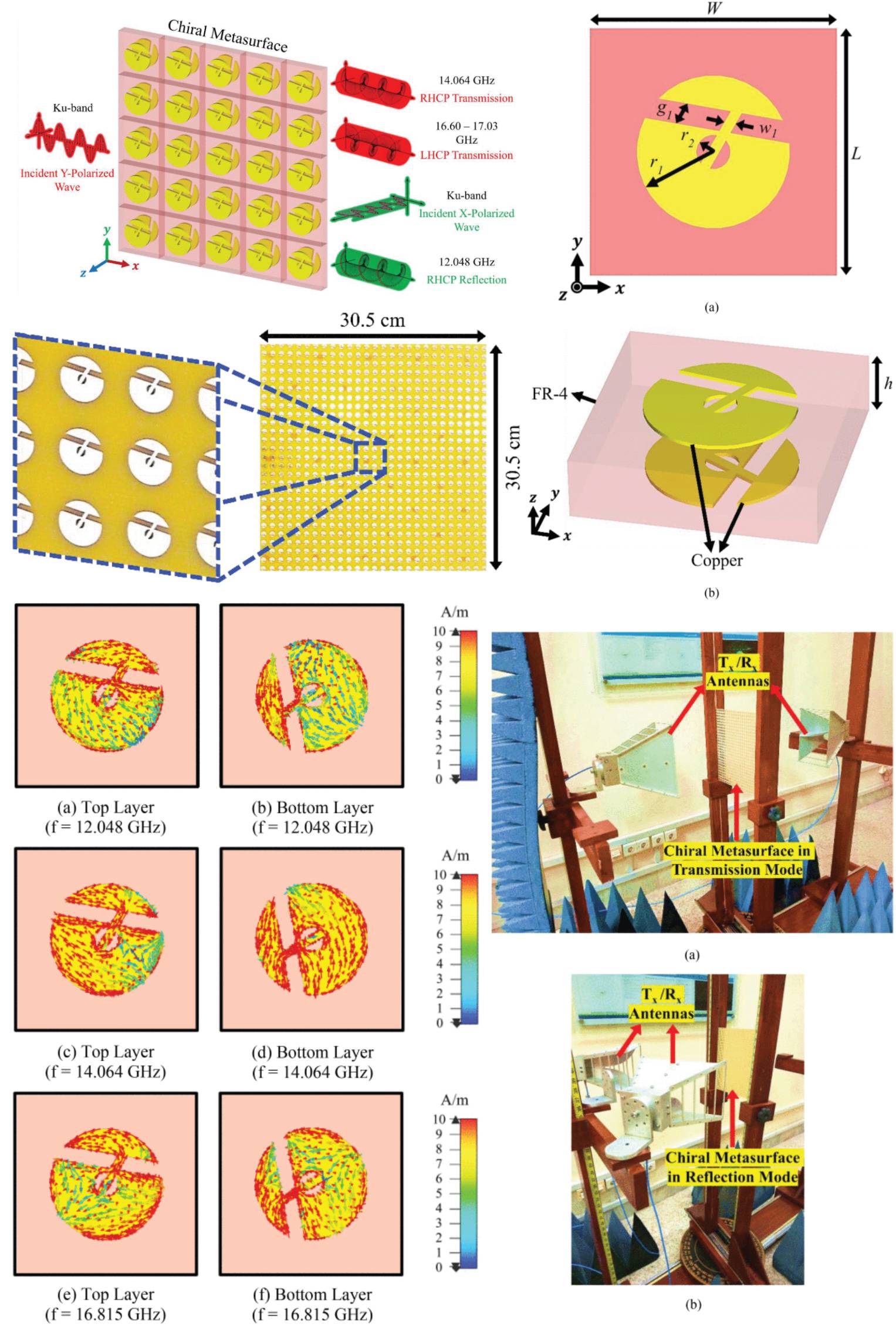
Circular Dichroism and Cross Polarization Conversion Using Chiral Metasurface
09 May 2025 Muhammad Noman, Hattan Abutarboush, Khurram K. Qureshi, Adnan Zahid, Farooq A. Tahir, Muhammad Imran and Qammer H. Abbasi present a novel dual-mode chiral metasurface (CM) designed to achieve strong circular dichroism (CD) in both transmission and reflection mode within the Ku-band. The proposed dual-mode CM demonstrates CD i.e., an efficient conversion of linearly polarized (LP) electromagnetic (EM) waves into circularly polarized (CP) waves, both within a broader spectrum as well as at single frequencies in both transmission and reflection mode, exhibiting asymmetric transmission (AT) response. This is achieved through a judiciously designed unit cell structure, which eliminates the requirement for intricate supercell configurations or active circuitry.
-

Mechanically Scanned Leaky-Wave Pillbox K-Band Antenna With Dual Radiating Layers Using Variable Permittivity Substrate and Nonuniform Patches
09 May 2025Ahmed Jasim, Mahdi Moosazadeh, Christophe Fumeaux and Amin Abbosh present a low-profile, high-gain leaky-wave pillbox K-band antenna with mechanical beam scanning. The antenna consists of three layers: one feeding network layer and two radiating layers. A substrate-integrated waveguide wide-angle H-plane horn feed is connected to a one-dimensional reflector using vias rows, forming a closed pillbox reflector to prevent parasitic wave leakage. A simple coaxial feeding port is used to reduce the antenna’s complexity and cost.
-
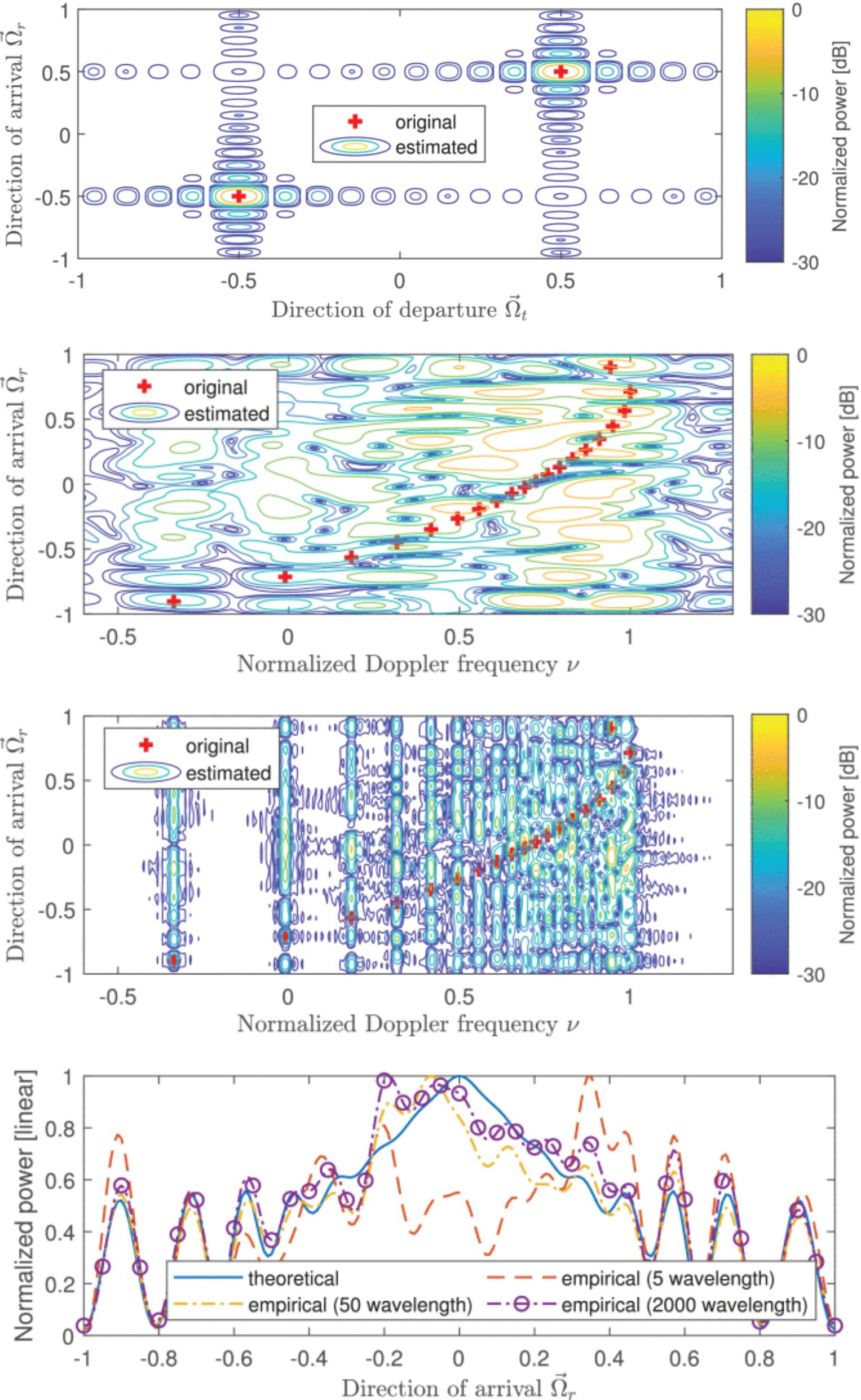
Fourier Analysis of the Prefaded Signal Synthesis in MPAC Setup
08 May 2025 Yilin Ji, Chunhui Li and Wei Fan address the frequently asked question of the prefaded signal synthesis (PFS): (i) the minimum sufficient spatial sampling density within the test zone when solving probe weights, and (ii) the effect of the antenna radiation pattern of different DUT’s on the emulated channel. The team addresses these questions analytically from the perspective of the power spectral density function in the direction and Doppler frequency domain, i.e., the Fourier dual of the spatial and temporal correlation function.
-

Efficient Calculation of Propagation Coefficients in Anisotropic Media Through Transfer Matrix Method Based on Eigenvalue Analysis
08 May 2025 Jiuyang Fan, Zhixiang Huang, Xiaoli Feng and Yuxian Zhang adopt eigenvalue (EV-) analysis to implement the transfer matrix method (TMM), abbreviated as EV-TMM, enabling the accurate capture of propagation coefficients with different polarizations under the inhomogeneous multi-layer background. When the plane waves carrying electromagnetic information enters an anisotropic medium from air, it will excite four beams with different energies and propagation directions in the medium.
-
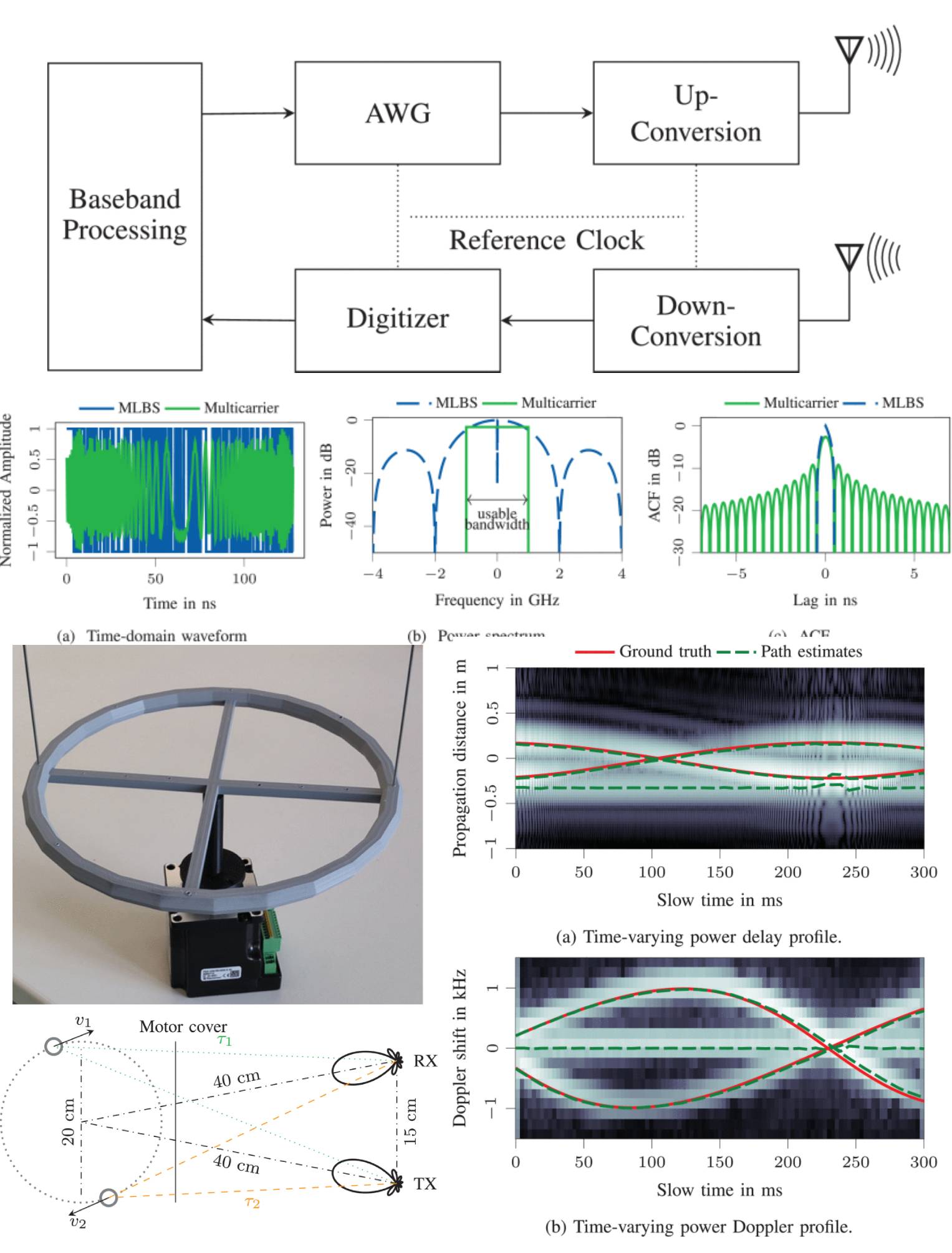
Metrology of Multicarrier-Based Delay-Doppler Channel Sounding for sub-THz Frequencies
02 May 2025 Jonas Gedschold, Diego Dupleich, Sebastian Semper, Michael Döbereiner, Alexander Ebert, Giovanni Del Galdo and Reiner S. Thomä propose and discuss an over-the-air artifact allowing a joint verification of delay and Doppler parameters in a multipath scenario. The evaluations of exemplary sub-THz measurements with a multicarrier-based sounder highlight the strong interplay between sounder hardware and estimation algorithms, especially when coping with the mutual interference of parameters from multiple propagation paths. Hence, a metrological assessment always requires considering the full processing pipeline from the unprocessed measurements up to the extracted propagation parameters.
-

A Wideband and Low-SAR Antenna Design at 2.45 GHz for Biomedical Applications
30 April 2025 Sami Ullah Khan, Muhammad Aamir, Muhammad Abbas, Uzman Ali, Usman Ali and Toni Björninen design a miniaturized implantable antenna for biomedical applications operating within the industrial, scientific, and medical band (ISM, 2.4–2.48 GHz). The proposed implantable antenna has a compact size of 5.5 × 5.5 × 0.64 mm and is manufactured using a biocompatible substrate, Roger RO3010 with permittivity of εr=10.2 and losstangentof tan(δ)=0.0022. To enhance safety, a superstrate and a silicon coating around the antenna are employed to isolate the antenna from the surrounding biological tissues. The simulation software from the HFSS and CST studio suite was utilized to simulate and optimize the proposed implantable antenna, followed by fabrication and testing.
-

A Single-Bit Reconfigurable Folded Reflectarray/Transmitarray Antenna
30 April 2025 Manting Wang, Jiachen Du, Dashuang Liao and Chi Hou Chan introduce a novel receiving-transmitting (RA-TA) metasurface unit cell for folded transmitarray/reflectarray antennas (FTAs/FRAs). The unit cell comprises two substrates with an air gap to ensure optimal transmission and integration of PIN diodes. Polarizer grids are employed for selecting desired polarization while each grid metal provides DC bias independently to a single unit cell with two PIN diodes surface-mounted and their orientation perpendicular to each other, i.e., along 1450, respectively, enabling 1-bit phase compensation and polarization conversion. Thus, the proposed antenna achieves 1-bit reconfigurability and maintains polarization consistency with the feeding source.
-

Multipolar On-Resonance Interference For Super-Gain Electrically Small Dielectric Resonator Antenna (Esdra) Design
25 April 2025 Ahmed Abdelraheem, Duhan Eroglu, Karim Seddik and Dimitrios Peroulis propose a Mie scattering-based approach, employing multipolar decomposition to tailor the dielectric resonator multipoles. The poor radiation efficiency associated with small size (ka < 1) is remedied by on-resonance multipole overlapping, subsequently increasing aperture efficiency and gain. Two simple single-ported ESDRAs with the smallest reported ka of 0.99 and 0.62 are presented. Driven by a deeply subwavelength, poorly radiating elementary electric dipole, high-efficiency ESDRAs are obtained.
-
Dielectric EBG Leaky-Wave Antenna: Design and Experimental Validation
25 April 2025 Ludovica Tognolatti, Paolo Baccarelli, Cristina Ponti, Silvio Ceccuzzi, Vakhtang Jandieri and Giuseppe Schettini propose a novel Electromagnetic Band-Gap (EBG) leaky-wave antenna (LWA) operating in the K-band with enhanced directivity at broadside. A rigorous method that combines the analysis of the band diagrams of Bloch waves propagating within two-dimensional (2-D) EBG structures and the properties of bound and leaky modes in transversely open lattice waveguides is used to design the antenna. For the first time, a three-dimensional (3-D) realistic configuration of the EBG structure is designed, manufactured, and measured in the K-band.
-
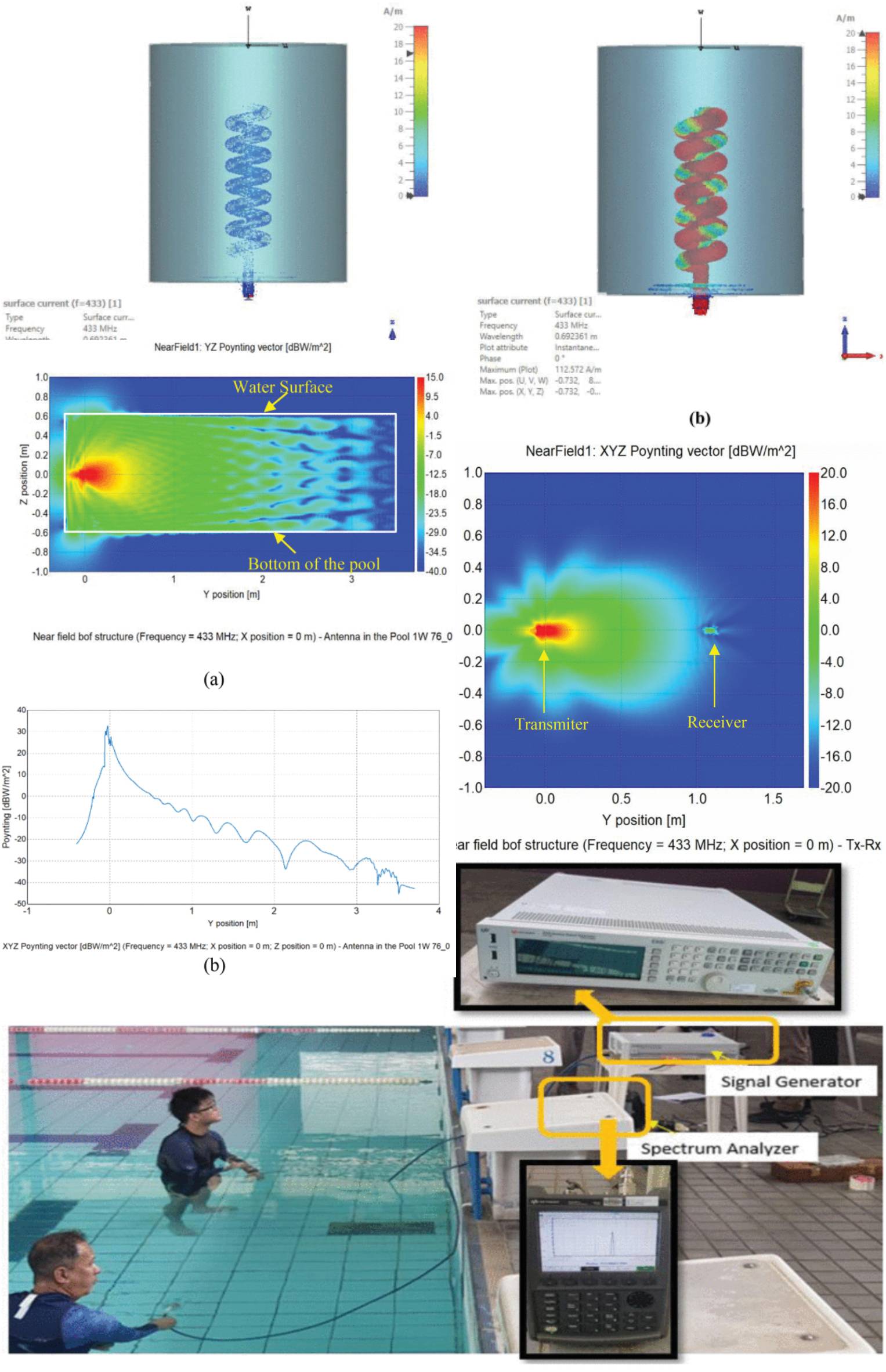
Electromagnetic Analysis of Radio Propagation in Fresh Water and Measurement by Axial Mode Helical Antenna at 433 MHz
21 April 2025 Afiza Nur Jaafar, Hajar Ja’Afar, Yoshihide Yamada, Nurul Huda Abd Rahman, Naobumi Michishita, Norsiha Zainudin, Fatemeh Sedeghikia, Rina Abdullah clarify antenna design and electrical performance in underwater use. Then, analysis of electric field distributions underwater and radio link design equation are clarified using electromagnetic simulations. A frequency of 433 MHz is selected from the ISM band. For a high gain antenna, an axial mode helical antenna is selected because of structural simplicity and adaptability of gain change by changing number of turns. The antenna is placed in a capsule to prevent direct contact with surrounding water. In order to achieve effective antenna gain, it is shown to fill the capsule with distilled water of zero conductivity.
-
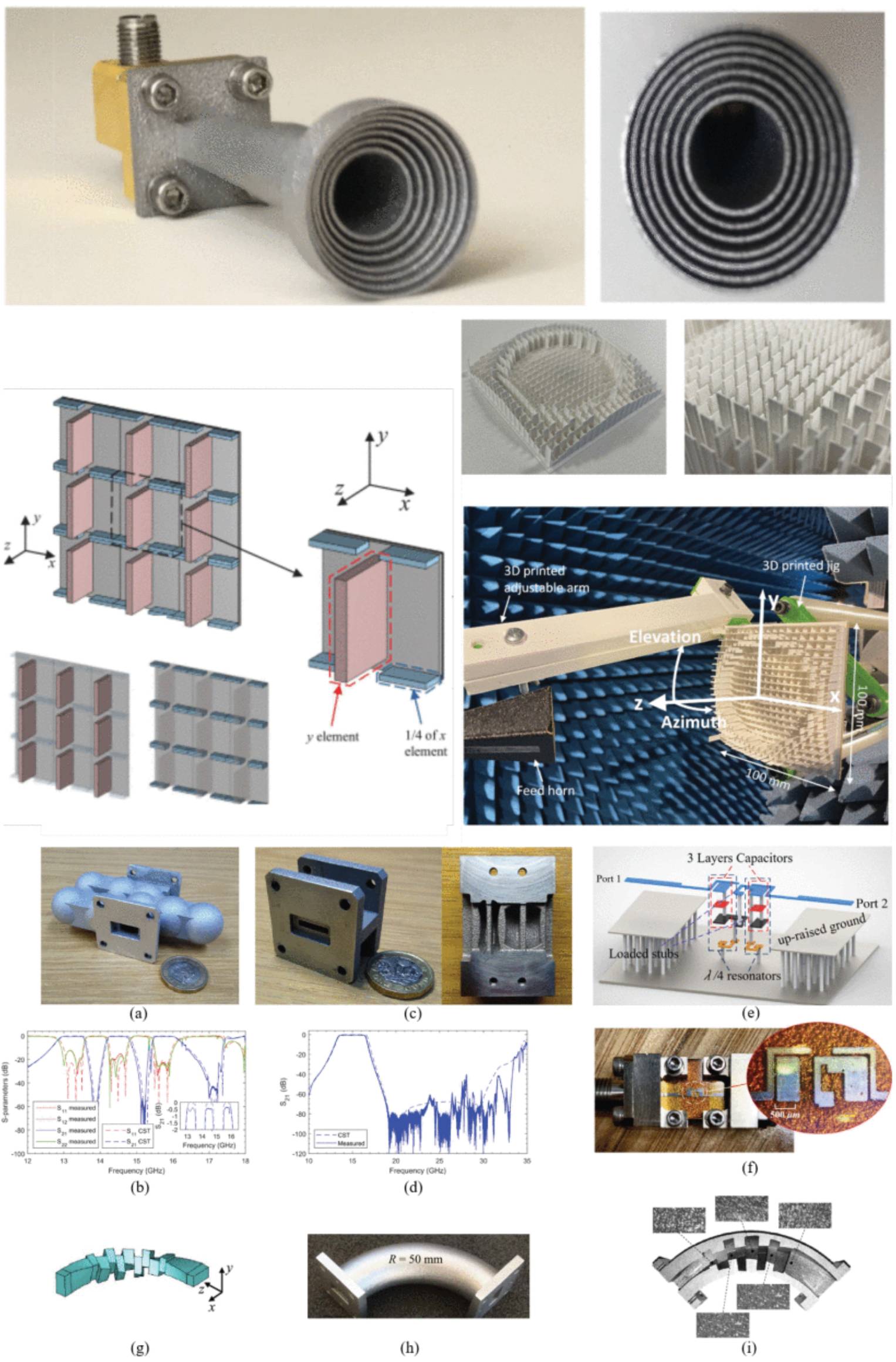
Additive Manufacturing of Antennas and RF Components for SATCOM: A Review
18 April 2025 Hafsa Talpur, Ulan Myrzakhan, Juan Andres Vasquez-Peralvo, Shuai Zhang and Symeon Chatzinotas provide a review of current state-of-the-art AM printed antennas and RF components incorporating different additive manufacturing (AM) techniques and materials to obtain specific design characteristics such as high gain, wide bandwidth, beamforming, and better power handling capacity, particularly for Ku, K, and Ka-band satellite communication (SATCOM).
-
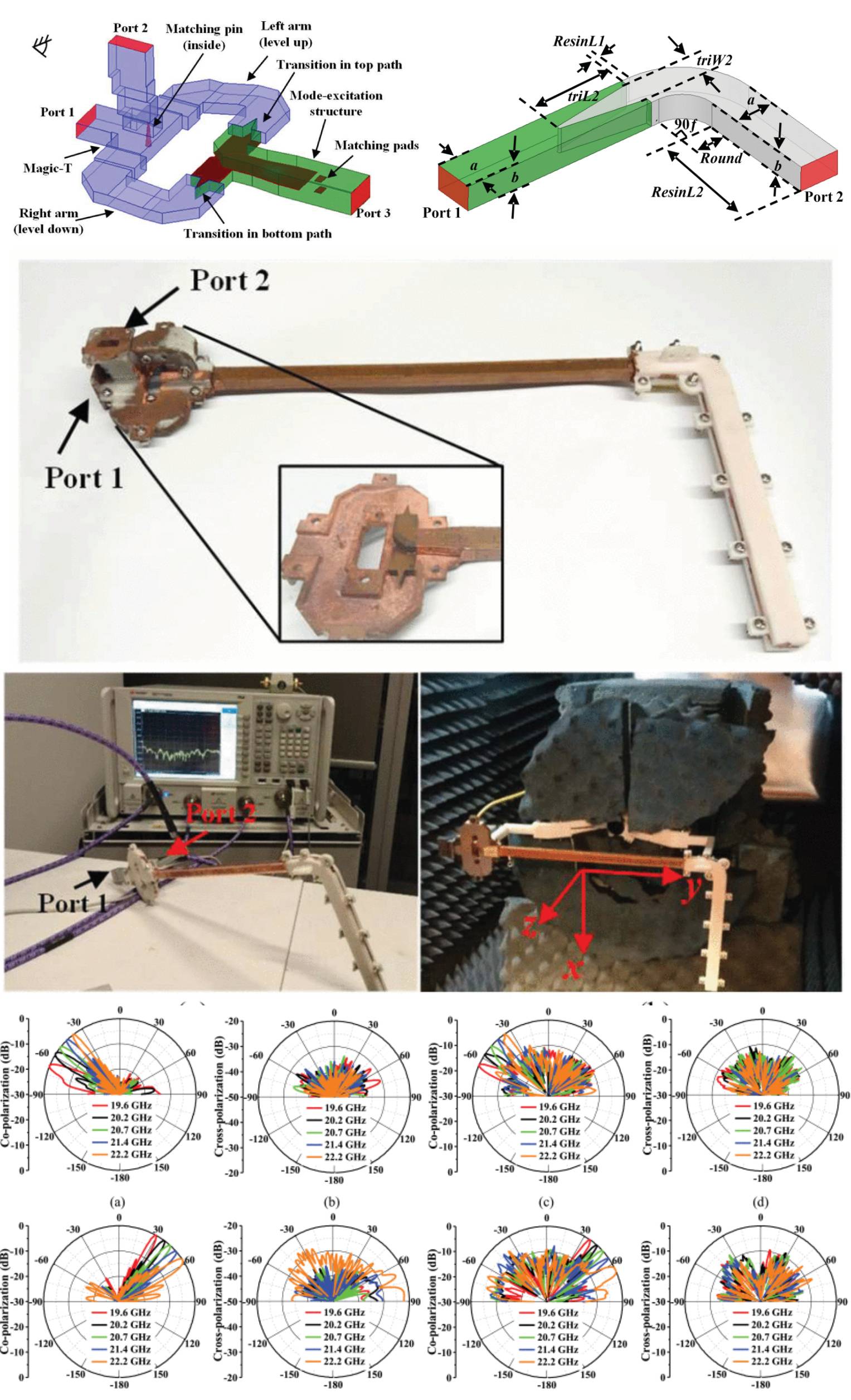
Investigation of Orthogonal Modes in a Periodic Structure and Application to Two-Separate Beams Steering Within the Same Frequency Band
18 April 2025 Yunhao Fu, King Yuk Chan, and Rodica Ramer investigates orthogonal modes and their space harmonics in a dielectric-filled rectangular waveguide (RWG) leaky-wave structure. The dispersion analysis on orthogonal modes in periodic structures aims to determine the feasibility of two individual beams steering in different spatial regions. The Brillouin diagrams explain the basic principles of the constructed leaky-wave structure; a feeding network is developed for mode excitation. The proposed two-port prototype utilizes standard printed circuit board (PCB) and 3D printing techniques, and the dispersion properties reveal an agreement between measurements and simulations. From 19.6 to 22.2 GHz, the measurements showcase two separate beams steered for each port excitation.
-

A Novel Quad-Band Electrically Small Antenna With Low Q
25 March 2025 Hanguang Liao and Atif Shamim present a novel method to design a quad-band fully Electrically Small (ES) antenna. The proposed method is based on the even and odd modes of a split-ring antenna and uses radio frequency trap loading to achieve dual-band operation for each mode. The proposed antenna is ES for all bands. At each band, the radiating structure uses almost the whole available volume, so a good bandwidth is obtained for all four bands. The proposed antenna is fabricated, and the performance at each band is measured in a proper setup designed for multi-band ES antennas.
-

An Anisotropic Metamaterial Cover Layer for Scan Range Enhancement of Patch-Antenna Phased Arrays in Both Principal Planes
24 March 2025 Mohammad Soltani and George V. Eleftheriades introduces a metamaterial cover layer designed to extend the scan range of patch-antenna phased arrays in both principal planes without compromising directivity. The key innovation lies in the anisotropic properties of the cover layer which suppress the excitation of the fundamental surface-wave (SW) mode, effectively mitigating scan blindness within the desired angular range. This suppression mechanism is simply not possible with a conventional dielectric-slab wide-angle impedance matching (WAIM) layer.
-

Active Retrodirective Rotman Lens Antenna for Wide-Angle RCS Enhancement
24 March 2025 Hanieh Kiani Amiri and Michal Okoniewski present measurement results and analysis of an innovative active retrodirective Rotman lens antenna architecture, designed to enhance the radar cross-section (RCS) for backscattering applications. Unlike conventional passive retrodirective systems, our design integrates custom-designed reflection amplifiers to significantly boost backscattered signal gain while maintaining low DC power consumption. A novel biasing technique enables independent phase and gain control of the amplifiers, ensuring a uniform array response and reducing DC power consumption by approximately 30%. Experimental monostatic RCS measurements at 5.15 GHz with a linearly polarized incident wave demonstrate a uniform RCS response over a ±40° scan angle.
-

A Triband Wearable Antenna for Location Tracking Using Cospas-Sarsat and GNSS
20 March 2025 Rais Ahmad Sheikh, Azremi Abdullah Al-Hadi, Thennarasan Sabapathy, Roy B. V. B. Simorangkir, Rizwan Khan, Prayoot Akkaraekthalin, Che Muhammad Nor Che Isa, Surentiran Padmanathan, Toufiq Md Hossain and Ping Jack Soh present the design of a tri-band antenna operating in the Cospas-Sarsat (C-S) and GPS/GNSS bands applicable for the Internet of Things (IoT). Implemented with flexible and robust materials, the antenna operates in three distinct frequencies: 406 MHz for C-S applications and 1227 MHz (L2) and 1575 MHz (L1) for GPS/GNSS applications. The measured 10-dB impedance bandwidth is from 1.517-1.587 MHz (in L1 band) and from 1.192-1.232 MHz (in L2 band). In C-S band, the measured 6-dB bandwidth is from 393 to 406.5 MHz. The 3 dB axial ratio (AR) bandwidth in the L1 and L2 bands are 17 MHz (1.08%) and 18 MHz (1.47%), respectively.
-

Distributed Phased-Array Radars Exploiting Collaborative Beamforming and Diversity Techniques for Remote Sensing Applications
18 March 2025 Sandra Costanzo and Giovanni Buonanno illustrate the analysis of phased-arrays exploiting the paradigm of collaborative beamforming together with excitation and position diversity in this work. Excitation diversity is based on a thinned arrays framework, while position diversity is implemented in terms of binned arrays paradigm. The proposed approach can fall under collaborative beamforming related to wireless sensor networks. After introducing the description of the above arrays and the related mathematical model, stochastic analysis is carried out to highlight the main characteristics, by modeling the excitation coefficients and the element positions in terms of random variables.
-

Low-Complexity Wideband Circularly Polarized Modular Scalable Phased Array for Vehicular Satellite Communication
14 March 2025Behzad Yektakhah, Abdelhamid M. H. Nasr, Abdel Halim Mohamed and Kamal Sarabandi present a low-complexity wideband circularly polarized (CP) array in X-band for vehicular satellite communication. The array comprises dual-polarized corner-fed patch elements for achieving wide bandwidth. The active elements are integrated in a modular manner using interposers that enables the scalability of the array and simplicity of routing RF signals, as well as dc bias and digital control lines on the array surface. The building block of the scalable array is a 2×2 subarray of dual-polarized patch elements and an interposer with an 8-channel beamformer integrated circuit mounted on it. The interposer circuit simplifies the routing of dc and digital lines on the surface of larger arrays, lowers the cost of fabrication, and makes the array debugging simple.
-

Active Antennas Beyond the Standard Impedance Matching Technique: Concepts and Applications
11 March 2025 Constant M. A. Niamien presents a new design concept for improving active antennas’ performances beyond the standard impedance matching technique. The proposed approach expands the mismatch at the antenna-amplifier interface to create a voltage excess, transferred to the matched output receiver using a voltage-type amplifier instead of a power type. Compared with a standard dual-input-output matching, this leads to comparable bandwidth and DC consumption but significantly improves the peak gain, gain-bandwidth-product (GBWP), stability, and noise figure. Experiments with a conventional dipole antenna confirm an improvement factor near two on gain and GBWP.
-

Design Guidelines of Stacked Dual-Band SIW Slot Array With Optimal Aperture Reuse Ratio and High Aperture Efficiency
10 March 2025 Yihong Su, Yulei Yang, Xian Qi Lin and Yong Fan propose the design guidelines of a stacked dual-band (28/35 GHz) substrate integrated waveguide (SIW) slot antenna array to achieve the optimal aperture reuse ratio and high aperture efficiency. The dual-band array consists of two-layer substrates, and each layer acts as an independent SIW slot antenna array. The upper substrate is composed of nonadjacent SIW slot sub-arrays for the high band operation, while the low band array is located in the lower substrate radiating through the gap between the high band sub-arrays. A dual-band antenna array with an 8×8 array in each band is designed and demonstrated as an example, where the center frequencies of the two bands are chosen to be 28 GHz and 35 GHz.
-

Application of Relational Databases to the Acceleration of Ray Tracing in High Frequency Asymptotic Techniques
10 March 2025 David Cabornero, Lorena Lozano, Iván González, Álvaro Somolinos and Felipe Cátedra present a new ray-tracing acceleration technique for electromagnetic simulation problems using the Uniform Theory of Diffraction and meshes of planar facets. The innovation involves using relational databases to accurately store spatial information, enabling spatial indexing through space partitioning with R-trees. This technique effectively reduces the computational cost of several critical phases, including the shadowing test. Additionally, there are multiple advantages to utilizing this technology, such as automated memory and disk management along with a query planner that organizes the instructions automatically. Direct rays, multiple reflections, multiple transmissions, simple diffraction, and combinations of these effects have been implemented in PostgreSQL and its spatial library PostGIS.
-

Optically Transparent Single-Layer Dual-Frequency Dual-Polarization Metasurface Applied in Close Proximity to Smartphone Millimeter-Wave Phased Array Antenna Systems
07 March 2025 Wen Fu, Igor Syrytsin, Rocio Rodriguez Cano, Peiye Liu, Andrey Kobyakov, Gert Frølund Pedersen and Shuai Zhang propose an optically transparent single-layer dual-frequency dual-polarization metasurface operating at 28 GHz and 38 GHz to enhance millimeter-wave transmission through glass. The unit cell design of the proposed metasurface has three distinct pattern types: square annular, Jerusalem cross, and circular. The former pattern can independently control the low-frequency resonance, while the latter two can control the high-frequency resonance. The proposed metasurface can achieve a large incident angle of 60 degrees for electromagnetic waves in TE and TM polarizations. After the metal layer of the proposed metasurface is meshed, the transparency of the metasurface is significantly improved.
-

A Wideband 4×4 Patch Array Antenna With Low Sidelobes for Radar-Based Obstacle Detection in Railway Transportation
05 March 2025 Thipamas Phakaew, Tiwat Pongthavornkamol, Danai Torrungrueng, Thomas Dallmann and Suramate Chalermwisutkul presents the design, fabrication, and measurement of a 4×4 patch array antenna for radar-based obstacle detection systems in railway transportation. Sidelobe suppression is achieved through amplitude tapering of sub-array elements in the E-plane and asymmetric power dividers in the feed network for the H-plane. The array antenna is framed by a coplanar ground conductor to further reduce sidelobes and fed by a coplanar waveguide port for enhanced impedance bandwidth. The proposed antenna offers an impedance bandwidth from 9.13 GHz to 9.76 GHz (6.3%) and a broadside gain of 18.15 dBi at the center frequency of 9.55 GHz. Sidelobe suppression exceeds 12.22 dB and 19.06 dB in the E- and H-plane, respectively.
-

An Anisotropic Metamaterial Cover Layer for Scan Range Enhancement of Patch-Antenna Phased Arrays in Both Principal Planes
04 March 2025 Mohammad Soltani and George V. Eleftheriades introduces a metamaterial cover layer designed to extend the scan range of patch-antenna phased arrays in both principal planes without compromising directivity. The key innovation lies in the anisotropic properties of the cover layer which suppress the excitation of the fundamental surface-wave (SW) mode, effectively mitigating scan blindness within the desired angular range. This suppression mechanism is simply not possible with a conventional dielectric-slab wide-angle impedance matching (WAIM) layer.
-

A Wideband and Low Sidelobe Magnetoelectric Dipole Antenna Array With Embedded Resistors
03 March 2025 Jianhui Huang and Kwai-Man Luk propose a simple and effective method, by using ‘0-1’ excitations, to reduce the sidelobe level (SLL) for a wideband magnetoelectric (ME) dipole antenna array. First of all, the multiple-population genetic algorithm (MPGA) is utilized to search optimal ‘0-1’ excitations for SLL reductions. Then, the ‘0’ and ‘1’ excitation can be achieved by incorporating the absorbing element embedded with a resistor and an ME dipole antenna element, respectively. Different from the traditional tapered excitation techniques, the proposed array utilizes an equal power divider to distribute the power to each element. Finally, a planar 16×16 stripline-fed antenna array according to the optimized array configuration is designed, fabricated, and measured.
-

Compressed Sensing Digital MIMO Radar Using a Non-Uniformly Spaced SIW Sparse Receiver Array
27 February 2025 Cristian A. Alistarh, Symon K. Podilchak, Dave J. Bekers, Laura Anitori, Wim L. van Rossum, Rob Boekema, Iram Shahzadi, Mathini Sellathurai, John S. Thompson and Yahia M. M. Antar propose a compressed sensing (CS) digital radar system based on a sparse array design for use in automotive collision-avoidance applications. The proof-of-concept radar system offers an enlarged antenna aperture, employing fewer elements and can distinguish targets at an angular separation of only 2 degrees for a bandwidth of 6.25%. This resolution is made possible using a multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) configuration from the original sparse array which was implemented and tested using substrate integrated waveguide (SIW) technology. More specifically, the total aperture size (of the effective virtual receiver array) is 23.5λ which is equivalent to a uniform-linear array (ULA) having 48 elements spaced at 0.5λ apart.
-

Efficient Neural Network-Based Reconstruction of Three-Dimensional Antenna Radiation Patterns From Two-Dimensional Cuts
21 February 2025 Saeed Jan, Yuanzhi Liu and Costas D. Sarris present a novel solution to the classical problem of interpolating three-dimensional antenna radiation patterns from two-dimensional, orthogonal pattern slices. They introduce a neural network model that performs this interpolation with high accuracy across a wide range of patterns, including cases where conventional interpolation methods struggle. This model is beneficial for three-dimensional modeling methods, such as ray-tracing, where a full antenna radiation pattern is needed, whereas only principal plane patterns are available from measurements or data sheets.
-

Stability Analysis of the EFIE-IBC Formulation and Regularization via Spatial Filtering
21 February 2025Subuh Pramono, Josaphat Tetuko Sri Sumantyo, Muhammad Hamka Ibrahim, Ayaka Takahashi, Yuki Yoshimoto, Hisato Kashihara, Cahya Edi Santosa, Steven Gao and Koichi Ito proposes a novel antenna substrate that is realized based on low-temperature co-fired ceramic (LTCC) technology using cordierite ceramic (2MgO 2Al2O3 5SiO2). Compared to other existing ceramics, it has an impressive low dielectric constant (ϵr) of 4.674 and a loss tangent (tan δ ) of 0.0723 at 5.3 GHz, which makes it ideal for creating an ultra-wideband (UWB) circularly polarized (CP) array antenna. In addition, cordierite ceramic is suitable for high-temperature environments, its coefficient of linear thermal expansion is about 1.8×10−6 /K (40°C– 800°C), and it expands only 0.1% of its room temperature dimensions even in a 1000°C environment. Through a sputtering process, platinum with a melting point of 1768°C and very good oxidation resistance is used as a conductive material on the cordierite ceramic substrate.
-

Temperature-Dependent Over-the-Air Measurements of Total Isotropic Sensitivity for Minimum Uncertainty
20 February 2025 Jiyu Wu, Francesco de Paulis and Yihong Qi suggest a new total isotropic sensitivity (TIS) method that measures TIS at the device’s thermally stable condition, thus redefining TIS not a single value but rather as a function of the transmitter’s power, reducing uncertainty and ambiguity in TIS measurements for wireless and 5G devices. Based on measurement results in this paper, the TIS measurement exhibits a variability of up to 1 dB due to the effects of temperature and transmitting power levels, distinct from the inherent measurement uncertainty of 0.28 dB specified by the standard. A more complex yet accurate measurement procedure is proposed while varying the power level. The proposed method is applied and experimentally verified, demonstrating its usefulness to extract the TIS profile instead of a single value, with a result of the TIS variation as a function of the transmitting power.
-

Synthesis of Shaped-Beam Radiation Patterns With Efficient Optimization Algorithm
19 February 2025 Ting Zang and Gaobiao Xiao extend the efficient optimization algorithm for synthesizing shaped beams to the synthesis of radiation patterns of planar current sheets that have different beams and polarizations on the two sides of the source plane. The radiation pattern is described with a real-valued function, which is expressed with the superposition of entire functions and its extrema can be quickly located by searching on a fixed uniform grid in the k-space. By flexibly tuning the positions of the extrema, the ripples in the main beam and the levels of the sidelobes can be effectively controlled.
-

Frontiers in Quantum Antennas: Theoretical Foundations, Practical Applications, and Future Outlook
25 February 2025 Abdoalbaset Abohmra, Muhammad Zubair, Masood Ur Rehman, Hasan Abbas, Muhammad A. Imran and Qammer H. Abbasi provide an overview of the theoretical foundations for quantum antennas as open quantum systems, discussing how strong coupling and quantum state manipulation can be harnessed for practical implementations. They then examine groundbreaking advancements in quantum antenna design, including the integration of novel material configurations, such as quantum dot arrays and their interactions with photonic reservoirs. The review explores the unique quantum phenomena exhibited by these antennas, including Rabi oscillations, solitons, and non-reciprocal behavior, which set them apart from classical antennas.
-

A Review on Antenna Technology Developments for Sub-THz Wireless Communication: Applications, Challenges and Opportunities
25 February 2025 Jordi C.F. Zandboer, Gabriele Federico, Ulf Johannsen and A. Bart Smolders analyze state-of-the-art antenna concepts in the higher millimeter-wave frequency range (90-300 GHz), commonly referred to as the sub-THz frequency range. As the sub-THz range is still an emerging field of research, the aim of this review is to present and discuss different approaches and concepts reported in literature in the areas of antenna-in-package (AiP), antenna-on-chip (AoC) and other sub-THz antenna technology, focusing on the gain and occupied area parameters. Based on the analysis, it is concluded that AiP and AoC systems are very promising for highly integrated solutions requiring a small form factor, such as inter-device communication. At the same time, other concepts such as lens antennas provide a better solution for high-gain applications like fronthaul/backhaul scenarios.
-

Reflective and Transmissive Linear Polarization Rotators: A Review
19 February 2025 Ahmed Abdelmottaleb Omar provides a comprehensive literature review of design principles and topologies for both reflective and transmissive polarization rotators. It begins with an overview of polarization rotators and their applications, setting the stage for an in-depth exploration of design methodologies. Reflective polarization rotator designs are first discussed, focusing on two primary approaches: tilted resonators and coupled current techniques. The article then examines various strategies for designing transmissive polarization rotators, including tilted resonators between grids, coupled currents, substrate-integrated waveguides, aperture coupling, meander lines, multilayer inclined wire gratings, and electromagnetic wave coupling techniques.
-

Evaluating Vegetation Attenuation Characteristics at the 300-GHz Band
19 February 2025 Keisuke Matsui, Hiroaki Nakabayashi and Akihiko Hirata examine the seasonal variation in vegetation loss and the effects of moving foliage on signal propagation at the 300 GHz band. The variation in vegetation loss across seasons aligns well with the ITU-R model when parameters are adjusted for the month exhibiting maximum vegetation loss. During leafless seasons, slow fading is characterized by a frequency component below 0.2 Hz and occurs predominantly due to branch vibrations caused by wind. In environments where foliage consistently obstructs the line of sight between transmitter and receiver (quasi-line-of-sight, QLOS), rapid fading occurs due to foliage movement, with frequency components reaching up to 20 Hz.
-

Fixed-Frequency 2-D Wide-Angle Scanning Leaky-Wave Array With Reconfigurable Probe-Fed Magneto-Electric Dipole
18 February 2025 Kai Qin, Bingjie Xiang and Kwai-Man Luk propose a new 2-D scanning leaky-wave antenna (LWA) design with a scanning range larger than competitors. It consists of a 1-bit reconfigurable magneto-electric (ME) dipole array and a pillbox beam-forming network (BFN). The probe-fed ME dipole is minimized to fit the holographic method and is introduced in LWA for the first time. A p-i-n diode is loaded in the L-shaped directly-fed probe to control whether it radiates. The dispersion characteristic of the linear LWA is examined to validate the effectiveness of the holographic method. A procedure is proposed to select the port and hologram for any-angle 2-D beam scanning.
-
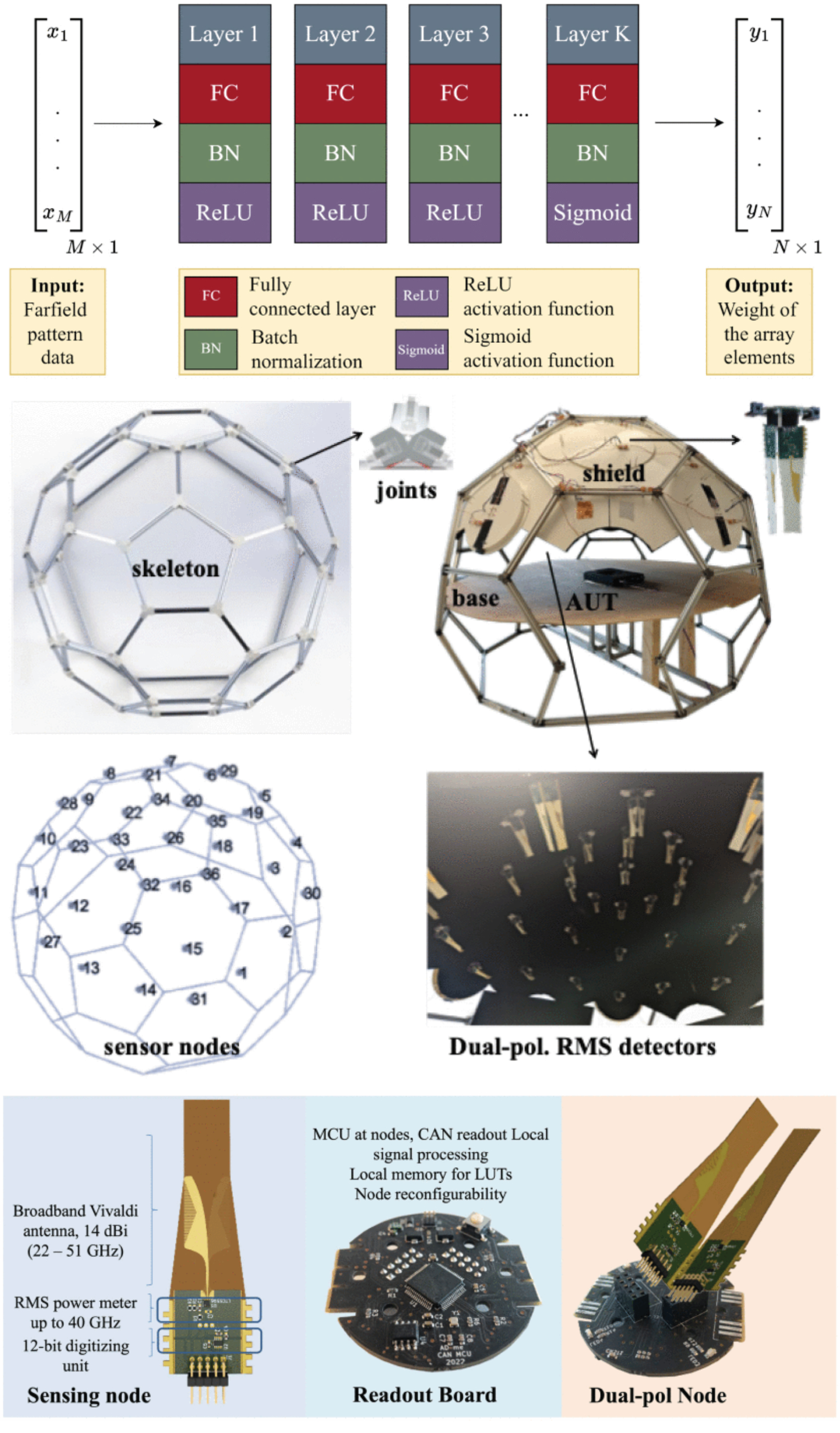
Detection of Faulty Elements From Sparse Far-Field Data in Active Phased Arrays via Machine Learning
14 February 2025 Aparna Kannan, Nehir Berk Onat, Marco Spirito, Alexander Yarovoy and Yanki Aslan analyze machine learning-assisted solutions to tackle real-time fault detection in large-scale active phased array antennas. The challenge of integrating the circuit component nonlinearities and mutual coupling effects in fault-finding methodologies is addressed. A novel machine learning (ML) solution based on an array theory-enhanced neural network (NN) is proposed. To address the practical constraints of large array measurements, sparse far-field (FF) measurements are considered.
-

Metamaterial-Based Wide-Angle Scanning Circularly Polarized Phased Array With Stable Gain
12 February 2025 Xiangyu Yin, Wu Ren, Zhenghui Xue and Weiming Li propose a wide-angle scanning circularly polarized phased array with stable gain. The proposed antenna array is composed of truncated microstrip antennas, four rows of mushroom metamaterials, and two tensor holographic metasurfaces. The mushroom metamaterials generate TM10 mode on the same plane as the antenna elements, compensating for the imbalance between horizontal and vertical polarization when the beam pattern of the phased array is steered to a wide-angle point. Meanwhile, the tensor holographic metasurfaces convert surface waves into circularly polarized leaky waves, which superimpose on the radiation of the antenna array, thereby improving the axis ratio and increasing the realized gain.
-

Dual-Mode, Dual-Polarization Fully-Woven Textile Antenna for Simultaneous Wireless Information and Power Transfer Applications in the 2.4 GHz Band
12 February 2025 Miguel Fernández, Carlos Vázquez and Samuel Ver Hoeye present a dual-mode, dual-polarization fully-woven textile antenna for simultaneous wireless information and power transfer in the 2.4 GHz band. It is based on a square patch with two independent ports. The first port is implemented with an offset T-match structure, to which a singlediode rectifier is connected. The selected feeding technique allows to obtain complex-conjugate impedance matching with the rectifier and right-hand circular polarization for the wireless power transfer mode. On the other hand, for the information transfer mode, a coaxial probe is used to excite the antenna with left-hand circular polarization, in order to minimize the coupling between both modes.
-

Stability Analysis of the EFIE-IBC Formulation and Regularization via Spatial Filtering
04 February 2025Margaux Bruliard, Marcello Zucchi and Giuseppe Vecchi devise two “ground truth” test examples starting from a physical metasurface, then approximated via Impedance Boundary Condition (IBC). Comparison to ground truth results shows that the standard Electric-Field Integral-Equation with IBC (EFIE-IBC) may lead to significant errors, and that these may be challenging to detect. Conversely, the regularized system yields stable results that well match the ground truth of the physical structure of which the IBC is an approximation. Conversely, the regularized system yields stable results that well match the ground truth of the physical structure of which the IBC is an approximation.
-

Dual-Fed DRA Subarrays Featuring Versatile Polarization Reconfigurability With High Port Isolation and Suppressed Cross-Polar Radiations
04 February 2025 Satyajit Chakrabarti and Debatosh Guha explore a near square Dielectric Resonator Antenna (DRA) geometry with dual-aperture feeding. This aims in achieving a number of attractive features from a standalone unit as well as a 4-element subarray. Unlike the earlier designs, it demonstrates four reconfigurable polarization states which are realized by conceiving a new near square shape of the DRA along with a novel feeding concept, proposed for the first time. They enable the subarray to significantly enhance the cross-polar discrimination (XPD). The design principles for dual-linear and dual-circular polarizations have been demonstrated and experimentally verified using a set of S-band prototypes. microcontroller through RC filter.
-

A Sub-Aperture-Based Calibration Algorithm for MIMO Antenna Arrays
31 January 2025 Matthias Linder, Daniel Schmidt, Dominik Schwarz, Nico Riese and Christian Waldschmidt propose the deployment of sub-apertures to avoid near-field effects and to reduce the calibration effort, which is in this work related to the number of measuring points in the calibration measurement. An algorithm to create beneficial sub-apertures from a large array based on clustering is described. This allows the far-field distance to be reduced, as well as the effort required for state-of-the-art calibration methods, which depends on the aperture size. The trade-off between the benefits and error propagations as well as other limitations by the deployment of an increasing number of sub-apertures is demonstrated by simulations and measurements. Exemplary measurements show that even for large arrays in compact measuring chambers, far-field like conditions can be created.
-

Point Cloud-Based Diffraction Path Extraction for Dynamic Human Body Shadowing Channel at 300 GHz
27 January 2025 Chechia Kang, Xin Du and Jun-Ichi Takada propose a method that estimates the diffraction paths from a complex human body as the ones from the cross-section of the human body. The extracted diffraction paths are used for the uniform theory of diffraction (UTD) simulation. The proposal was evaluated by an indoor measurement (3.3 m) of the human body shadowing channel and a simulation based on the modified edge representation and equivalent edge currents (MER-EECs) method. The proposal was found four times more accurate than the conventional point cloud (PC)-based vertical screen model and available for predicting the Doppler frequencies with complex human motions.
-

A Design of Orthomode Transducer Loaded With Polarization Grid
22 January 2025 Yuying Li, Zhaoran Chen, Kaiyan Huang and Xiayuan Yao propose a design of an Orthomode Transducer (OMT) loaded with a polarization grid based on the traditional T-junction OMT structure. Additionally, a conical horn is integrated into the presented OMT. The entire system was subjected to simulation, fabrication, and measurement. In 29.8–32.2 GHz, both the simulated and tested Voltage Standing Wave Ratio (VSWR) values for the two orthogonal ports remain below 1.2, with a measured isolation of 60–75 dB. At 31 GHz, there is a good agreement between the simulated and measured far-field patterns for the main polarization, with cross polarization levels measured at less than −15 dB.
-

6G RIS in Indoor Environments: Assessment of Exposure Variability in Human Users and Non-Users
16 January 2025 Silvia Gallucci, Martina Benini, Serena Fiocchi, Gabriella Tognola and Marta Parazzini assess the exposure of human users and non-users in indoor scenarios due to novel technology that will be integrated in 6G network in order to overcome the obstacles in NLOS area: Reconfigurable Intelligent Surface (RIS), here tuned in FR1-band. The exposure assessment was conducted in two simplified indoor scenarios, single room and office, where the transmission angle of the RIS were varied mimicking the RIS following the user, and the Specific Absorption Rate (whole-body and brain SAR) were calculated. Five human models from Virtual Population (ViP) were considered differing between each other for anatomical characteristics.
-
A Design Method to Increase the Bandwidth of Reflectarray Antennas
16 January 2025 Christos Exadaktylos, Anastasios G. Koutinos, Constantinos L. Zekios and Stavros V. Georgakopoulos introduce a novel design methodology to redesign traditional reflectarray antennas (RAs) with bandwidths in the order of 15% and double their bandwidth without increasing their design complexity. A wideband RA unit cell (UC) is designed utilizing multiple connection points between the radiating and phase shifting structure. Notably, to properly set the desired phase shift at each UC of the RA aperture across the entire frequency band, true-time-delay (TTD) lines are connected to each element. To validate the performance of our proposed approach a traditional microstrip patch-based RA is used as an example.
-

Beam Shaping by Phase-Only Waveform Encoding for Transmitting Array Antennas in Radar Applications
14 January 2025 Lior Maman, Shlomo Zach and Amir Boag propose and compare two beam broadening methods for active electronically scanned array (AESA) antennas with uniform amplitude excitation: phase tapering optimization (PTO) and a novel time-varying phase tapering (TPT). The PTO is a simple and efficient approach assuming continuous polynomial phase distribution and requiring optimization of only few parameters. The TPT is valid mainly for radar applications, taking advantage of the fact that radars typically transmit pulse trains for coherent integration. By incorporating waveform encoding and varying the array elements’ phases from pulse to pulse, the TPT achieves effective amplitude tapering, enabling precise beam shaping and the realization of any amplitude aperture illumination using phase-only control, thus providing a method of beam shaping, occasionally with a simple analytic form.
-

Synthesis of Wide-Angle Scanning Arrays Through Array Power Control
13 January 2025 Pietro Rosatti, Giacomo Oliveri and Andrea Massa propose a new methodology for the synthesis of wide-angle scanning arrays.It is based on the formulation of the array design problem as a multi-objective one where, for each scan angle, both the radiated power density in the scan direction and the total reflected power are accounted for. A set of numerical results from full-wave simulated examples - dealing with different radiators, arrangements, frequencies, and number of elements - is reported to show the features of the proposed approach as well as to assess its potentialities. A widening of the field-of-view percentage of up to 22% with respect to standard scanning methods is demonstrated.
-

Near-Ground Propagation Channel Modeling and Analysis in Underground Mining Environment at 2.4 GHz
08 January 2025 Isam Eddine Lamri, Mourad Nedil, Mohamed Nasr Eddine Temmar and Nahi Kandil present a detailed measurement and performance analysis of near-ground propagation channels in an underground mine for both Line-of-Sight (LOS) and Non-Line-of-Sight (NLOS) scenarios. The analysis is derived from channel measurements conducted at a frequency of 2.4 GHz with a bandwidth of 200 MHz, utilizing four different combinations of transmitter-receiver (Tx-Rx) antenna heights ranging from 10 cm to 120 cm. Key channel characteristics such as large-scale path loss, time dispersion, and coherence bandwidth are reported and evaluated. The study suggests that a multi-slope (four-slope) path loss model is more effective in predicting path loss across various propagation segments in the mining environment.
-

Optimal Frequencies for Wireless Power Transfer Through Biological Tissues
06 January 2025Nam Ha-Van, Sergei A. Tretyakov and Constantin R. Simovski present a comparative theoretical study of a basic wireless power transfer (WPT) system for two cases: when both transmitting and receiving loops are inside a biological tissue (human body) and when the transmitting loop is outside while the received loop is inside. The study aims to find and compare optimal frequency ranges of WPT, distinguishing the regimes of maximal efficiency and maximal transferred power for both of these cases. It is found that the impact of the interface results in a significant increase in the frequencies that are optimal for the maximum power transfer efficiency: from dozens of MHz for a WPT system entirely located in the medium to the GHz range for a WPT system with the transmitting antenna in free space.
-

Digitally Controlled Beam-Steerable Printed Dipole Antenna
3 January 2025 Rajesh Shukla, Sandeep Kumar Yadav and Soumava Mukherjee propose a digitally controlled beam steerable printed dipole antenna operating in ISM band using PIN diodes switching mechanism. The proposed antenna provides effective solution of beam steering by establishing adequate coverage in elevation plane using a single dipole element. The beam steering of antenna has been digitally controlled by varying the effective length of one dipole arm by switching the PIN diodes integrated on it. For effective digitally controlled beam steering, the DC biasing voltage applied for switching PIN diodes is regulated by Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) signal generated from STM32F407VG microcontroller through RC filter.
-

A Compact Shared-Aperture Antenna With 2-Transmit and 2-Receive Highly-Isolated Ports for Full-Duplex MIMO Systems
01 January 2025 Junhui Rao, Zhaoyang Ming, Jichen Zhang, Zan Li, Chi-Yuk Chiu and Ross Murch propose a compact multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) In-band full-duplex (IBFD) antenna featuring two co-polarized transmit (Tx) ports and two co-polarized receive (Rx) ports that is suitable for use in mobile devices. The design is one of the first to include MIMO into IBFD antennas. The fabricated and measured proposed antenna exhibits over 32 dB self-interference (SI) isolation between Tx and Rx ports and less than −18.2 dB mutual-coupling (MC) within Tx and Rx pairs. All radiation patterns are in the broadside direction and it operates in the 2.5 GHz frequency band.
-
Pattern Compensation for Faulty Phased Array Antenna Based on Deep-Learning Technique
23 December 2024 Shu-Min Tsai, Ming-Tien Wu, Yu-Han Chen, Hong-Wei Yan and Ming-Lin Chuang propose an approach to compensate for pattern distortion in a phased array antenna caused by antenna element failures. The proposed approach utilizes a deep-learning network explicitly trained for a phased array antenna with damaged elements to generate the necessary excitation, producing a new pattern closely resembling the intact phased array antenna. Compared to alternative methods that focus on reducing side-lobe level, this compensation approach offers the advantages of rapid response and minimal computational overhead for the re-synthesis of the desired pattern that is close to the original pattern. This approach makes it particularly suitable for scenarios involving faulty phased array antennas, such as those on satellites or mountain-top antenna towers, where replacement or repair is not readily feasible in a short timeframe.
-

Compact High Selectivity Patch Antenna Under Triple-Mode Resonance via Loading Symmetrical Slots
19 December 2024 Mingli Sun, Qianwen Liu and Lei Zhu propose a compact filtering patch antenna on a single-layer substrate under triplemode resonance by loading two pairs of stepped slots. Initially, four straight slots are symmetrically etched along the radiation edges of a square patch radiator to reshape the radiation and resonant properties of its two higher-order TM02 and TM12 modes for bandwidth enhancement when maintaining the performances of the fundamental TM10 mode unchanged. Owing to the specific field distributions of the reshaped TM02 and TM12 modes, two radiation nulls can be produced nearby. In order to move the radiation nulls outside the desired passband for highly-sharpened wideband filtering radiation, the straight slots are then properly modified with their stepped ones in configuration.
-

AMC-Based Miniaturized Waveguide With Reconfigurable Pass-Bands Below Cut-Off Frequency and Quasi-TEM Mode
18 December 2024 Vikrant Singh, Maryam Khodadadi, Mohsen Khalily, Rahim Tafazolli and Ahmed A. Kishk introduce an innovative miniaturized transverse electromagnetic (TEM) waveguide design, which is 60% smaller than conventional metal waveguides. The proposed waveguide offers two distinct electronically reconfigurable passbands well below the cutoff frequency. This has been achieved by using sidewalls composed of reconfigurable artificial magnetic conductors (AMC), optimized to operate at 3.51 GHz and 4.37 GHz. By replacing the metal sidewalls with an AMC structure, a TEM mode can be sustained within the confined space enclosed by the waveguide structure, which otherwise would not exist in a conventional metal waveguide. This eliminates typical cut-off frequency constraints that limit the size of conventional waveguides, thereby enabling a significant miniaturization of the waveguide design.
-

Fluid Brilliance: Expanding the Horizons in MIMO Diversity Using Liquid Antenna
17 December 2024Viswanadh Raviteja Gudivada and Yi Huang present a six-port liquid dielectric resonator antenna designed to enhance diversity for Wi-Fi applications operating at 2.45 GHz, leveraging the fluidic properties of liquids. The proposed design incorporates both conventional and modified intrusive feeding mechanisms, specifically utilizing extended copper lines with vertical dielectric wall support. This arrangement is aimed at realizing six pattern and polarization-independent TM 02δ+1 , HEM y21δ+1 , HEM 122δ , HEM 222δ , HEM x21δ+1 , and HEM y12δ+1 higher-order modes belonging to the TM and HEM mode family.
-

Compact Dual-Band, Dual-Circular Polarized Microstrip Antenna Array for K/Ka-Band Application
16 December 2024 Nohgyeom Ha, Gyoungdeuk Kim, Hyun-Cheol Bae and Sangkil Kim propose a novel dual-band and dual-circularly polarized microstrip antenna design for a small AAV or a low earth orbit (LEO) satellite applications at K/Ka-band. Utilizing arrow-shaped and T-shaped stubs, the proposed design ensures right-hand and left-hand circular polarization across two frequency bands. The design activates orthogonal modes (TM10/TM01 and TM30/TM21) simultaneously, leveraging arrow-shaped and T-shaped stubs to finely tune resonant frequencies. The dimensions of these stubs facilitate independent adjustment of each operational band, ensuring optimized antenna functionality across different frequencies.
-

Electrically Large Complex Objects Recognition Based on Gated Recurrent Residual Network (GRRNet)
13 December 2024 Shangyin Liu, Lei Xing, Xiaojun Hao, Shuaige Gong, Qian Xu and Wenjun Qi propose a novel deep model based on gated recurrent residual network for electrically large complex objects recognition. It can fully exploit the data envelope information and temporal correlation to improve the system recognition performance. Electromagnetic (EM) scattering property measurements for electrically large objects are costly and time-consuming, affected by various environmental factors. The high-frequency approximate technique, namely the shooting and bouncing ray method (SBR), is introduced to quickly acquire high resolution one-dimensional range profile (HRRP) of electrically large complex objects. Both the corner reflector and the model car are measured to validate the accuracy of the SBR method. The method is employed to establish HRRP database for various vehicles in traffic scenarios. Deep learning can automatically study data deep features and show outstanding performance in various classification tasks.
-

GPS Interference Cancelation Using Metamaterials
11 December 2024 Amir Jafargholi and Romain Fleury introduces a novel passive method and structure designed to mitigate unwanted interference at the antenna in conventional Global Positioning System (GPS) applications. In contrast to traditional approaches that typically utilize high-impedance structures with limited cancelation or antenna arrays employing null-steering techniques, which often result in increased complexity and cost, this study proposes the use of a single-element circularly polarized truncated microstrip patch antenna radially loaded by a magneto-dielectric metamaterial (MTM) structure. The problem is analytically examined, and an appropriate meta cell is chosen, designed, and fabricated.
-

Reflective Metasurface for Multi-Band Polarization Conversion for Satellite Applications in 6G Networks
09 December 2024 Humayun Zubair Khan, Abdul Jabbar, Jalil Ur Rehman Kazim, Jamal Zafar, Masood Ur-Rehman, Muhammad Ali Imran and Qammer H. Abbasi introduce a reflective polarization converter based on metasurface, designed to offer both Linear-to-Linear polarization (LLP) and Linear-to-Circular polarization (LCP). The design comprises two periodically arranged split ring resonators with a slotted stripe that operate in the X, Ku, and K bands. The three discrete frequency bands demonstrate over 90% Polarization Conversion Rate for LLP for oblique incidence waves up to 45°. Additionally, the proposed converter achieves Left-Hand Circular Polarization (LHCP) in two sub-bands and Right-Hand Circular Polarization (RHCP) in two sub-bands for oblique incidence waves up to 45°.
-

A Numerical Integration Method for Calculating the Bit Error Rate of Time-Modulated Array
04 December 2024 Kexin Wang, Jian Zhang, Gang Xin, Xue Lei, Jun Gao and Tianpeng Li present a novel approach for computing the bit error rate of time-modulated array using the Laplace inversion integral. They express the bit error rate as a Laplace inversion integral and select the integration path using the saddle point method. The integration result is obtained through numerical integration, and they derive the upper bound of the truncation error. The time-modulated array under consideration includes a single pole double throw switch array, which can independently exist in two states. This calculation method can be readily extended to time-modulated arrays with multiple states.
-

A Millimeter-Wave Single-Bit Reconfigurable Intelligent Surface With High-Resolution Beam-Steering and Suppressed Quantization Lobe
03 December 2024 Aditya S. Shekhawat, Bharath G. Kashyap, Russell W. Raldiris Torres, Feiyu Shan and Georgios C. Trichopoulos present a 1-bit reconfigurable intelligent surface (RIS) operating at millimeter-wave frequencies that suppresses the undesired grating lobes encountered in binary phase modulation schemes and achieves high resolution beam steering. They incorporate fixed, random phase delays at each unit cell of the surface which breaks the periodicity of the phase quantization error and suppresses side lobes. Additionally, the random phase delays reduce the beam pointing error – a limitation of binary RISs - which can be beneficial in applications that require high resolution beam steering. The proposed topology allows for scalable RIS apertures that are compatible with printed circuit board (PCB) fabrication technology.
-

A Multibeam Solar Grid Antenna Integrated With Monocrystalline Silicon Solar Cell
02 December 2024 Fuwei Wang, Xuechen Zhang, Rong Sun, Bokai Ding, Ke Li and Chen He propose a multibeam grid antenna integrated with a monocrystalline silicon solar panel first time, which consists of a grid antenna in microstrip form and a monocrystalline silicon solar cell. Multiple feeders are set at different positions of the grid antenna to adjust the current phase on the short side of the grid antenna to achieve beam scanning. The antenna is designed to operate in the 24 GHz radar band and can be installed in field Internet of Things devices for vehicle monitoring and communication, meeting requirements for communication rate, sensing sensitivity, detection, and interconnectivity. The multibeam characteristic can effectively enhance the communication and sensing detection range of the antenna. Meanwhile, the grid-like structure of the antenna ensures good optical transmission, allowing it to be positioned above the solar panel without significantly affecting the performance of the solar cell.
-

Design and Characterization of Line-Waves Waveguides for Microwave Applications
26 November 2024 Alessio Monti, Stefano Vellucci, Mirko Barbuto, Valentina Verri, Francesco Vernì, Claudio Massagrande, Davide Ramaccia, Michela Longhi, Zahra Hamzavi-Zarghani, Luca Stefanini, Alessandro Toscano and Filiberto Bilotti report a simple and straightforward workflow for designing waveguides supporting one-dimensional modes propagation. The design is based on the analytical relations existing between the surface impedance of the propagating modes and the sheet impedance of the metasurfaces, which allow quick retrieval of the geometrical parameters of the complementary metasurfaces sustaining the line-wave propagation. This approach is used to design several waveguiding layouts and compare their transmission performance through full-wave simulations accounting for dielectric and ohmic losses.
-

Application of Aperiodic “Einstein” Monotile in Phased Arrays With Limited Beam Scanning Range
14 November 2024Yunfei Qiang, Xiaochuan Fang, Rui-Xin Wu, Qian Chen and Wei Wang propose a phased array with a limited beam scanning range based on the ‘Einstein’ monotile (Hat polykite), characterized by low grating lobe levels and high aperture efficiency. The proposed phased array reduces implementation complexity compared to periodic subarrays and enhances engineering practicality relative to other aperiodic tiles, particularly in load-bearing lattice configurations. Two examples of Hat polykite-based phased arrays are presented in this paper. Example A presents a sparse phased array, where each element is embedded within a Hat polykite, optimized for a maximum grating lobe level of −15 dB. Example B features a subarray comprising eight antenna elements based on the Hat polykite.
-

Compact Uplink Circularly Polarized 2.4GHz Short Backfire Antenna for Geostationary Amateur Radio Satellite Es’Hail-2 (QO-100)
14 November 2024 Michal Cerveny and Pavel Hazdra describe a compact circularly polarized antenna designed for the 2.4GHz band with a gain of 15dBic designed for communication (uplink) with a geostationary amateur radio satellite Es’Hail-2 (QO-100). The proposed antenna upgrades a standard short backfire antenna (SBA) by utilizing two metasurfaces with the first acting as a high-impedance surface (HIS) allowing for a reduction of the distance between the sub-reflector and main reflector and the second enhancing the sub-reflector while functioning both as a tunable polarization divider and phase shifter to form the circular polarization. This novel concept enables the use of a simple, linearly polarized patch antenna as a feeder with no complex feeding networks.
-

Additively-Manufactured, Magnetically Controlled, Frequency and Polarization Reconfigurable Phased Array Antenna
11 November 2024 Ulan Myrzakhan, Farhan A. Ghaffar, Mohammad Vaseem and Atif Shamim present an additively manufactured phased array antenna that provides simultaneous reconfiguration in frequency, polarization, and beam direction solely in response to magnetic tuning of the underlying ferrite substrate. This design obviates the need for integrated active components, which have been fundamental elements enabling tuning operation in traditional reconfigurable array antennas. The array element of the proposed array antenna consists of a waveguide-based phase shifter, realized by printing metallic walls on a ferrite substrate, which is then monolithically integrated with a printed circular patch antenna. Depending on the magnitude and polarity of the applied magnetic field (solenoids) to the patches, the array antenna can operate in a linearly polarized (LP) mode at 7.2 GHz or in dual circularly polarized (CP) modes in two continuously tunable frequency bands, 5.9–6.5 GHz and 7.6–7.95 GHz.
-

Balancing the Potential Gauging Process Applied to Wave Propagation for Arbitrary Space-Times
06 November 2024 Thomas Reum addresses possibilities to compensate an unwanted side effect arising in the widely used gauging process of electrodynamic potentials due to mathematical conditions applied to describe propagating electromagnetic (EM) waves with a focus on radio frequency (RF). Previous studies have shown by means of guided propagation that phase velocities which differ from intuitive understanding occur for several components of potentials when deviating from a specific gauge determined by physical relationships. Two solution strategies are provided in a way that the changed temporal behavior of affected potentials is balanced directly or by adapted spatial relations. In this regard, appropriate changes of the metric are suitable since the choice of gauge is closely related to the space-time of a model. For this purpose, only the metric tensor of affected potential components is modified throughout this work.
-

A Dual-Port Dual-Wideband Dual-Sense Circularly Polarized DRA With a Novel Feeding Mechanism
05 November 2024 Li Zhang, Jian-Wei Liu, Bo Chen, Liang-Yong Yi, Dian Liu, Zi-Bin Weng and Yong-Chang Jiao investigate and demonstrate a dual-wideband dual-sense circularly polarized (CP) dielectric resonator antenna (DRA) based on a novel feeding technique. The proposed antenna is composed of a cylinder DR, a ground plane with a double cross-slot and two rectangle slots, and a novel feeding structure. In the lower band, the DR is fed by two vertical metal probes, and the antenna can be fed by a novel feeding method in the upper band. Based on these feeding mechanisms, a pair of orthogonal modes can be excited in the lower band, and the slot modes can be obtained in the upper band.
-

Indoor Deterministic Simulations and Statistical Modeling at Sub-THz Frequencies for Future Wireless Networks
05 November 2024 Nektarios Moraitis and Konstantina S. Nikita present a detailed analysis of the indoor channel at sub-THz frequencies, modeling its temporal and spatial characteristics for line-of-sight (LOS) and non-line-of-sight (NLOS) conditions, relying on extensive deterministic simulations. According to the results, frequency selective characteristics are revealed. The obtained root-mean-square delay spread is in the range of 4.4–10.3 ns for LOS, and 6.9–18.8 ns for NLOS scenarios, respectively. A high spatial degree of freedom is also observed based on the increased azimuth spreads with a mean value of 57.4° for LOS, and 88.1° for NLOS locations, which is associated with the environment geometry.
-

A Novel Pixel-Based Reconfigurable Antenna Applied in Fluid Antenna Systems With High Switching Speed
01 November 2024 Jichen Zhang, Junhui Rao, Zan Li, Zhaoyang Ming, Chi-Yuk Chiu, Kai-Kit Wong, Kin-Fai Tong and Ross Murch demonstrate that using mechanical movement or liquids in Fluid Antenna Systems (FAS) is equivalent to radiation pattern reconfiguration. Using this observation, we propose a pixel-based reconfigurable antenna design for FAS (PRA-FAS) that supports microsecond FAS port switching for packet-by-packet adaptability. The proposed PRA-FAS provides 12 FAS ports across an equivalent length of 1/2 wavelength. Simulation and experimental results of a PRA-FAS prototype operating at 2.5 GHz indicate that the PRA-FAS can meet the FAS requirements, including port correlation and impedance matching. System-level simulations and experiments, using a MIMO testbed, demonstrate that the correlation of PRA-FAS ports aligns well with those that use mechanical movement or liquids.
-

Dual-Band Circularly-Polarized Transparent GNSS Antenna for Vehicular Applications
29 October 2024 Quoc Hung Dang, Nghia Nguyen-Trong, Thomas Kaufmann, Timo Saarnimo, Chris Hide and Christophe Fumeaux propose a dual-band circularly-polarized transparent antenna for Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS). The antenna is designed with resonance frequencies centered at 1176 MHz and 1582 MHz, targeting the simultaneous coverage of the L5 and L1 bands. Aiming at integration into the glass sun-roof of a vehicle, the antenna is designed using an unperturbed single-substrate layer, i.e., without any via or probe feed. A fine metal mesh based on printed copper is used to achieve around 90% transparency while maintaining satisfactory antenna gain and radiation efficiency within both operation bands.
-

Transparent Graphene-Based RIS for 6G Communications in the THz Spectrum
29 October 2024 I. Marasco, C. Cantore, G. V. Bianco, G. Bruno, A. D'Orazio and G. Magno present a numerical investigation and the optimized design of a transparent graphene-based RIS operating in the THz spectrum. The aim of the paper is twofold: the former is to demonstrate the reconfigurability of the proposed RIS by exploiting two methods, referred to as “digital” and “analogical”. The latter is to demonstrate the effects of the losses and of the mutual coupling among unit cells on the power flow pattern. This aspect is crucial in the design of the RIS and cannot be overlooked, differently from other papers reported in the literature which analyze the RIS as an “ideal” structure evaluating only an analytical estimation of the array factor and neglecting the interaction among the unit cells.
-
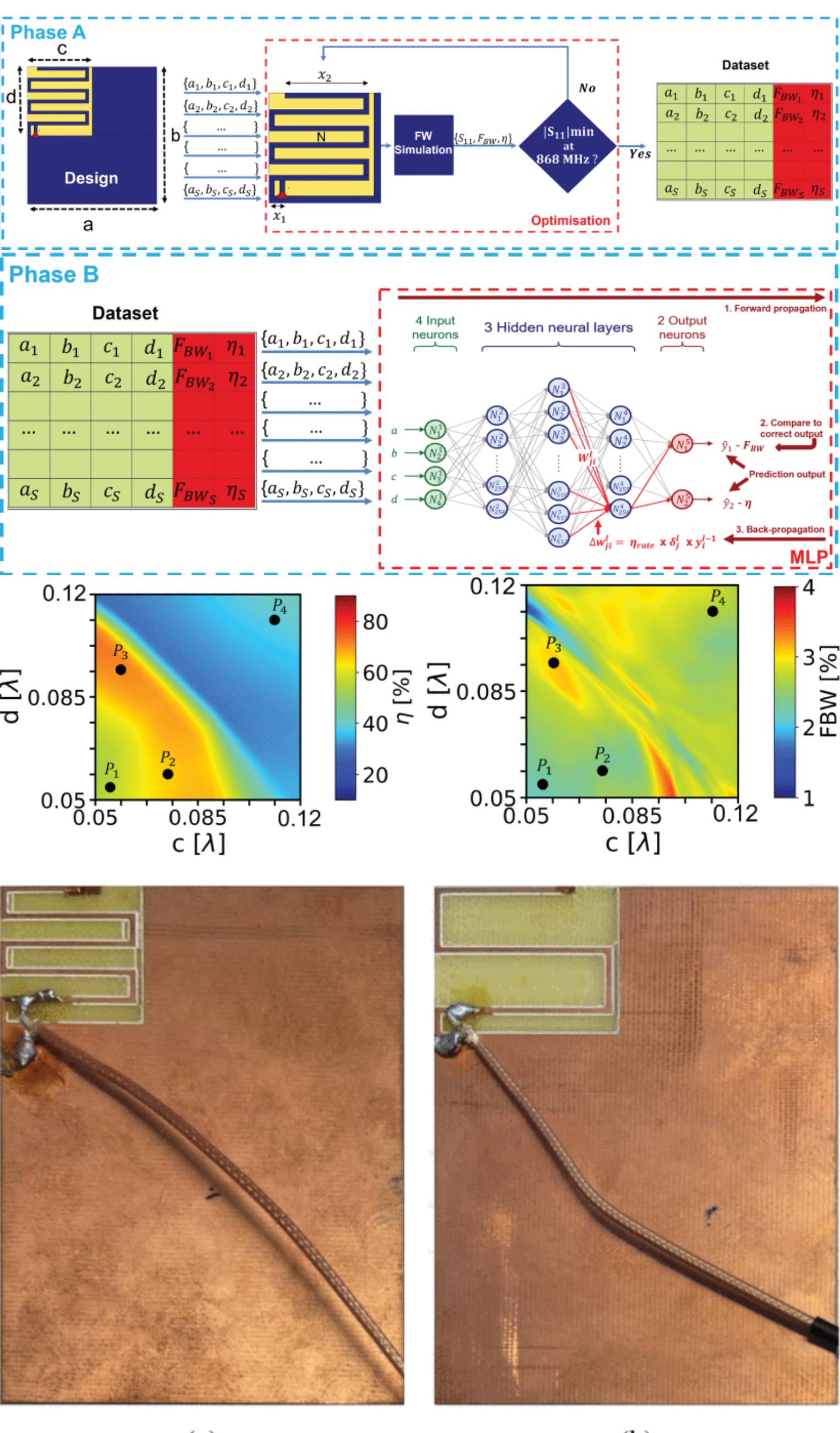
Predicting the Maximum Achievable Antenna Bandwidth and Efficiency Using Machine Learning: A Terminal-Integrated Meander IFA Case Study
28 October 2024 Julian Roqui, Alain Pegatoquet, Luca Santamaria and Leonardo Lizzi propose an approach based on Machine Learning (ML) to predict the maximum achievable performance (fractional bandwidth and total efficiency) of a printed Inverted F-antennas (IFAs) integrated into compact IoT terminals. This original approach relies on the use of a Multi-Layer Perceptron (MLP) artificial neural network (ANN), which is trained using data from numerical simulations that take into account the constraints of practical implementations. The effectiveness of the approach is demonstrated through comparisons with numerical and experimental results, as well as with theoretical results available in the literature.
-

An Efficient Curvature-Based Synthesis Methodology for Rotationally Symmetric Shaped Reflector Antennas
25 October 2024 Manushanker Balasubramanian and Douglas H. Werner extend and apply a previously proposed B-spline curvature-based synthesis technique to the design of rotationally symmetric reflector antennas with shaped beam patterns. The approach is based on representing a reflector as a single curve that can be modified to alter the reflector’s shape. The curvature is evaluated and represented using B-spline polynomials. First, the control points of the spline curve are defined as variables and then a new curvature profile is generated. Following this step, the corresponding curve is synthesized using the proposed iterative algorithm. This process of optimizing the curvature using B-spline polynomials offers the ability to better control the shape of a reflector with very few design variables.
-

Wireless Multi-Coil Transmission With a Rotating Part of the Internal Winding
24 October 2024Josef Pokorny, Premysl Dohnal and Petr Marcon discusse the basic principles of concentrating the radiated near non-radiant magnetic field by changing the angle of the winding sector of the spiral coils designed on a substrate for a standard PCB (printed circuit board). The relevant principles include: 1) Changing the shape and design of the movable inner part of the coil winding; together with the static part, the moving item can form a concentrated magnetic field in space, thus creating a magnetic vector. 2) The 2×2 matrix of these coils comprises individual resonators changing the shape of the magnetic field according to the shape, distance, and position of the receiver.
-

H-Matrix Accelerated Direct Matrix Solver for Maxwell’s Equations Using the Chebyshev-Based Nyström Boundary Integral Equation Method
24 October 2024 Jin Hu, Emrah Sever, Omid Babazadeh, Ian Jeffrey, Vladimir Okhmatovski and Constantine Sideris formulate, test, and profile an H-matrix accelerated direct solver employing the high-order Chebyshev-based Boundary Integral Equation (CBIE) method for performance on high contrast dielectric materials and electrically large perfect electric conductor objects. The matrix fill performance of the CBIE proves to be fast for small to moderately sized problems compared to its counterparts, e.g., the locally corrected Nyström (LCN) method, due to the way it handles the singularities by means of a global change of variable method.
-

Electromagnetic and Thermal Co-Analysis of an Implanted Dipole Antenna
18 October 2024 Ala Alemaryeen and Sima Noghanian focus on examining tissue temperature elevation near implanted antennas, specifically a simple dipole antenna, to identify design parameters that significantly impact thermal performance. Key parameters include body phantom type and size, thermal boundary conditions, bioheat model parameters, implantation depth, antenna orientation, and input power. The study aims to provide guidelines for designers on optimizing antenna parameters to accurately predict and manage biological tissue heating. It was found that the size of the phantom, blood perfusion, volume thermal losses, antenna orientation, and input power constitute the major effects on tissue heating.
-

A mmWave Transmitting Time Modulated Array Using Bespoke GaAs Integrated Circuits—Prototype Design and Laboratory Trials at 73 GHz
16 October 2024 Edward A. Ball and Sumin David Joseph present a prototype design and testing of an E band mmWave Time Modulated Array (TMA). The PCB based array has a 3 dB RF bandwidth of 71-73 GHz and a peak gain of −2 dBi on the first harmonic steered beam. The TMA second harmonic beam gain is within 0.9 dB of a conventional phase-shifter based array, in a like-for-like theoretical comparison. An array gain of +11.5 dBi is predicted for a full on-chip implementation. Good agreement between theoretical and prototype measured gains and array patterns are reported. Beam steering and phase correction are implemented using an FPGA, requiring only 2 digital lines per array element.
-

Beam Shaping of a Dual-Reflector Antenna Using a Reflectarray as Subreflector and Embedded Unit Cell Patterns
09 October 2024 Marzieh Mehri Dehnavi and Jean-Jacques Laurin propose a phase-only synthesis technique for shaping the beam of a circularly polarized dual-reflector antenna with a subreflector consisting of a reflectarray and a main parabolic reflector. The proposed technique exploits the element patterns of each reflectarray unit cell embedded in the whole system, including a feed horn, a reflectarray, and a main reflector. By using a penalty function that forces only the fitting of the desired and obtained patterns, the algorithm leads to a quasi-random phase distribution on the reflectarray and a poor radiation pattern. A term for minimizing the Laplacian of the phase distribution is added to the penalty function to force a smoothly varying phase distribution on the reflectarray.
-

Transparent Low-Profile and Wideband ITO-Glass Microwave Absorber
07 October 2024 Ahmed Hosameldin Khadrawy and Ahmed Abdelmottaleb Omar propose a transparent wideband microwave absorber by integrating Indium Tin Oxide (ITO) with glass in order to achieve both high microwave absorption and optical transparency. The design is constructed from three layers of glass substrate with etched ITO with different sheet resistance on each layer. The absorber features a combination of high dielectric constant material to accomplish the low-profile design and matching layer to achieve wide absorption bandwidth. The absorber demonstrates 115.64% fractional bandwidth from 3.48 GHz to 13.02 GHz with a structure thickness of 0.077 λmin , where λmin is the free-space wavelength at the lowest operating frequency.
-

A Hybrid Frequency Selective Absorber With Dual-Polarized Wireless Communication and Ultra-Wideband Absorption
30 September 2024 Youquan Wen, Sai-Wai Wong, Chunlin Ji, Ruopeng Liu and Yejun He propose a circuit design of decoupling between frequency selective absorbers layer and antenna layer. The hybrid FSA with antenna circuit achieves in-band wideband dual-polarized transmitting/receiving and ultra-wideband absorption of both in-band and out-of-band. The two circuit layers operate independently, resolving the problems of inter-layer interference of conventional multi-layer FSA with antenna circuit. Additionally, the antenna configuration allows for excitation at the receiving end, providing broadband radiation capability without affecting in-band absorption.
-

X-Band Waveguide Reflectionless Filtering Antenna Array With High Selectivity
30 September 2024 Jun Ma, Fuchang Chen and Kairan Xiang propose a waveguide reflectionless filtering antenna array with high selectivity. Instead of reflecting the out-of-band signal back to the source, the proposed antenna array dissipates the energy through a lossy network, which can reduce the interference to the former stage. The prototype circuit of the reflectionless filtering antenna array based on the complementary duplex theory is established, consisting of a bandpass network and a bandstop network, whose responses are completely complementary. High selectivity is achieved by introducing non-resonating nodes (NRNs) and configuring the transmission zeros (TZs) of the bandpass network and the reflection zeros (RZs) of the bandstop network to be set at the same frequency.
-

Multibeam Antennas Based on 3-D Discrete Lenses With Magnified Field-of-View
27 September 2024 Lisa Berretti, Renaud Loison, Esteban Menargues, Lucas Polo-López, Giovanni Toso and María García-Vigueras introduce and numerically analyze a new type of beamforming network (BFN) based on three-dimensional (3D) discrete lenses as an antenna system capable of generating multiple beams within a large Field-of-View (FoV). To enhance scanning capabilities, these lenses have their back part and associated feed array magnified relative to the front part. It is also shown that the radiating elements constituting the front part of the lens, due to the shape of their element factor, tend to limit the pointing direction of the overall antenna pattern, but their influence decreases as the lens dimension. Accordingly, a large front array is chosen to scan wide angles and mitigate this limitation.
-

Performance Analysis of Iterative Methods in Microwave Imaging With Various Regularization Techniques
26 September 2024 Reihaneh Ahmadi Vanhari, Ahmad Bakhtafrouz and Sima Noghanian conduct a comparative analysis to evaluate the performance of traditional regularization techniques such as Truncated Singular Value Decomposition (TSVD), Tikhonov regularization, and the truncated Landweber algorithm with choosing different regularization parameters, within the framework of these established methods. The lack of explicit mention of optimal parameter values and comparison of regularization methods highlights a gap in the existing literature. Investigating and comparing different regularization methods and their corresponding optimal parameter values for different structures and features within the framework of linearization methods can provide valuable insights into effectively solving inverse problems in MWI.
-

Design and Analysis of a Carbonyl Iron Powder/Epoxy Composite-Based Ultra-Wideband Multi-Pyramidal Magnetic Absorber Using an Equivalent Circuit Model
25 September 2024 Aparna Parameswaran, Nohgyeom Ha, Soo Hyun Kim, Sukjin Kwon, Byeongjin Park and Sangkil Kim present a CIP/epoxy composite based ultra-wide band electromagnetic multipyramidal absorber. The constituent parameters of the CIP/epoxy composite is experimentally extracted using a waveguide measurement setup. This raw data is then quantified using a least-square fit polynomial based curve fitting technique to facilitate its use in the design and the analysis of the pyramidal absorber. Four asymmetrical truncated pyramids supported by a grounded base constitute the absorber unit cell. The absorption bandwidth of the design ranges from 3.21 GHz to 40 GHz (FBW of 170.3%, S - band to V - band) and stable absorption characteristics under oblique incidences is observed up to 35°.
-

Efficient Synthesis of Large Finite Patch Arrays for Scanning Wide-Angle Anomalous Reflectors
24 September 2024 Sravan Kumar Reddy Vuyyuru, Risto Valkonen, Sergei A. Tretyakov and Do-Hoon Kwon propose a design methodology for planar loaded antenna arrays to synthesize a perfect anomalous reflection into an arbitrary direction by optimizing the scattering characteristics of passively loaded array antennas. It is based on efficient and accurate prediction of the induced current distribution and the associated scattering for any given set of load impedances. For a fixed array of finite dimensions, the deflection angles can be continuously adjusted with proper tuning of each load.
-

Path Loss Modeling of Wireless Signals in Underground Tunnels
24 September 2024Yaning Li, Baoguo Yu and Lu Huang propose a hybrid model describing the propagation attenuation of wireless signals in underground tunnels which divides the propagation channel into three subdomains according to the length of the tunnel, namely, the region of the free space propagation model, the region of the multimode propagation described by the ray tracing method, and the region of the improved waveguide model by adding the influences of tunnel roughness, tunnel inclination, and metal pipes. The determination of the breakpoints separating each region depends on the variation of the angle between the arrival direction of the signal ray and the axial direction of the tunnel.
-

Frequency Diverse Array for Signal Geofencing in Wireless Communications: Does it Work?
23 September 2024 Simone Del Prete, Marina Barbiroli and Franco Fuschini carry out a detailed analysis of the sensitivity of the geofencing effectiveness to the main array parameters. The analysis covers many aspects of the design, including the selection of the geometrical layout and the number of elements of the array, the frequency increase policy and the frequency offset across the elements and their spacing. The study also discusses the trade-offs between different design choices and provides insights into the performance in terms of focus efficiency and size of the focus area. Results show that bidimensional layouts, e.g., circular or planar, often represent effective solutions, whereas the linear arrangement can be a viable option only in case the frequencies are spread across the elements in a random-like fashion.
-

Advanced Metasurface-Based Antennas: A Review
23 September 2024 Wanchen Yang, Jinghao Li, Dongxu Chen, Yue Cao, Quan Xue and Wenquan Che present an analytical model for an antenna-embedded wall, also called signal-transmissive wall. In the signal-transmissive wall, multiple antenna elements are distributed periodically on both wall sides, and connected back-to-back through coaxial cables. Numerical full-wave simulations of the signal-transmissive wall are computationally demanding due to the fine meshes required in the cables while having an electrically large wall size. Therefore the simulations above 8 GHz are not feasible even with a powerful cluster computer of the authors’ research site. The analytical model is an attractive alternative to the full-wave simulation of the wall, which combines the individual transmission characteristics of the bare wall, realized gains of antenna elements and cable losses.
-

Dual-Polarized Wideband Filtering Antenna Array Based on Stacked-PCB Structure
23 September 2024 Matti Kuosmanen, Sten E. Gunnarsson, Johan Malmström, Juha Ala-Laurinaho, Jari Holopainen and Ville Viikari investigate a thin low-pass filtering antenna array based on dual-polarized Vivaldi elements. The low-pass filtering in the antenna elements reduces the requirement for the front-end filtering between the antenna and the microwave electronics, resulting in improved overall out-of-band suppression, size reduction, and lower cost. The array employs a novel stacked-PCB structure, where simple two-sided PCBs are stacked on top of each other. The via-connected metal layers of all PCBs form a tapered slotline along the surface normal of the PCBs. The filtering effect is realized by corrugating the tapered slotlines, which provides effective, space-saving integration of the filters that fit into a half-wavelength lattice.
-

A Metallo-Dielectric Groove Gap Waveguide Slotted Array Antenna With Hybrid Glide-Symmetric Holes & “Mushroom”-Type Metasurfaces
23 September 2024 Panagiotis Petroutsos and Stavros Koulouridis present a hybrid multilayer slot array antenna, targeting next-generation wireless communication systems, particularly in mmWave bands like the Ka-band. The hybrid structure utilizes a high-performance metal Groove Gap Waveguide (GGW) feeding network and facilitates the practical manufacturing of slotted antennas and dielectric substrate metasurfaces using printed circuit boards. The proposed antenna incorporates a hybrid glide symmetric holey metasurface into the GGW feeding. This integration addresses assembly challenges between metal and dielectric layers, avoiding delicate welding techniques. It prevents energy leakage between the two different materials, even when a small air gap is maintained between them.
-

Compact Dual-Band Dual-Sense Circularly Polarized Fragmental Patch Antenna Optimized by Improved Simulated-Annealing-Based Algorithm
19 September 2024 Tianyu Shu, Bowen Feng, Long Zhang, Chuyue Chen, Hui Chen, Yaling Chen and Qinyu Zhang present a compact dual-band dual-sense circularly polarized (CP) fragmental patch antenna that advanced by an improved simulated-annealing-based optimization algorithm. This design replaces truncated corners of traditional truncated patch antennas with fragmental structures, generating dual-band dual-CP radiation with a small frequency ratio and a high front-to-back ratio. The proposed optimized framework tackles the multi-objective optimization problem through hierarchical optimization to achieve an optimal balance among various performance metrics.
-

Spillover Analysis and Mainbeam Characterisation of Arctic Weather Satellite Radiometer Using Method of Moments
17 September 2024 Roland Albers, Mustafa Murat Bilgic, Karl-Erik Kempe, Alistair Bell and Axel Murk present the Arctic Weather Satellite (AWS) is a single instrument mission consisting of a microwave sounder operating in the 54, 89, 183 and 325 GHz bands. The optical design of the instrument consists of a feedcluster directly illuminating a crosstrack scanning mirror, keeping the instrument compact. Due to the simple optics, the beams are not co-aligned and none are in the scanning mirror focal point, leading to beam divergence, asymmetry and scan angle dependent variations in spillover. Using Method of Moment (MoM) simulations of the optics as well as instrument structure, the complete farfield sphere of the instrument can be simulated up to 183 GHz. This paper contains detailed analysis of spillover, beam divergence and intercomparison of physical optics, MoM and nearfield antenna measurements for the mainbeam.
-

Active Gain-Controlled Beam-Steering Transmissive Surface
17 September 2024 Seyed Ehsan Hosseininejad, Amirmasood Bagheri, Fan Wang, Mohsen Khalily and Rahim Tafazolli propose a gain-controlled beam-steering polarization-engineered transmissive surface to tackle the limitation on gain performance for limited space in scenarios for large-distance communication. To implement such a functionality, a transmissive unit cell properly integrated with transistors and phase shifters is introduced with the ability of simultaneous manipulation of phase, amplitude (reduction and amplification), and polarization. Then, a supercell including the array of unit cells with desired linear phase gradient is designed and analyzed using Floquet approach to tilt the transmitted beam. Finally, to verify the proposed idea, a surface including 12×12 unit cells is designed, fabricated and verified. It is demonstrated that a maximum gain of 25 dB compared to air aperture and 11 dB compared to the passive one are achieved by assuming a constant size at 5 GHz.
-

Enhancing Transparent Circularly Polarized Antenna Performance for Automotive Applications
17 September 2024 Maryam Faizi Khajeim and Rashid Mirzavand investigate the impact of the vehicle body on the transparent circularly polarized (CP) antenna’s performance when installed on the vehicle windshield. The incorporation of an absorber layer on the vehicle floor to improve the antenna’s performance has been proposed. The study also evaluates how the placement of the antenna on the windshield affects its performance. Utilizing a transparent CP spiral slot antenna operating at 1.227 GHz and 1.575 GHz, the results reveal that the radiation performance of CP antennas on windshields significantly depends on their positioning.
-

Pushing Piezoelectric Transmitters to the MHz Regime
16 September 2024 Tristan A. Wilson, Srinivas Prasad Mysore Nagaraja, Stewart Sherrit, Devin Willey, Adam Wildanger and Darmindra D. Arumugam demonstrate that transmitters driven by piezoelectric resonators are capable of radiating quasistatic electromagnetic waves in the low frequency and very low frequency (LF and VLF) bands. These devices make use of the inverse piezoelectric effect to convert continuous-wave excitation into mechanical stress and strain that is oscillatory in nature. This is the first time that radiation has been shown with lithium niobate (LiNbO3) acoustically-driven transmitters operating in the MHz regime. The measured results from a line-of-sight spatial power drop-off experiment show great promise for physically realizable transmitters much smaller than the current state-of-the-art at these frequencies. These devices offer great potential to be used as compact low-power transmitters on platforms constrained by power and volume, such as drones, quadcopters, and microsatellites.
-

Recent Advances in Antennas for Biotelemetry and Healthcare Applications
16 September 2024 Riqza Y. Khattak, Qasim Z. Ahmed, Sultan Shoaib, Pavlos I. Lazaridis and Temitope T. Alade provide a detailed examination of recent advancements in antenna design tailored specifically tailored for applications in biotelemetry and healthcare. It contains a detailed analysis of over 60 journal papers retrieved from the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) database within the past five years. Each paper is briefly discussed, emphasizing its simulation and/or practical results. Furthermore, the paper draws conclusions based on various performance parameters, highlighting key shortcomings in existing literature designs, and identifying prerequisites for future high-performance antennas.
-

Through-the-Wall Human Activity Recognition Using Radar Technologies: A Review
12 September 2024 Jawad Yousaf, Satanai Yakoub, Sara Karkanawi, Taimur Hassan, Eqab Almajali, Huma Zia and Mohammed Ghazal presents an in-depth review of Ultra-wideband (UWB) radar systems for recognizing human activities in a room and through-the-wall (TTW) with other diverse applications. After briefly discussing different UWB radar working principles and architectures, the study explores their role in various TTW applications in real-world scenarios. An extensive performance comparison of the legacy studies is presented, focusing on detection tools, signal processing, and imaging algorithms. The discussion includes an analysis of the integration of machine learning models.
-

Wideband Solar-Cell Integrated Yagi-Uda Antenna
12 September 2024 Ahmed Ali, Heesu Wang, Yong Bae Park and Ikmo Park present a wideband ultra-low-profile Yagi-Uda type of solar-cell integrated antenna. The proposed antenna consists of a driver, reflector, and director, and is also designed to function as a solar cell. An ultra-low-profile copper indium gallium selenide (CIGS) based solar cell is used as a driver, and a slit is cut from it to make a built-in solar-cell antenna. A CIGS solar cell-based reflector and director are added to increase the impedance bandwidth and gain of the proposed antenna. A narrow slit is used, and the spacings between the reflector, driver, and director are minimized to increase the solar-cell form factor. A coaxial-to-microstrip line transition type feeding structure is used to excite the antenna, which is printed under the second substrate.
-

Single-Motor Controlled Mechanically Frequency Reconfigurable Unidirectional Antenna Array With Stable Radiation Patterns
12 September 2024Abubakar Muhammad Sadiq, Minglve Liu, Xiao Zhang, Yu Luo, Yan Chen and Kaixue Ma present a mechanically frequency-reconfigurable monopole antenna and array that offers a wide tuning range, gain enhancement, and stable beamwidth. The monopole is positioned above a large reflector plate to achieve unidirectional radiation and increased gain. By adjusting the height between the monopole and reflector plate at λ/4 according to resonant frequencies, the frequency band and gain stability can be achieved. A single-motor controlled mechanical system enables the reconfiguration of resonant frequencies and gain enhancement. Measured results demonstrate that the frequency can be adjusted from 1.17 to 3.08 GHz (basic mode) with a relative bandwidth of 89% for a single monopole over the reflector.
-
Circular Polarized Dual-Band Wearable Screen-Printed MIMO Antenna Integrated With AMC for WBAN Communications
12 September 2024 S. Arulmurugan, T. R. Suresh Kumar, Johan Sidén and Zachariah C. Alex propose a novel dual-band circularly polarized MIMO wearable antenna that is screen-printed on a cotton polyester fabric to operate at 2.45 and 5.8 GHz wireless body area network communications. The MIMO fabric antenna is realized with two circularly polarized wearable antennas arranged in orthogonal directions, which provides a less than −10 dB bandwidth of 400 MHz from 2.2 to 2.6 GHz and 800 MHz from 5.3 to 6.1 GHz, with impedance bandwidth of 17 and 14% for lower and higher bands, respectively. The antenna provides an axial ratio bandwidth (below 3 dB) of 3% from 2.4 to 2.47 GHz and 8% from 5.45 to 5.94 GHz.
-

Analytical Characterization of a Transmission Loss of an Antenna-Embedded Wall
11 September 2024 Lauri Vähä-Savo, Lorenzo Veggi, Enrico M. Vitucci, Clemens Icheln, Vittorio Degli-Esposti and Katsuyuki Haneda present an analytical model for an antenna-embedded wall, also called signal-transmissive wall. In the signal-transmissive wall, multiple antenna elements are distributed periodically on both wall sides, and connected back-to-back through coaxial cables. Numerical full-wave simulations of the signal-transmissive wall are computationally demanding due to the fine meshes required in the cables while having an electrically large wall size. Therefore the simulations above 8 GHz are not feasible even with a powerful cluster computer of the authors’ research site. The analytical model is an attractive alternative to the full-wave simulation of the wall, which combines the individual transmission characteristics of the bare wall, realized gains of antenna elements and cable losses.
-

Series Arrangement Technique for Highly-Directive PCB Leaky-Wave Antennas With Application to RFID UHF Frequency Scanning Systems
06 September 2024 Miguel Poveda-García, Alejandro Gil-Martínez, Astrid Algaba-Brazález, David Cañete-Rebenaque and José Luis Gómez-Tornero propose the efficient series connection of planar leaky-wave antennas (LWA) to obtain directive frequency beam scanning. Conditions for the proper performance are here derived, showing that the distance between antennas must be minimized while optimizing the phase shift introduced by the interconnection. Consequently, the methodology to design the transition is presented by an example using SMA connectors and a meander coaxial cable. Such series arrangement is useful to overcome the restricted directivity of planar LWAs in the UHF band due to limited PCB standard manufacturing sizes, while optimizing the radiation efficiency. The presented theory is validated with practical design examples of microstrip LWA arrays operating in the 900 MHz UHF band.
-

A Dual-Band Circularly-Polarized Transmitarray Antenna With Simultaneous Low Side-Lobe and Cross-Polarization Level
05 September 2024 Shi Sun, Meng Wang, Zhang Wen Cheng, Tie Jun Cui and Hui Feng Ma propose a dualband circularly-polarized (CP) transmitarray antenna (TA) with simultaneous low SLL and CPL. The proposed antenna is based on a metasurface with independent amplitude and phase control at dual-band. The element of metasurface consists of dual-band receiver-transmitter (Rx-Tx) structures constructing CP receiving patches and transmitting patches. The amplitude and phase modulations at each band can be achieved dependently by adjusting the impedance-matching characteristics and the rotation angles of the Tx patches, respectively. By applying amplitude-phase modulation at dual-band, the antenna can achieve high directivity, low SLL and CPL simultaneously.
-

Design of a Circularly-Polarized Microstrip Antenna by Utilizing Mutually-Coupled Resonators
04 September 2024 Jia-Xiang Hao, Hui-Dong Li and Lei Zhu propose a design method for a circularly-polarized (CP) antenna, which is realized by using coupling effects. Initially, the desired electric(magnetic) coupling between two identical λ /4 short-circuited microstrip line (MS-L) resonators can be generated when the short-circuited (opencircuited) ends of the resonators are in close proximity to each other. Besides, an orthogonal arrangement in space for these two resonators has been adopted to yield two orthogonal linearly-polarized (LP) waves. Therefore, a desired CP rotation can be achieved by choosing corresponding coupling types. Meanwhile, two equivalent circuit models are established and analyzed to deduce the formulas of the mutual inductance and mutual capacitance for the desired CP radiation.
-

Path Loss Modeling and Environment Features Powered Prediction for Sub-THz Communication
03 September 2024 Xi Liao, Ping Zhou, Yang Wang and Jie Zhang conduct extensive vector network analyzer-based radio propagation measurements at 140 GHz and 220 GHz in indoor hallway and lobby environments and at 280 GHz in an indoor laboratory environment. Omnidirectional and best directional path loss are modeled by empirical single-band and multi-band path loss models. Numerical results demonstrate that large-scale close-in model in this paper is simpler and more physically-based compared to floating-intercept model. In particular, a path loss prediction method based on environment features is proposed, which can predict path loss directly by utilizing random forest method, and the propagation environment are defined and extracted by scatterer features and related features of the transmitter and receiver.
-

Beamforming Analysis of Dual Beam Antenna Array Using Theory of Characteristic Modes
26 August 2024 Mahrukh Khan, Talha Murad and Nicholas Lusdyk present a novel and insightful approach to beamforming a 2×2 antenna array using the theory of characteristic modes. The array comprises four rectangular patch antenna elements designed on an FR-4 substrate resonating at 2.4 GHz. The characteristic mode analysis (CMA) presented a fascinating physical insight into the surface current directions and the radiation characteristics of the array structure. The excitation of a specific characteristic mode led to the design of a dual-beam antenna array. After feed excitation, characteristic mode analysis (CMA) was employed to understand multi-beam pattern reconfigurability in the multi-port structure.
-

Simplification of Linear Beam-Forming Networks by Applying a Novel Phase Interpolation Technique
22 August 2024 Elizvan Juarez, Marco A. Panduro, David H. Covarrubias and Alberto Reyna present a new design proposal for the simplification of linear beam-forming networks by applying a novel phase interpolation technique. This paper proposes the strategic utilization of 1-to-3 division nodes and 2-to-1 recombination nodes to reconstructing the cophasal values necessary for radiation beam scanning in linear phased array systems. This novel technique simplifies the beam-forming network, achieving a reduction of phase shifters by up to 60% and ±18° of scan angle. These benefits are obtained using uniform amplitude excitation and without additional amplitude controls.
-

Characterization of Effective RCS for Fixed NLoS Sub-THz Links With Single Scattered Reflections
22 August 2024 Demos Serghiou, Mohsen Khalily, Tim W. C. Brown and Rahim Tafazolli present wideband channel measurements for indoor Non-Line-of-Sight (NLoS) fixed links operating at sub-Terahertz (sub-THz) frequencies (92.110 GHz) with single scattered reflections. Seemingly “smooth” surfaces generate substantial internal multipath causing frequency selective scattered reflections owing to the short wavelength. Unlike specular reflections, no single well-defined reflection point aligns the incidence angle ( θi ) and reflection angle ( θr ) to form the lowest path loss. This means that the scattering effect of the reflective surface gives reason to search for the best angular alignment of the Receiver (Rx) antenna given a specific angle from the Transmitter (Tx) antenna.
-

Radiation of an Antenna Enclosed by a Spherical Radome Made of an Orthorhombic Dielectric-Magnetic Medium
21 August 2024 Hamad M. Alkhoori and Mousa Hussein treated the radiation of a structure comprising a spherical radome enclosing an antenna and made of an orthorhombic dielectric-magnetic medium semi analytically in this paper. Inside the radome, the radiation field phasors due to the antenna and reflected field phasors due to the radome are expanded into vector spherical wave functions of the radome’s medium. This yields two sets of unknown expansion coefficients: the radiation-field expansion coefficients, and the reflected-field expansion coefficients. The radiation-field expansion coefficients are obtained in terms of the current distribution in the antenna upon using the bilinear-form dyadic Green functions of the radome’s medium.
-

Optimizing Isolation in Interleaved Co-Frequency Orthogonally Polarized Circular Patch Array Antennas Using Conformal Mantle Cloaks and Integrated Decoupling Patches
19 August 2024 Reza Masoumi, Robab Kazemi and Aly E. Fathy present two interleaved, tightly spaced circular patch array antennas that operate at the same frequency but with orthogonal polarizations. The arrays are arranged in the E-plane, with one array rotated 90 degrees to achieve orthogonal polarization—Array-I is x-polarized, while Array-II is y-polarized. This configuration provides both spatial and polarization diversity, which helps reduce signal degradation caused by multipath fading and enhances overall channel capacity. They also investigate the effectiveness of conformal mantle cloaks and decoupling patches in isolating two interleaved co-frequency circular patch array antennas.
-

Ascertaining Operating Points of Harmonic Transponders Using Intermodulation Responses
16 August 2024 Jeff Frolik, Elsie Anthonio, Rye Fought and Tara Harte propose leveraging the harmonic transponders’ nonlinearity by interrogating with two closely spaced signals and then measuring the second harmonics and nearby second and fourth intermodulation distortion products. The results show that it is able to remotely determine the power incident at the device, over a 25 dB range and within ±1 dB, using only the relative ratios between these received components. This result has applications in characterizing the loss of unknown channels and in conducting over-the-air characterization of fully integrated transponders.
-

Adaptive Radio Frequency Sensor Enabled by Electromechanically Controlled Stretchable Rectifying Antenna Systems
06 August 2024 Zebin Zhu, Bingyang Li, Yajiao Ke, Yuchao Wang, Zequn Wang, Shihao Sun, Ping Lu, Furong Yang, Chaoyun Song, Hongxing Dong, Long Zhang and Cheng Zhang propose a low-cost, substantially simplified solution utilizing a stretchable rectenna, a microcontroller unit (MCU), and feedback control systems to overcome the high costs of high-performance spectrum analyzers and RF signal analyzers in radio frequency detection or ambient spectrum sensing. By exploiting the dynamic correlation between the resonant frequency and the tensile ratio of the stretchable antenna, the incoming frequency can be determined by recording the maximum rectifier DC power output as a function of the electromechanically controlled tension ratio of the stretchable antenna.
-

A Low Distortion Radiation Pattern Ultra-Wideband TEM Horn Antenna
02 August 2024 Mahdi Zoghi, Farrokh Hodjatkashani and Mir Emad Lajevardi introduce a low distortion radiation pattern ultra-wideband (UWB) transverse electromagnetic (TEM) horn antenna designed to operate in the 2 to 18 GHz frequency range. The modification is achieved using a non-uniform antenna feed without changing the antenna’s flare structure. The main-lobe radiation pattern of the antenna at higher frequencies eliminates ripples by using a non-uniform feeding technique compared to conventional TEM horn antennas, in which this issue exists. The measurement results pursue simulation results with a good agreement.
-

3-D Chipless RFID Tag for Anti-Counterfeiting Applications
02 August 2024Suvadeep Choudhury, Filippo Costa, Giuliano Manara and Simone Genovesi propose and investigate a novel methodology for designing Chipless Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) tags realized using the Additive Manufacturing technologies and exhibiting a high number of identification states. An encoding scheme based on the resonances and anti-resonances of the input impedance of the resonator is employed for identifying the tag, which is achieved by exploiting the set of zero-crossing points of the tag reactance. A tolerance analysis is also performed to avoid any ambiguity in the reading process and to minimize the redundancy, thus providing unique electromagnetic signatures which are also suitable for anti-counterfeiting applications. Several prototypes have been fabricated and tested to assess the practical implementation of the proposed encoding scheme.
-

A Study of Wideband Dielectric Resonator Antennas Loaded With Special Dispersive Materials
01 August 2024 Xiantao Yang, Elliot Leon Bennett, Ilkan Calisir, Qiang Hua, Jianliang Xiao and Yi Huang present a comprehensive study of wideband dielectric resonator antennas (DRAs) loaded with special dispersive materials. The concept and theory for a new class of wideband and compact DRAs are introduced for the first time using the new material whose relative permittivity is inversely proportional to the frequency power of n (i.e., εr (f)=k / fn , k is a constant). Traditional DRAs are normally of limited bandwidth and unstable radiation patterns. The proposed new DRAs exhibit excellent advantages in bandwidth enhancement, size reduction, single-mode purity (predominantly supporting a single mode with minimal interference from other unwanted modes), and stable radiation patterns.
-

Contactless Moisture Content Sensor Based on Wheeler Cap for Waste-to-Energy Plants
01 August 2024 Prakorn Pratoomma, Adam Narbudowicz and Suramate Chalermwisutkul presents a novel nondestructive, contactless moisture content sensor based on the Wheeler Cap measurement technique. The sensor comprises an electrically small antenna enclosed within a compact metallic cap, along with the material under test. The operating frequency of the sensor without material under test is 268.25 megahertz. By measuring the reflection coefficient at the input port of the antenna enclosed in the metallic cap, the moisture content of the material under test can be determined. The proposed sensor is aimed for moisture content measurement of the municipal solid waste, the primary feedstock for refuse-derived fuel utilized in waste-to-energy power plants.
-

Beam Steering for Time Modulated Arrays
23 July 2024 Gonzalo Maldonado, Abdoalbaset Abohmra, Alberto Reyna, Luz. I. Balderas, Marco A. Panduro and Jesús Cruz Garza propose an analytical method to calculate the switch-on sequences that provides Time Modulated Antenna Arrays (TMAA) with beam scanning in the sideband region. Such time sequences can be calculated to locate the main beam both in the azimuth and elevation planes. A comparison between H. Shanks’ method and the method proposed in this paper is presented. The radiation patterns of uniform linear, square and circular arrays are presented to demonstrate the efficacy of the proposed method.
-

Electromagnetic Scattering Properties of Metal Powder Cloud for Laser Powder Bed Fusion (LPBF) Additive Manufacturing (AM)
22 July 2024 Farzaneh Ahmadi, Jiming Song and Reza Zoughi investigate the potential for employing a well-established electromagnetic (EM) model to monitor the scattering properties of spatters. This approach serves as a potential tool to identify variations in spattering behavior that might be associated with defect generation during the process. The study explores how parameters, such as spatial distribution and the number of particles (in a given volume), impact the scattering properties, accuracy, and efficiency of the method. Changes in spattering spatial distribution resulting from variations in processing parameters, including laser power, scan speed, and chamber pressure, were investigated.
-

A Low-RCS, High-Gain and Polarization-Insensitive FP Antenna Combing Frequency Selective Rasorber and Metasurface
11 July 2024 Shaojie Wang, He-Xiu Xu, Mingzhao Wang and Shiwei Tang present a novel method to engineer high-gain and polarization-insensitive Fabry-Perot (FP) antenna with low scattering by combining a polarization-insensitive broadband frequency selective rasorber with partially reflective surface (FSRP) and a reflective metasurface. The FSRP element consists of an upper indium tin oxide layer printed on polyethylene glycol terephthalate substrate, a metallic loop, and a metallic patch in the middle and bottom layer, respectively, which is designed to absorb most of out-of-band incidence while achieving in-band reflection. The bottom metallic patch is a partially reflected surface which is utilized to construct an FP resonant cavity with the reflective metasurface to ensure in-band radiation.
-

Design an Omnidirectional Circularly-Polarized Antenna for Azimuth Wide-Angle Scanning Array
11 July 2024 Xin Guan, Yijing He, Zhenghui Xue, Wu Ren and Weiming Li propose an omnidirectional circularly-polarized antenna. Specifically, a thin and compact open cavity loaded with a capacitive impedance surface is used to provide the horizontally-polarized electrical-field component. While the verticallypolarized electrical-field component is achieved by a thin open cavity placed above the metal ground with a small gap. Connecting the two radiating cavities with a metal plate, the omnidirectional circularlypolarized antenna can be constructed using one simple feed. Outstanding azimuth gain variation of less than 1 dB and axial ratio less than 3 dB are obtained for the proposed antenna. Owing to the proposed antenna has omnidirectional characteristics, it can be applied to a wide-angle scanning array.
-

Low-Profile ESPAR Using Metamaterial-Inspired Structure
10 July 2024 Amir Jafargholi, Mahmood Safaei, Romain Fleury and Rahim Tafazolli addresses the 3D nature of traditional Electronically Steerable Parasitic Array Radiators (ESPARs). Additionally, the required distance between the main radiator and the parasitic elements usually affects the antenna’s electrical size and the frequency bandwidth. To overcome these issues, the cylindrical parasitic elements in conventional ESPARs are replaced with Metamaterial-inspired structures that mimic artificial magnetic conductors (AMC). The AMC is realized by a capacitively loaded loop (CLL). PIN diodes electrically control the CLL’s behavior while radially loading a printed loop antenna. Switching ON/OFF the diodes changes the direction of the main lobe, resulting in a compact, single-layer, low-profile, and cost-effective structure.
-

Preliminary Design and Test of a Microwave Inline Moisture Sensor for the Carasau Bread Industry
18 July 2024Giacomo Muntoni, Matteo B. Lodi, Alessandro Fedeli, Andrea Melis, Claudia Macciò, Matteo Pastorino, Andrea Randazzo, Giuseppe Mazzarella and Alessandro Fanti present the design and validation of a methodology for the water content estimation in the Carasau bread manufacturing process, within the framework of the recent agri-food technological advancement. Within the framework of the recent agri-food technological advancement, following a thorough evaluation of the dough dielectric properties, a suitable antenna layout has been selected, pointing out the advantages in the choice of a contactless narrow-band antenna in comparison to wide-band and dual-band ones. The presented simulated results are then validated using a prototype sensor and an ad hoc measurement system to confirm the antenna ability to discriminate among doughs with different water content.
-

Time-Domain Channel Sounder Calibration at Low Terahertz Band
10 July 2024Tobias Doeker, Johannes M. Eckhardt, Carla E. Reinhardt and Thomas Kürner provide a comprehensive overview of calibrating a correlation-based channel sounder designed for the low terahertz (THz) frequency range. The calibration process outlined herein encompasses fundamental aspects, including the calibration of the measured delay and amplitude of the channel impulse response (CIR). Specifically, it discusses the influence of the utilized waveguides during a back-to-back (B2B) calibration, as well as the effects of antennas, and noise floor estimation. Furthermore, the calibration procedure is enhanced through deconvolution to mitigate the impact of the measurement system itself.
-

High Isolation and Band Enhanced Radio Altimeter Antenna for Avionics Applications
08 July 2024 Omar M. Khan and Jean-Jacques Laurin introduce the concept of ringed stacked patch antenna with low side lobe level and enhanced bandwidth for radio altimeter avionics applications. One dimensional electromagnetic band gap is designed using metallic vias with circular rings along the radiating patches on multilayered substrate for providing high isolation in H-plane and reducing lateral surface currents. A stacked patch antenna configuration is used for enhancing the bandwidth of the antenna. Simulation and analysis are performed for the optimization of the frequency response and sidelobe levels of the proposed antenna. Gain of more than 12 dB with sidelobe levels less than −42 dB were measured for a fabricated prototype.
-

Wideband Series-Fed Patch Antenna Array With High Gain and Low Sidelobe: Linearly and Circularly Polarized for 5G V2X Applications
05 July 2024 Khaled A. Alblaihed, Abdoalbaset Abohmra, Masood Ur Rehman, Qammer H. Abbasi, Muhammad A. Imran and Lina Mohjazi present a single-element linearly polarized (LP) patch antenna characterized by a wide impedance bandwidth and low profile, optimized for 5G V2X applications. By inserting air gaps into the LP patch antenna structure, a circularly polarized (CP) antenna is generated. Moreover, a cross-stubs technique is employed to generate CP from LP, thereby enhancing the axial ratio (AR) bandwidth. In this work, they consider both linear and circular polarization patch antennas designed to operate suitable for V2X applications. The resonating structure for both antennas is designed on a 0.787 mm Rogers RT-duroid 5880 substrate with a relative permittivity of 2.2. The proposed design demonstrates resonance within the frequency range of 24 to 34 GHz and an AR bandwidth from 26.4 to 32.1 GHz.
-

A Study of Wideband and Compact Slot Antennas Utilizing Special Dispersive Materials
05 July 2024 Xiantao Yang, Ilkan Calisir, Lyuwei Chen, Elliot Leon Bennett, Jianliang Xiao and Yi Huang present a novel technique for enhancing the slot antenna bandwidth using special dispersive materials for the first time. The dispersive material whose relative permittivity is inversely proportional to the frequency by the power of n is selected and exploited for antenna bandwidth enhancement and size reduction. The concept and theory behind this work are explored. A slot antenna loaded with the new material is proposed and it is shown that the bandwidth of slot antennas using the material with power n=2 can be significantly improved with more than 4 times larger than the traditional case ( n=0 ).
-

Ultra-Wideband Frequency-Invariant Beamforming Using a Generalized Nesting Array
05 July 2024Taeho Yu, Jin Myeong Heo, Cheolsun Park, Yong Ku Jeon and Gangil Byun propose an ultra-wideband frequency-invariant beamforming (FIB) using a generalized nesting array. To implement ultra-wideband (9:1 bandwidth ratio) FIB with a reduced number of array elements, the target frequency band is divided into subbands. The subarrays have integer multiples of inter-element spacing of half-wavelength at the maximum frequency according to the bandwidth ratio of subbands. Due to this integer multiple relationships, the array elements of the subarrays are superimposed so that the total number of array elements is reduced while maintaining FIB performance over the target frequency band. Then, the FIB weights are derived based on the desired beam pattern using the inverse Fourier transform. A Bartlett beamformer is used to generate FIB patterns of the proposed nesting array.
-

Physical Optics and Reflection Locality in Designing Reconfigurable Intelligent Surfaces
03 July 2024 Javad Shabanpour, Yongming Li, Sergei Tretyakov and Constantin Simovski discuss the applicability conditions of the Physical Optics (PO) approximation and investigates its predictive power for far-field diffraction patterns of Reconfigurable Intelligent Surfaces (RISs) based on binary metasurfaces (BMSs). They compare the PO model with the approximation of socalled Reflection Locality (RL). Although these two approximations are conceptually different, in the case of BMSs, RL turns out to be a prerequisite of the applicability of the PO. If RL holds for such RISs, PO adequately predicts the diffraction pattern only in the case of large periods, which restricts the applicability of the PO to rather small deflection angles.
-

A Proton Irradiated CMOS On-Chip Vivaldi Antenna for 300 GHz Band Slat Array Implementation
03 July 2024 Hans Herdian, Chun Wang, Takeshi Inoue, Atsushi Shirane and Kenichi Okada propose an end-fire on-chip Vivaldi antenna on a standard 65-nm CMOS process for the 300 GHz band operation. The Vivaldi architecture was chosen for its broadband and end-fire radiation characteristics. End-fire antenna is required for slat array topology, which enables 2 D array implementation for transceivers with circuit area above 0.5λ0×0.5λ0. The antenna length was shortened to maximize beamwidth and reduce area. Additionally, comb-shaped slots were added to suppress side lobes and back radiation caused by the short length.
-

Analytic Approximation of Free-Space Path Loss for Implanted Antennas
02 July 2024 Mingxiang Gao, Sujith Raman, Zvonimir Sipus and Anja K. Skrivervik focuse on the free-space path loss of the implanted antenna, from the body-air interface to the external node to assess the total path loss between the implanted transmitter and external receiver. This is not trivial, as in addition to the inherent radial spreading of spherical electromagnetic waves common to all antennas, implanted antennas confront additional losses arising from electromagnetic scattering at the interface between the host body and air.
-

Circularly Polarized Reconfigurable Antenna Based on Liquid Metal Switching for Dual WiMAX Bands
02 July 2024 Vahid Sharbati, Xiulong Bao, John J. Healy, Nan Zhang, Khatereh Nadali and Max J. Ammann introduce an innovative reconfigurable antenna (RA) designed for circular polarization on the dual WiMAX frequency bands (3.5 GHz and 5.8 GHz) utilizing liquid metal switching capabilities. The antenna achieves circular polarization reconfiguration by employing a liquid metal switch connecting the parasitic element (R2) to the feed line. Notably, the liquid metal switch offers distinct advantages, including power savings in the ON state and precise control of liquid metal movement through applied voltage.
-

On Embedded Element Radiation Function and Beam Direction of Wide-Scanning Array Antennas
28 June 2024 Prabhat Khanal and Jian Yang presents a rigorous new analytical derivation of the theorem on the embedded element radiation function of ideally infinite planar array antennas, along with a formula for accurately calculating the main beam direction of finite-sized array antennas based on the theorem. It validates the previously established formula of the embedded element radiation function, where the amplitude is proportional to cosθ, based on the intuitive reasoning that the effective area of an element should be proportional to its projected area in the direction of interest angle θ, provided that the array antenna has no grating lobes for the full scan, no surface waves, no losses, and active impedance matched.
-

Optimal Design of Low Sidelobe Sparse Linear Arrays
20 June 2024 Li Wang, Fenggan Zhang and Banghuan Hou propose an improved Differential Evolution (DE) algorithm integrating the Cauchy-Gauss mutation strategy to optimize the antenna performance in a sparse linear array (SLA) subject to specific constraints of the antenna aperture, number of elements and element spacing. The initial value of the algorithm is generated through the chaotic Piecewise map, while the scaling factor is adjusted dynamically in line with the iterations and fitness values.
-

3-D-Printed Encapsulated Dielectric Resonator Antennas With Large Operation Frequency Ratio for Future Wireless Communications
18 June 2024 Reza Shamsaee Malfajani, Reza Damansabz, Sampada Bodkhe, Daniel Therriault, Jean-Jacques Laurin and Mohammad S. Sharawi introduce a novel Encapsulated Dielectric Resonator Antennas (E-DRAs) designed for operation at sub-6-GHz and mm-wave bands for 5G and beyond applications. The DRA part of the antenna consists of an array of small cylindrical DRAs (cDRA) encapsulated in a larger cylinder. At mm-wave band, the small cDRAs are radiating elements while the larger cylinder acts as a lens to enhance the gain and provide beam switching at discrete angles by switching the feed between the small cDRAs. At sub-6-GHz band, the large cylinder is the main radiator.
-

Unbalanced-Fed TCDA Performance Improvement Using a Scan Impedance Model
12 June 2024 Eric D. Robinson and Carey M. Rappaport present a scan impedance model which describes performance in terms of a combination of even and odd monopole and dipole radiating modes. An intermodal coupling term is included to account for performance when scanning in the E-plane. Each mode is calculated individually in a full-wave solver and the model is then validated by comparing the proposed combination to a full simulation of the unbalanced-fed TCDA. A coaxial extension technique is then introduced to increase the impedance of the monopole-like radiating even mode, allowing the unbalanced-fed array to match the performance of the balanced-fed version without shorting posts or significant redesign of the elements or lattice.
-

Consequences of the Potential Gauging Process for Modeling Electromagnetic Wave Propagation
12 June 2024Thomas Reum presents this predominantly theoretical article that focuses on a qualitative discussion of peculiarities, which are introduced in practical electromagnetic (EM) wave propagation scenarios when the gauge for the electrodynamic potentials is not chosen in accordance to the appropriate space-time metric of the underlying physical framework. Based on ordinary vector calculus, this is done for the viewpoint of radio frequency (RF) engineers by using two examples of guided EM waves: one large-scale case of a terrestrial scenario and one small-scale case involving a device level setup. Readers may benefit especially from this practical orientation, since gauging is often analyzed primarily mathematical by solely arguing on terms of equations instead of discussing concrete applications.
-

A Single Radiator-Based Circularly Polarized Antenna for Indoor Wireless Communication Applications
12 June 2024 Heng-Tung Hsu, Yi-Fan Tsao and Arpan Desai introduce a novel technique for inducing circular polarization in a single radiator through the implementation of a sequentially rotated feeding network. Analogous to the operational principles of sequentially rotated antennas employing multiple radiators, the creation of circular polarization (CP) with a solitary radiator becomes achievable through the distinctive phase and angular arrangement facilitated by the feeding network. This innovative approach not only results in a substantial reduction in complexity but also contributes to an overall reduction in antenna size, all while upholding commendable CP performance in terms of both axial ratio (AR) bandwidth and beamwidth.
-

A State-of-the-Art Survey on Advanced Electromagnetic Design: A Machine-Learning Perspective
11 June 2024 Masoud Salmani Arani, Reza Shahidi and Lihong Zhang present an overview of recent developments in optimization and design automation techniques for EM-component design and modeling. Limitations of conventional optimization methods are discussed, while the need for novel machine learning techniques capable of handling multiple objectives and large design spaces is highlighted. In this study, existing methods in the literature are reviewed from four viewpoints: structural view, algorithm view, component view, and application view. Different schemes in distinct design stages or applications are examined with advantages and drawbacks laid out for easier comprehension.
-

An Improved Uniaxial Perfectly Matched Layer Based on Finite Element Method for Hyperbolic Media
11 June 2024 Na Liu, Yansheng Gong, Rui Xu, Huanyang Chen and Guoxiong Cai analyze the reason for the failure of uniaxial perfectly matched layer (UPML) in absorbing electromagnetic waves with hyperbolic media (HM). They also propose an improved UPML based on the frequency domain finite element method (FEM) to truncate the unbound hyperbolic computational domain. Finally, the excellent absorption effect of the improved UPML is verified by representative examples such as an infinite HM, a linear-crossing metamaterial, and a Bessel beam.
-

Wideband and High-Efficiency Circularly Polarized Unit-Cell for X and Ka-Band Transmitarrays
10 June 2024 Alessandro de Oliveira Cabral Junior, Hamza Kaouach and André Barka present a novel approach for linear to circular polarization (LP-CP) conversion in transmitarray antennas. The proposed conversion mechanism differs significantly from previous published realizations. The concept utilizes a transmission line modeling-based excitation technique, in which a centralized via excitation is split into two striplines carefully designed to balance excitations and guarantee a phase quadrature. The striplines are embedded at the center of the patch antenna allowing a compact footprint and a simple design structure. The applied true-time delay (TTD) technique assures the radiation of a wideband and low axial ratio circularly polarized (CP) field.
-

Multibeam Compact Reflectarray Antenna With Low Scan Loss and Wide-Angle Performance Using a Multi-Feed Configuration
06 June 2024 Andrés Gómez-Álvarez, Álvaro F. Vaquero, Manuel Arrebola and Marcos Rodriguez Pino present two multibeam reflectarray antennas for Ka-band in a multi-feed configuration. Both feature a wide-angle scanning range with very low scan losses. They are designed using an iterative optimization process based on a phase-only optimization (POO) which allows fine control over the gain for each beam. The phase responses of the lattice cells are selected taking into account the illumination levels and radiation requirements of all feeds in the system. Minimization of scanning losses and overall antenna compactness are prioritized in the design. The feeding elements are placed along a tilted arc with a low F/D of 0.58. Compared to other beam scanning reflectarray designs in the literature, inter-feed blockage is avoided and thus simultaneous multibeam operation is supported.
-

State of the Art on Advancements in Wireless Capsule Endoscopy Telemetry: A Systematic Approach
05 June 2024 Sara Fontana, Simona D’Agostino, Alessandra Paffi, Paolo Marracino, Marco Balucani, Giancarlo Ruocco, Salvatore Maria Aglioti, Francesca Apollonio and Micaela Liberti prepare this systematic review according to PRISMA guidelines focuses on the main technological advances of data transmission from the in-body ingestible capsule to an external receiver in Wireless Capsule Endoscopy (WCE). A total of 142 studies were screened from a comprehensive literature search, performed in Scopus, Science Direct, and IEEE Xplore database. A final number of 47 met the inclusion criteria and were included in the review. The results highlight innovative technologies to optimize the wireless link efficacy and safety to an external receiver. High gain, wideband, omnidirectional radiation pattern, and low levels of specific absorption rate (SAR) are of crucial importance.
-

Sub-THz Conformal Lens Integrated WR3.4 Antenna for High-Gain Beam-Steering
1 June 2024 Akanksha Bhutani, Joel Dittmer, Luca Valenziano and Thomas Zwick demonstrates the first conformal lens-integrated rectangular waveguide antenna that achieves high-gain beam-steering in the sub-THz range of 230 GHz to 330 GHz, to the best of the authors’ knowledge. The antenna consists of a 2×32 array of elliptical slots (E-slots) fed by a standard WR3.4 rectangular waveguide, ensuring that the antenna operates in its dominant TE10 mode. The E-slots are spaced by less than half of the guided wavelength, which causes them to be fed with a constant phase difference, thus leading to a progressive phase shift along the antenna aperture. Consequently, the antenna main lobe steers from -71° to -16° as the operating frequency varies from 230 GHz to 330 GHz, respectively.
-

Gain Enhancement and Sidelobe Level Reduction of Microstrip Patch Antenna Under Operation of TM50-Like Mode
31 May 2024 Renan A. Santos, Helton S. Bernardo, Danilo H. Spadoti, Guilherme S. da Rosa and Rafael A. Penchel propose a microstrip patch antenna (MPA) operating in the TM50-like mode, designed for gain enhanced and sidelobe levels (SLLs) reduction. The methodology involves altering the resonator’s surface current distribution by introducing three groups of transverse slots at points of null electric field. Additionally, two symmetrically positioned stubs are utilized to the antenna’s gain enhanced. They verify that proper combinations of such artifacts on the proposed radiators significantly reduce the SLL while maintaining the high-gain characteristics of the TM50-like mode. A prototype was fabricated and characterized for operation around 7.6 GHz, in the C band.
-

A Dual-Band Dual-Polarized Antenna for Harvesting in Cellular and Digital Terrestrial Television Bands
30 May 2024 Khatereh Nadali, Neeraj Kumar Maurya, Patrick McEvoy and Max J. Ammann present an innovative printed dual-band dual-polarized antenna designed for ambient RF energy harvesting in IoT applications. The proposed antenna targets efficient RF energy conversion from the most prevalent cellular frequency bands (sub-1 GHz and 1800 MHz) and sub-700 MHz Digital Terrestrial Television. This antenna is a significant advancement in the field, boasting a wide circularly polarized 610-968 MHz bandwidth and a linearly polarized bandwidth covering the GSM/4G 1800 MHz band.
-

A Novel Theoretical Modeling of the Received Power for Phased Array-Based Wireless Power Transfer System in the Near-Field Region
30 May 2024 Nabanita Saha, Erik Pineda Alvarez and Ifana Mahbub propose, analyze and experimentally validate a novel theoretical model to calculate the received power from individual elements of the transmitter array antenna and estimate the received power, specifically in the near-field region. The proposed WPT technology utilizes a 2.4 GHz radiative near-field (Fresnel region) power transmission scheme. The calculated results using this analysis have been verified using a complete phased array antenna-based wireless power transfer system.
-

Electromagnetic-Informed Generative Models for Passive RF Sensing and Perception of Body Motions
30 May 2024Stefano Savazzi, Federica Fieramosca, Sanaz Kianoush, Michele D’Amico and Vittorio Rampa discuss two popular techniques, namely Variational Auto-Encoders (VAEs) and Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs), and their adaptations to incorporate relevant electromagnetic (EM) body diffraction methods. The proposed EM-informed GNN models are verified against classical EM tools driven by diffraction theory, and validated on real data. The paper explores emerging opportunities of GNN tools targeting real-time passive RF sensing in communication systems with dense antenna arrays. Proposed tools are also designed, implemented, and verified on resource constrained wireless devices.
-

Beamforming of Transmit Antennas Using Grey Wolf Optimization and L2-Norm for Performance Enhancement of Beyond 5G Communications
29 May 2024Samar I. Farghaly, Mostafa M. Fouda and Manal M. Emara proposes a new beamforming strategy based on a hybrid combination between grey wolf optimizer (GWO) with L2 -norm called proposed GWO. This approach is applied to synthesized uniform linear arrays (ULA), Chebyshav arrays, and shaped pattern arrays. Moreover, it is utilized for side lobe level (SLL) and size reduction of antenna elements. In this strategy, the GWO is utilized to optimize the element spacing to adjust the half-power beamwidth (HPBW) to save it the same as desired pattern. Furthermore, the excitations of the antenna elements are optimized via the L2 -norm minimization problem. The proposed GWO has low complexity (fewer iterations and computing time) compared to other algorithms.
-

A Mutual Coupling-Based Full Self-Online Calibration Method for Antenna Arrays in Uplink
28 May 2024 Aral Ertug Zorkun, Miguel A. Salas-Natera, Alvaro Araujo Pinto, Ramón Martínez Rodríguez-Osorio and Manuel Sierra Pérez propose a mutual coupling based self-calibration method for transmit mode large scale antenna arrays. In accord with the proposed active antenna array model, gain/phase uncertainties, antenna element position errors and mutual coupling effects are reduced to an error matrix. The expansion of equations of the proposed calibration method are presented. The proposed calibration procedure is capable of compensating the error matrix while the system is operating and is suitable for off-line, on-site and online calibration procedures.
-

Design of a Dual-Band Planar Sleeve Monopole Antenna With the Substrate-Integrated Coaxial Line Technology
28 May 2024 Ying C. Zheng, L. Zhu, C. Ni, J. Ding, K. Cao and B. Liu propose a dual-band sleeve monopole antenna with the substrate-integrated coaxial line (SICL) technology. Both the radiation structure and the feeding network are modified from the SICL structure. The antenna provides dual-band operation for LoRa (Long Range Radio) applications covering 433 MHz and 868 MHz bands. This antenna operates as a quarter-wavelength monopole with practical omnidirectional radiation performance for each band. The antenna exhibits a gain of 2.0 dBi at 433 MHz with more than 90% radiation efficiency, and a gain of 1.7 dBi at 868 MHz with more than 90% radiation efficiency.
-

Design Guidelines and Performance Analysis of a Wideband Coaxial Horn Antenna Fabricated via Additive Manufacturing
27 May 2024 Elígia Simionato, Ivan Aldaya, José A. de Oliveira, Andre L. Jardini, Julian Avila, Guilherme S. da Rosa and Rafael A. Penchel introduce a Ka-band coaxial horn antenna that incorporates a specialized dielectric supporting structure and a transition to a 2.4 mm connector. The inner and outer radii of the coaxial aperture were sized using an approximated model for an open-ended coaxial waveguide. The theory of small reflections was then used to account for the reflection coefficient resulting from an additional cascading cylindrical-conical section. A refined numerical model, representing more accurately a prototype, featured a transition region to standardized connectors and a dielectric structure that offers mechanical support for the inner conductor and impedance matching.
-

RF Circuit Analysis of UWB Planar Log Periodic Antenna for 5G Communications Using Theory of Characteristic Modes
08 May 2024 P. Sumithra, Mohammed Gulam Nabi Alsath, K. J. Jegadishkumar and D. Kannadassan present the systematic RF analysis, fabrication, and equivalent circuit modeling for sub-6GHz 5G application using theory of characteristic modes (TCM). The fabricated pLPA is designed to cover the 5G bands with a high gain of >5 dBi and a fractional bandwidth of >1. Using simulation tool based on method of moments, radiating and non-radiating modes are tracked and studied with detailed physics. These modes are modeled using analytically derived equivalent circuit and assembled in an RF/microwave circuit simulator.
-

Sub-GHz Wrist-Worn Antennas for Wireless Sensing Applications: A Review
06 May 2024 Sanjeev Kumar, Gholamhosein Moloudian, Roy B. V. B. Simorangkir, Dinesh R. Gawade, Brendan O’Flynn and John L. Buckley review wrist-worn Sub-GHz antennas reported in the literature, analyzing key antenna parameters such as antenna topology, size, impedance bandwidth, peak realized gain, radiation efficiency, and specific absorption rate (SAR). Additionally, it underlines antenna design challenges, limitations, current trends, and presents potential future perspectives.
-

Refinements to the Design of Traveling-Wave Waveguide Slot Arrays
03 May 2024 Jacob C. Coetzee presents a new design approach to traveling-wave waveguide slot arrays that not only ensures that sidelobes specifications are met, but also achieves good impedance matching and high efficiency. The procedure is demonstrated using a 21-element array in standard X-band waveguide and performance is validated though both simulation and measurement.
-

Ultra-Wideband Phased Antenna Array Time Delay Unit Architecture Optimization in Presence of Component Non-Idealities
01 May 2024 Daniel A. Ramirez, W. Joel D. Johnson and Gokhan Mumcu investigate the recently reported time delay unit architecture (TDU-A) optimization method based on integer linear programming for practical implementation of ultra-wideband (UWB) phased antenna arrays (PAAs). Specifically, the method is considered for linear UWB PAAs and their feed networks which include non-idealities when practical implementations of their circuit components are pursued. These non-idealities are shown to cause additional time delay errors that were unaccounted for in prior work. The errors are induced by frequency dependent variations in power divider isolation and load mismatch, component VSWRs, and dispersion.
-

Point Cloud-Based Prediction Models of Dynamic Human Body Shadowing at 58 GHz
29 April 2024 Chechia Kang, Xin Du and Jun-Ichi Takada propose screen models and an elliptic cylinder model based on the instantaneous point clouds (PC) of human geometry for the human body shadowing (HBS) channel simulation using the uniform theory of diffraction (UTD). The proposals enable fair evaluation via a simultaneous measurement of the HBS channel and the PC. The HBS gains at the 58 GHz band in an indoor environment (6.5 m) between the measured and the simulated results based on the proposed models are compared.
-

Experimental Phase-Encoded Linear Sampling Method Imaging With a Single Transmitter and Receiver
25 April 2024 Matthew J. Burfeindt, Hatim F. Alqadah and Scott Ziegler evaluate the phase-encoded linear sampling method (PE-LSM) using experimental data. They collect synthetic aperture data in an anechoic chamber using only a single transmit-receive channel. With the aid of a monostatic-to-multistatic transform, they generate reconstructions of each target via the PE-LSM. The results evince significant improvements in fidelity to the true target geometries compared to imagery generated by both conventional LSM processing and a conventional backprojection-based radar approach.
-

Improving the Performance of the Phaseless Sources Reconstruction Method for Antenna Diagnostics and Characterization
24 April 2024 Yuri Álvarez López, María García Fernández, Jaime Laviada Martínez and Fernando Las-Heras Andrés explore the possibility of improving the convergence of the iterative phase retrieval methods by reducing the number of unknowns involved in the minimization problem. They propose the use of meshless basis functions to characterize the Antenna Under Test (AUT). In particular, Fourier expansion and wavelets will be analyzed. An offset reflector antenna, measured at a spherical range in anechoic chamber as well as with a UAV-based antenna measurement system, were considered for validation purposes.
-

Wi-Fi-Based Human Activity Recognition for Continuous, Whole-Room Monitoring of Motor Functions in Parkinson’s Disease
24 April 2024 Shih-Yuan Chen and Chi-Lun Lin proposes a novel approach for human activity recognition using Wi-Fi signals. Traditional methods for signal processing are avoided by converting the ratio of channel state information from antenna pairs into images. These images are then processed using a convolutional neural network to detect movements related to diseases in a large dataset. The experiments utilize a laptop PC with Intel Wi-Fi Link 5300 and a receiver equipped with three external 12 dB omnidirectional antennas in the 2.4 GHz band and cover various daily activities. The proposed method has demonstrated remarkable accuracy, with an average recognition rate of 93.8% in validation. It also showcased a consistent accuracy range of 91.9% to 95.2% in generalization tests, proving its effectiveness in different environments, with various individuals, and under assorted Wi-Fi configurations.
-

Fully Embedded Dual-Element Dielectric-Based Antenna for Sub- and Terahertz Applications
23 April 2024 Ehsan Rahmati, Pascal Burasa, Elham Baladi and Mohammad S. Sharawi present a completely embedded, planar, dual-element dielectric based antenna directly fed by a substrate integrated insulated guide within the same layer in Sub-THz band. A dielectric layer is employed to make the structure stable. The proposed structure is compatible with the standard planar millimeter-wave and terahertz manufacturing technologies. To minimize the reflection loss, matching air holes inside the guiding channel of the waveguide and air holes with a smaller perforation radius surrounding the antenna are created. The proposed compact antenna, which has been successfully tested, covers the frequency range of 234.5-278.1 GHz with a measured impedance bandwidth of 17.01%, a proper simulated average radiation efficiency of 93.6%, and a maximum gain as well as average gain of 16.08 dBi and 12.56 dBi from measurement results, respectively.
-

Synthesis and Design of 3-D Microwave Absorber With 70° Angular Stability for C-Band and X-Band
22 April 2024 Tian-Xi Feng, Lei Zhu and Hui Li present the synthesis and design of 3-D microwave absorber with 70° angular stability for C-band and X-band. The operating principle is firstly investigated, where the absorber is considered as an energy convertor. With the help of our proposed universal equivalent transmission line (TL) model, the absorptive performance can be accordingly synthesized. Then, a design method for efficient absorption under large angles is presented. By selecting a proper synthesized angle (SA), the angular stability can be effectively improved.
-

Channel Measurements at 300 GHz for Low Terahertz Links in a Data Center
22 April 2024 Johannes M. Eckhardt, Tobias Doeker and Thomas Kürner present comprehensive double-directional channel measurements with time-domain channel sounding at 300 GHz that characterize the channel of wireless links in a data center. The channels are classified into three scenario-dependent use cases and are individually analyzed providing channel parameters as a function of the required signal-to-noise ratio of the prospective communication system. The spatial and temporal analysis of the channel reveals relevant propagation effects such as the influence of scattering and derives relations between the channel parameters of the propagation and the radio channel.
-

Wireless Power Transfer for Implantable Medical Devices: Impact of Implantable Antennas on Energy Harvesting
22 April 2024Amine Essa, Eqab Almajali, Soliman Mahmoud, Rony E. Amaya, Saqer S. Alja’Afreh and Muhammad Ikram present a thorough review of the main techniques used for wireless power transfer (WPT) in implantable medical devices (IMDs) with a specific focus on the techniques that employ implantable antennas for energy harvesting (electromagnetic (EM) WPT techniques). The techniques are first analysed and compared based on the IMD application, power transfer efficiency (PTE), transfer distance, implantation depth, implant size, operating frequency, and specific absorption rate (SAR). The study provides a critical analysis of the main WPT system’s as well as implantable antennas’ design parameters that control the PTE and hence the charging rate of the IMD. The investigated design parameters include the WPT TX-RX antennas’ gain, WPT-RX size, transfer distance, and the WPT TX-RX antennas’ alignment.
-

A Machine Learning Approach to Wireless Propagation Modeling in Industrial Environment
22 April 2024 Mohammad Hossein Zadeh, Marina Barbiroli and Franco Fuschini harnesses the power of Machine Learning to model propagation markers like path loss, shadowing, and delay spread in the industrial environment in this article. By employing Machine Learning techniques, the objective is to achieve flexibility and adaptability in modeling, enabling the system to effectively generalize across diverse industrial scenarios. The proposed model relies on a combination of predictive algorithms, including a linear regression model and a Multi-Layer Perceptron, working collaboratively to model the relationship between the considered propagation markers and input features like frequency and machine size, spacing, and density. Results are in fair overall agreement with previous studies and highlight some trends about the sensitivity of the propagation parameters to the considered input features.
-

Fading in Reflective and Heavily Shadowed Industrial Environments With Large Antenna Arrays
12 April 2024 Sara Willhammar, Liesbet van der Perre and Fredrik Tufvesson perform measurements in an operating factory environment at 3.7 GHz with a co-located massive multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) array and a unique randomly distributed array. Channel hardening can appear when the number of antennas is increased such that the variations of channel gain (small-scale fading) is decreased and it is here quantified. The cumulative distribution function (CDF) of the channel gains then becomes steeper and its tail is reduced. This CDF is modeled and the required fading margins are quantified. By deploying a distributed array, the large-scale power variations can also be reduced, further improving reliability.
-

Energy Autonomous Dual-Band Antenna System for RFID-Based Real-Time Battery Level Monitoring
10 April 2024 Braden P. Smyth, Hamed Khoshniyat, Mahdi Barati, Samuel Clark, Rashid Mirzavand and Ashwin K. Iyer presents an energy-autonomous antenna system that combines energy harvesting (EH) with radio frequency identification (RFID) communication to measure the battery charge level in real time. The system employs a dual-band patch antenna, a dual-band matching stub, and a diplexer, which are designed with metamaterial-based electromagnetic bandgap technology (MTM-EBG). Due to the MTM-EBG’s uniplanar and via-less design, it can be directly embedded into the antenna and microstrip feed components, thereby contributing to their compactness, lowering cost, and simplifying fabrication.
-

60 GHz Programmable Dynamic Metasurface Antenna (DMA) for Next-Generation Communication, Sensing, and Imaging Applications: From Concept to Prototype
10 April 2024 Abdul Jabbar, Mostafa Elsayed, Jalil Ur Rehman Kazim, Zhibo Pang, Julien Le Kernec, Muhammad Ali Imran, Qammer H. Abbasi and Masood Ur-Rehman present the complete design of a dynamic metasurface antenna (DMA) array at the 60 GHz millimeter-wave (mmWave) industrial, scientific, and medical (ISM) band. First, a novel complementary electric inductive-capacitive (CELC) metamaterial element (unlike conventional rectangular CELC) is designed to resonate around 60.5 GHz. The proposed CELC meta-element in its resonance state manifests dispersive characteristics and exhibits significant left-handed metamaterial properties such as negative group refractive index, negative effective permittivity, and negative group velocity, which are thoroughly elucidated.
-

RF-MEMS Switch for Reconfigurable With Half-Moon Slots on Elliptical-Shaped Patch Antenna for 5G Applications
10 April 2024 Ketavath Kumar Naik and Bokkisam Venkata Sai Sailaja design a compact dual-band reconfigurable elliptical-shaped patch antenna. The proposed patch antenna with rectangular strip lines and an elliptical with half-moon slots presented to operate dual bands. To achieve the reconfigurability, RF-MEMS switches proposed on rectangular strip lines of the patch antenna. The capacitive shunt type RF-switch designed the proposed elliptical antenna to operate at 5G applications. The displacement of the proposed RF-MEMS switch with an air gap of 3 μ m, the actuation of 5.02 V, and the stress of the proposed beam is bearable up to 85.7 MPa is observed. The reconfigurable elliptical-shaped patch antenna resonates at 8.34 GHz and 10.47 GHz with a reflection coefficient of −32.28 dB and −22.7 dB respectively.
-

Application of Machine Learning-Assisted Global Optimization for Improvement in Design and Performance of Open Resonant Cavity Antenna
04 April 2024 Koushik Dutta, Mobayode O. Akinsolu, Puneet Kumar Mishra, Bo Liu and Debatosh Guha explore machine learning (ML)-assisted antenna design techniques aiming to improve and optimize its major radiation parameters over the maximum achievable operating bandwidth. A state-of-the-art method, e.g., parallel surrogate model-assisted hybrid differential evolution for antenna synthesis (PSADEA) has been exercised upon a reference ORCA geometry revealing a fascinating outcome. This modifies the shape of the cavity which was not predicted by EM-based analysis as well as promising significant improvement in its radiation properties.
-

Integrated Solar Panel Slot Antennas Certified for CubeSat Missions
04 April 2024 Mahmoud N. Mahmoud and Reyhan Baktur present three prototypes of cavity-backed slot antennas integrated with solar panels. The antenna design is straightforward and requires minimal alteration on the solar panel’s geometry. The antennas and solar cells are on the same surface and are effectively independent of each other. This eliminates the need for custom designed solar cells required in previous studies. The integrated solar panel antennas were demonstrated using all commercial-off-the-shelf space-qualified components and printed circuit board technology.
-

A Compact Dual-Band Tripolarized Patch Antenna With Simple Structure and Very High Isolation
01 April 2024 Son Xuat Ta, Tran Hien Bui, Khac Kiem Nguyen and Nghia Nguyen-Trong present a compact dual-band tripolarized antenna with simple structure and high isolation operating at 2.45 GHz and 3.5 GHz bands. The design is composed of a slotted patch and a monopolar patch connected together by four vias. The antenna uses a double differential-fed scheme for x- and y-horizontally polarized broadside radiations and a single-ended port at the center for vertically-polarized omnidirectional radiation. The combination of slotted patch, monopolar patch, and vias yields several interesting features, which are exploited in the design to achieve dual-band tripolarized operation.
-

Miniaturized Design of Dual Transmission Frequency Selective Rasorber With Wide Angular Stability
28 March 2024 Mehran Manzoor Zargar, Archana Rajput and Kushmanda Saurav propose a miniaturized design of dual transmission frequency selective rasorber (FSR) with absorption-transmission-absorption-transmission (A-T-A-T) feature. Initially, low frequency resonators are incorporated on the square ring shaped lossy resistive layer for expanding the broad absorption towards the lower spectrum of frequency. Then the dual bandpass frequency selective surface (FSS) with transmission bands lying within the absorption spectrum is integrated with the resistive layer. Further, a cross-loop resonator is integrated inside the square ring of the resistive layer due to which a dual transmission pole is achieved through the resistive layer aligning with the dual operating frequencies of bandpass FSS.
-

Synthesis of Reactively Loaded Sparse Antenna Arrays Using Optimization on Riemannian Manifold
28 March 2024 Albert Salmi, Anu Lehtovuori and Ville Viikari introduce a method for computing reactive terminations for scatterer elements in antenna arrays. With the fixed scatterer elements, they shape embedded element patterns of sparse arrays to focus the radiation into a grating-lobe-free limited field of view. The reactive terminations of the scatterer elements are determined by optimizing reflection coefficients on a Riemannian manifold. In addition, they show that widening the grating-lobe-free field of view is possible by tilting the field of view. They design both 5-element linear and 4-by-4-element planar reactively loaded antenna arrays with 1.4-wavelength inter-element distances.
-

Investigation of a Circularly Polarized Log-Periodic Dipole Antenna
20 March 2024 Kunpeng Wei, Xiaopeng Zhang, Libin Sun and Changjiang Deng investigate a circularly-polarized (CP) log-periodic dipole antenna (LPDA). Eight crossed dipole cells with a logarithmically increased λ /8 separation are employed to form the proposed CP LPDA. The dipoles with increased length and spacing are fed in series by an air-filled parallel line. The working mechanism of the generation of back-fire CP radiation is illustrated by an array analyzation. Besides, the LPDA design factors for both polarizations are analyzed in detail to realize an optimized CP performance.
-

Effects and Models of Offset-Via in Electromagnetic Band Gap Structure
20 March 2024 Luohao Liu, Fan Yang, Shenheng Xu and Maokun Li investigates the effects of the via in a mushroom-like EBG structure and propose an equivalent circuit model of the via. It is revealed that when the via in the mushroom-like structure is offset, the element reflection phase will vary within 720 degrees instead of 360 degrees phase range in a conventional design. This phenomenon can be explained by a new circuit model that introduces a mutual inductance, and the corresponding electromagnetic properties of mushroom-like EBG structure can be quantitatively analyzed by this model.
-

Frequency-Diverse Reflection Metasurface Antenna Design for Computational Microwave Imaging
18 March 2024 Aobo Li, Mengran Zhao, Dónal Patrick Lynch, Shitao Zhu, Muhammad Ali Babar Abbasi and Okan Yurduseven propose the design of a computational microwave imaging (CMI) oriented frequency-diverse reflection metasurface antenna (FDRMA). Designing a FDRMA for CMI requires a careful synthesis framework, from the topology of metamaterial elements to the statistical analyses of the metasurface and the evaluation of its CMI performance. Consequently, they begin with an investigation of different metamaterial element topologies with the aim to choose the optimal one to constitute a desired reflection metasurface. The FDRMA is then designed by randomly distributing the metamaterial elements with diverse structural parameters. The orthogonality of the reflected field patterns is investigated by means of a spatial-correlation evaluation and a singular value decomposition.
-

Modeling of the Fault Detection Problem for a 3-D Hybrid Antenna Array: Analysis and Evaluation
18 March 2024 Somayeh Komeylian and Christopher Paolini implement the ADMM method under the joint sparsity setting to solve the regularized l2,1-norm problem for a number of samples of the degraded radiation pattern of the HAAwBE rather than computing its array factor, which requires significant and complex mathematical computation. The proposed ADMM technique under the joint sparsity setting allows for minimizing the cost function of the problem with respect to both model parameters and variable vectors. They have further increased accuracy and stability of the performance of the HAAwBE in the two problems of fault detection and DoA estimation by deploying three different optimization methods: LS-SVM, NN-RBF, and NN-MLP, and compared to each other.
-

Low-Profile CO-CSRR and EBG Loaded Tri-Quarter Circular Patch EWB MIMO Antenna With Multiple Notch Bands
18 March 2024 Hemalatha T and Bappadittya Roy develop and simulate a novel and miniaturized design featuring a Co-directional Complementary Split Ring Resonator (CO-CSRR) loaded Tri-Quarter Circular (TQC) Extremely Wideband (EWB) Multiple-Input Multiple-Output (MIMO) antenna. This proposed antenna demonstrates high isolation and exhibits multiple notch characteristics. The configuration consists of two TQC patches positioned adjacent to each other with a common partial ground plane (PGP), achieving an Extremely Wideband (EWB) capability of 85.8 GHz.
-

A Single-Antenna Full-Duplex Subsystem With High Isolation and High Gain
18 March 2024 Li Zhang, Miao Lv, Zhi-Ya Zhang, Yu Wang, Fanchao Zeng, Can Ding and Chenhui Dai propose a single-antenna full-duplex subsystem, consisting of a high isolation network and a stacked patch antenna with reflector. The employed patch antenna is fed by two ports with very similar input impedances to make the reflected signals identical. The high isolation network composed of two hybrids and two circulators plays a crucial part in achieving high transmitting to receiving (Tx-Rx) isolation. It is able to cancel out the inevitable reflected signals from the antenna ports and the leakage signals from the circulators.
-

Intelligent Signal Coverage Employing Hybrid-Mode Excitation in 5G Spoof Surface Plasmon Polaritons Antennas
14 March 2024 Behnam Mazdouri and Rashid Mirzavand consider different radiation features and signal levels in the spoof Spoof Surface Plasmon Polariton (SPP) antenna employing either separated or combined k−1 space harmonic or odd-mode. They propose a phase shift stub (PSS) for providing required phase delay. Then, the PSS is connected to a sinusoidally impedance-modulated spoof SPP antenna for hybrid-mode excitation. The antenna supports radiation features of the mentioned modes in separate and hybrid-modes, depending on phase delay value of PSS at the operating frequencies of 26 GHz-30 GHz.
-

Design of Wideband Reflectarray and Transmitarray Antennas With Low Sidelobe and Cross-Polarization Levels Using a Multifunctional Ultrathin Metasurface
12 March 2024 Yufang Wang, Yuehe Ge, Zhizhang Chen and Ziheng Zhou introduce an innovative approach for designing wideband, high-gain, low-sidelobe, and low-cross-polarization reflectarray (RA) and transmitarray (TA) antennas. The methodology leverages a groundbreaking metasurface endowed with the capability for independent amplitude and phase manipulation in both transmission and reflection modes. Initial characterization robustly verifies the metasurface’s proficiency in independently controlling amplitude and phase in reflection and transmission modes.
-

A WLAN Dual-Polarized Beam-Reconfigurable Antenna
08 March 2024 Saiju Li, Meie Chen, Zheng Li, Jianqiang Chen and Junhong Wang develop a novel wireless local area network (WLAN) antenna with dual-polarized and beam-reconfigurable ability for WLAN 2.4 GHz band application. The antenna is composed of a horizontally polarized (HP) antenna and a vertically polarized (VP) antenna. The radiation pattern of the HP antenna can be switched between an omnidirectional beam and four directional beams in the azimuth plane, while the VP antenna can generate an omnidirectional beam and eight directional beams. Then the antenna prototype is fabricated and measured.
-

Analysis of Scattering Characteristics Based on Crank-Nicolson Direct-Splitting Algorithm for Remote Sensing Problems
08 March 2024 Shida Gao, Hua Jiang, Yong Fan, Yongjun Xie, Haolin Jiang and Peiyu Wu propose an alternative Crank-Nicolson Direct-Splitting algorithm in open regions. To infinite extension of the computational domain, convolutional perfectly match layer with higher order formulation is proposed not only to further enhance the absorption at low-frequency band but also to decrease the reflections during the entire time domain simulation. Efficient method is proposed for scattering characteristics evaluation which ranges from near-field to far-field. Radar remote sensing Problems including ground penetrating radar and early warning radar are introduced to demonstrate the effectiveness of the algorithm.
-
Using Open Source to Accelerate Development of a Finite Element-Boundary Integral Code
07 March 2024 Niklas Wingren and Daniel Sjöberg describe how a finite element-boundary integral code using the adaptive cross approximation was developed by combining different existing open-source software packages with new code in Python. They provide a brief overview of the numerical methods used, but our focus is on the implementation and insights that might be useful to others who could benefit from using open-source software in their work. Three numerical examples are also presented to demonstrate accuracy, performance and use of complex materials. Our code is provided at github.com/nwingren/fe2ms both to demonstrate how the open-source packages were combined in practice, but also for those who wish to test the code themselves.
-

Low-Cost Indoor Localization Using Dual-Chip RFID Tag
05 March 2024 Jawad Ali, Kamol Kaemarungsi, Thipamas Phakaew, Muhammad Uzair, Adam Narbudowicz and Suramate Chalermwisutkul propose a low-cost dual-chip RFID tag antenna for indoor localization. The antenna integrates two RFID chips, each generating opposing radiation patterns. Angle-of-arrival based localization is performed with a single reader by analyzing the Received Signal Strength Indicator (RSSI) and the RSSI ratio of both chips. The antenna incorporates a mechanically adjustable reflector at the back that allows simple beam elevation control to tune the antenna for different indoor environments. The proposed dual-chip tag was measured in an indoor environment with different beam configurations.
-

Quasi-Deterministic Channel Propagation Model for Human Sensing: Gesture Recognition Use Case
29 February 2024 Jack Chuang, Raied Caromi, Jelena Senic, Samuel Berweger, Neeraj Varshney, Jian Wang, Chiehping Lai, Anuraag Bodi, William Sloane, Camillo Gentile and Nada Golmie describe a quasi-deterministic channel propagation model for human gesture recognition reduced from real-time measurements with our context-aware channel sounder, considering four human subjects and 20 distinct body motions, for a total of 120000 channel acquisitions. The sounder features a radio-frequency (RF) system with 28 GHz phased-array antennas to extract discrete multipaths backscattered from the body in path gain, delay, azimuth angle-of-arrival, and elevation angle-of-arrival domains, and features camera / Lidar systems to extract discrete keypoints that correspond to salient parts of the body in the same domains as the multipaths.
-
Multiband Operation With Antenna Boosters Using Matching Network Synthesis
28 February 2024 Alejandro Fernández, Aurora Andújar, Jussi Rahola, Joan L. Pijoan and Jaume Anguera propose a rapid and straightforward approach for designing multiband antenna systems utilizing antenna boosters to address the demand for wireless connectivity to a multitude of devices. In this method, the antenna booster is presented as an impedance box, with a multiband matching network comprising lumped components that determine the number of frequency bands. The multiband matching network is created using a synthesizer, taking into account the measured antenna booster input impedance and simulated radiation efficiency. To validate the process, a multiband antenna system operating at 824-960 MHz and 1710-2690 MHz is implemented.
-

28-GHz Rural Close-to-Ground Propagation Field Test Results and Models
28 February 2024 Sumin David Joseph, Bill Gavin and Edward A. Ball conduct a set of 28 GHz close-to-ground propagation measurements for different rural outdoor scenarios at the National Spectrum Centre, Aberystwyth. A bespoke correlation based channel sounder and horn antennas are employed in the measurement system. The measurements provide large-scale path loss, time domain impulses and channel measurements that will be beneficial for rural future millimeter wave communication systems. Different scenarios, such as straight and elevated paths, zig-zag curved road and curved road in woods are explored and log-normal models are extracted.
-

Simple and Low-Cost Shared-Aperture Antenna Module for 5G N78 and N257 Applications
22 February 2024 Danle Ma, Jiawei Zhu, Runjie Diao, Ruiping Liang, Huiming Li, Jun Huang, Hui Tang, Yue Cao and Jian-Xin Chen propose a simple and low-cost shared aperture antenna module for 5G N78 and N257 applications. This module integrates a microwave (MW) patch antenna and a millimeter wave (MMW) substrate-integrated waveguide (SIW) slot antenna. The MW part employs splits etched on the patch and shorting vias to excite TM01, TM20, and TM21 modes simultaneously and generate a wide band covering N78 band. In the MMW part, beveled SIW cavities with additional metal vias are set on the same substrate of the patch antenna and extend the bandwidth of the slot antennas covering N257 band. The shared-aperture antenna module provides high port isolations, and high and flat gains for both bands.
-

Design and Optimization of an Ultra-Wideband Millimeter-Wave Circularly Polarized Metalens Antenna With Deep Learning Method
21 February 2024 Wen-Qiang Deng, H. Zhu, Yu-Xuan Xie, Zhengji Xu and Shu-Yan Zhu propose a novel approach that optimizes reference phases and transmission magnitudes at multiple frequencies assisting with deep learning method to design an ultra-wideband mm-wave circularly polarization antenna. The first neural network intelligently provides the required geometric parameters of the unit cells, while the second neural network validates the phase shifts and predicts the transmission magnitudes based on inputs from the first neural network. The particle swarm optimization (PSO) algorithm is also utilized to optimizes the reference phases at multiple frequencies to minimize the matching errors. To validate the design, a 3-D printed compact CP antenna is fabricated and measured.
-

Analysis and Design of Planar Surface Wave Lenses and Application to Leaky-Wave Antennas
19 February 2024 Maksim V. Kuznetcov, Davide Comite, Symon K. Podilchak, Alois P. Freundorfer and Yahia M. M. Antar present planar metasurface lens structures based on microstrip technology, optimized to control the propagation of surface waves (SWs). Two different lenses are studied, i.e., a converging or plane-wave-like lens and a diverging lens. Near-field simulations and measurements are reported to demonstrate the guiding features of the designed lenses, which have also been proposed as a feeding system for planar leaky-wave antennas (LWAs). Far-field results show improvements in terms of reduced cross polarization and sidelobe level as well as increased realized gain when compared without these SW lenses.
-

Wideband Single and Dual Linearly Polarized Magneto-Electric Dipole Array Antennas for 5G/6G Millimeter-Wave Applications
19 February 2024 Lei Xiang, Fan Wu, Kai Chen, Renrong Zhao, Sai Ma, Yuanwei Zhu, Chao Yu, Zhi Hao Jiang, Yu Yao and Wei Hong propose a new taper-shaped linearly polarized (LP) magneto-electric (ME) dipole, excited by the U-shaped microstrip line through a coupling slot. An ultra-wide simulated impedance bandwidth of 85% (20.5-50.6 GHz) and 1.5-dB gain bandwidth of 73% (22.3-47.9 GHz) with a peak gain up to 7.7 dBi are achieved, combining the advantages of simple and compact structure, high integration, easy assembling and stable radiation characteristics. For proof-of-concept demonstration, a 4x4 LP array antenna is then implemented with an ultra-wide measured impedance bandwidth of 91.8% (18.8-50.7 GHz) and 3-dB gain bandwidth of 69.3% (19.8 to 40.8 GHz) as well as a peak gain of 18.0 dBi.
-

A Center-Fed Beam-Steerable Series Antenna Array With a Wide Matching Bandwidth
16 February 2024Sungeun Kim, Haegwon Park and Byung-Wook Min present a center-fed beam-steerable series antenna array that has both a wide matching bandwidth and easy control. The proposed matched feeding network for the series array is composed of impedance transformers and voltage-controlled phase shifters, and has a fractional bandwidth of 74%. The phase shifters are designed in a reflection-type configuration to minimize loss and reduce size. The 3-way power divider used in the proposed center-fed series array enable beam steering with only two control voltages for phase shifters.
-

A Way to Address Inherent Weakness in Conceiving the Ground Plane Geometry for a Microstrip Antenna
16 February 2024 Chandreyee Sarkar, Sk Rafidul, Chandrakanta Kumar and Debatosh Guha present an insight into the nature of ground plane (GP) current of a microstrip patch which is truly adverse in terms of generating cross-polar (XP) fields and minimally contributing to the primary radiation. This study also uses a theoretical basis in exploring a simple solution to mitigate the high XP values, specifically over the diagonal planes (D-planes). This actually turns out to be an engineered GP by clipping off its four corners. This has been thoroughly studied for a set of representative patch geometries and experimentally verified. A consistent XP reduction by 12–13 dB over D-planes has been ensured without affecting the impedance matching or antenna gains.
-

Reflectarray Antenna for Simultaneous Near-Field Fronthaul and Far-Field Backhaul Links in Next 5G FR2 Femtocells
14 February 2024 Álvaro F. Vaquero, Borja Imaz-Lueje, Marcos R. Pino and Manuel Arrebola present a reflectarray-based base station antenna to integrate both backhaul (BH) and fronthaul (FH). The reflectarray operates at 28 GHz in dual linear polarization, using one polarization for the BH and another for the FH. The BH is a pencil beam of maximum gain pointing in a certain direction, while the FH defines the coverage for a femtocell. The FH is used to generate the coverage within the near field radiated by the base station. The synthesis of the FH is carried out by means of a near-field phase-only synthesis (NF-POS), while the BH is analytic.
-

Optimization and Evaluation of a 3-D Ray Tracing Channel Predictor Individually for Each Propagation Effect
14 February 2024 Michael Schweins, Lennart Thielecke, Nils Grupe and Thomas Kürner present a 3D ray tracing channel predictor, which takes into account the relevant propagation phenomena like free space propagation, reflection, scattering, diffraction and transmission. The predictor is validated by two types of measurements and the relevance of the various propagation phenomena is analyzed based on predictions in a city using real base station locations and building data.
-

A Novel Yagi Element Integrated Nested Loop Quasi-Self-Complementary Dual-Port Combiner Radiator
13 February 2024 R. Gopika, Chinmoy Saha and Yahia M. M. Antar present a quasi-self-complementary radiator structure designed to operate simultaneously as a combiner and an antenna. The dual-port architecture comprises axially symmetric nested microstrip loops. The upper half of the radiator structure placed on the top plane is nearly complementary to the lower half on the bottom plane. The nested loop is loaded with a Yagi element for improved performance. This additional element in the radiator enhances the end-fire radiation from the nested loop wideband dual port structure without disturbing the parallel combiner action.
-

2-D Ray-Tracing Model for Multilayer Dielectric Dome Arrays With Inner Reflections
12 February 2024 Maria Pubill-Font, Francisco Mesa, Astrid Algaba-Brazález, Sarah Clendinning, Martin Johansson and Oscar Quevedo-Teruel present a streamlined implementation of ray tracing for fast and efficient numerical analysis of the far-field radiation performance of 2D multilayer dielectric lenses combined with phased arrays. Unlike commercial physical-optical methods, the proposed ray-tracing method is capable of computing the effects of internal reflections in the dome in a multilayer configuration. In addition, the method estimates the absorption losses as a result of the Joule effect.
-

Kriging Methodology for Uncertainty Quantification in Computational Electromagnetics
08 February 2024 Stephen Kasdorf, Jake J. Harmon and Branislav M. Notaroš present the implementation and use of the Kriging methodology, i.e., surrogate models based on Kriging interpolation, in uncertainty quantification (UQ) in computational electromagnetics (CEM). They provide consistent, unified, and comprehensive description, derivation, implementation, use, validation, and comparative study of accuracy and convergence of several advanced Kriging approaches, namely, the universal Kriging, Taylor Kriging, and gradient-enhanced Kriging methods, for reconstruction of probability-density function in UQ CEM problems.
-

Improving DOA Estimation via an Optimal Deep Residual Neural Network Classifier on Uniform Linear Arrays
05 February 2024 Haya Al Kassir, Nikolaos V. Kantartzis, Pavlos I. Lazaridis, Panagiotis Sarigiannidis, Sotirios K. Goudos, Christos G. Christodoulou and Zaharias D. Zaharis improve and evaluate the effectiveness of the neural network (NN) architecture in the domain of estimation of direction of arrival (DOA), with an emphasis on a multi-class classification task with grid resolutions of 0.25 and 0.1. Specifically, a comprehensive assessment is performed to determine the competence of a residual NN (ResNet) in predicting the angle of arrival (AOA) of intercepted signals. Such signals are received by a 16-element uniform linear array and are subjected to real-world noise conditions.
-

Beam Steering Performance of an X-Band Offset Parabolic Cylindrical Reflector Fed by Triple-Mode Horn Integrated With Risley Prism and Phase Correcting Dielectric Lens
05 February 2024 Kaushik Debbarma, Satish Kumar Sharma, Jia-Chi Samuel Chieh and Nhat Truong present a broadband 1-D high-gain beam steering solution to steer sum and difference patterns for tracking the optimum common scatter volume of troposcatter links at X -band. The novel steering arrangement consists of a D=70 cm offset parabolic cylindrical (OPC) reflector fed by a triple-mode circular waveguide (TM-CW) horn antenna integrated with a two-element dielectric wedge-based Risley prism and a parabolic phase correcting dielectric lens (PCDL). The proposed hybrid beam steering reflector-feed obviates the need for complex 3-axes based gimbals to mechanically steer the conventional reflector-feed assembly.
-

Compact High Gain Wideband Circularly Polarized Non-Uniform Metasurface Antenna Through Improved Mode Coupling
01 February 2024 Komal Iqbal, Qasim Umar Khan and Zubair Ahmed present a wideband, high gain circularly polarized (CP) metasurface (MTS) based slot antenna. The designed nonuniform slots provide wider bandgap regions and extra degree of freedom in tuning to obtain wider impedance bandwidth through improved mode coupling for fixed optimum feed location along with improved 3-dB axial ratio bandwidth and gain. The extra radiation edges provided by nonuniform slots within the unit cell help in improving mode coupling thus resulting in increased performance of the designed antenna. Improved mode coupling in case of the proposed antenna is explained and verified using characteristic mode analysis (CMA).
-

Going Beyond a Simple RIS: Trends and Techniques Paving the Path of Future RIS
31 January 2024 Kinza Shafique and Mohammad Alhassoun review recent developments in reconfigurable intelligent surfaces (RIS) technology with a special emphasis on tuning techniques, hardware concepts, RIS empowered by artificial intelligence techniques, and applications for next generation of networks. Finally, a viewpoint on the difficulties and potential directions of intelligent metasurfaces are also presented.
-

The Effective Number of Degrees of Freedom of the Far-Fields Radiated by Rectangular Current Sheets
30 January 2024 Ting Zang and Gaobiao Xiao evaluate numerically the number of degrees of freedom (NDF) of the electromagnetic far-fields generated by current sheets under certain noise level in the environment by directly sampling on the constellation of the propagation modes in free space. The electric fields in the far region are efficiently calculated by using the far-field approximation, and the effective numbers of degrees of freedom (ENDFs) are obtained through singular value decomposition (SVD) incorporating noises. The results show that ENDF is proportional to the area of the current sheets.
-
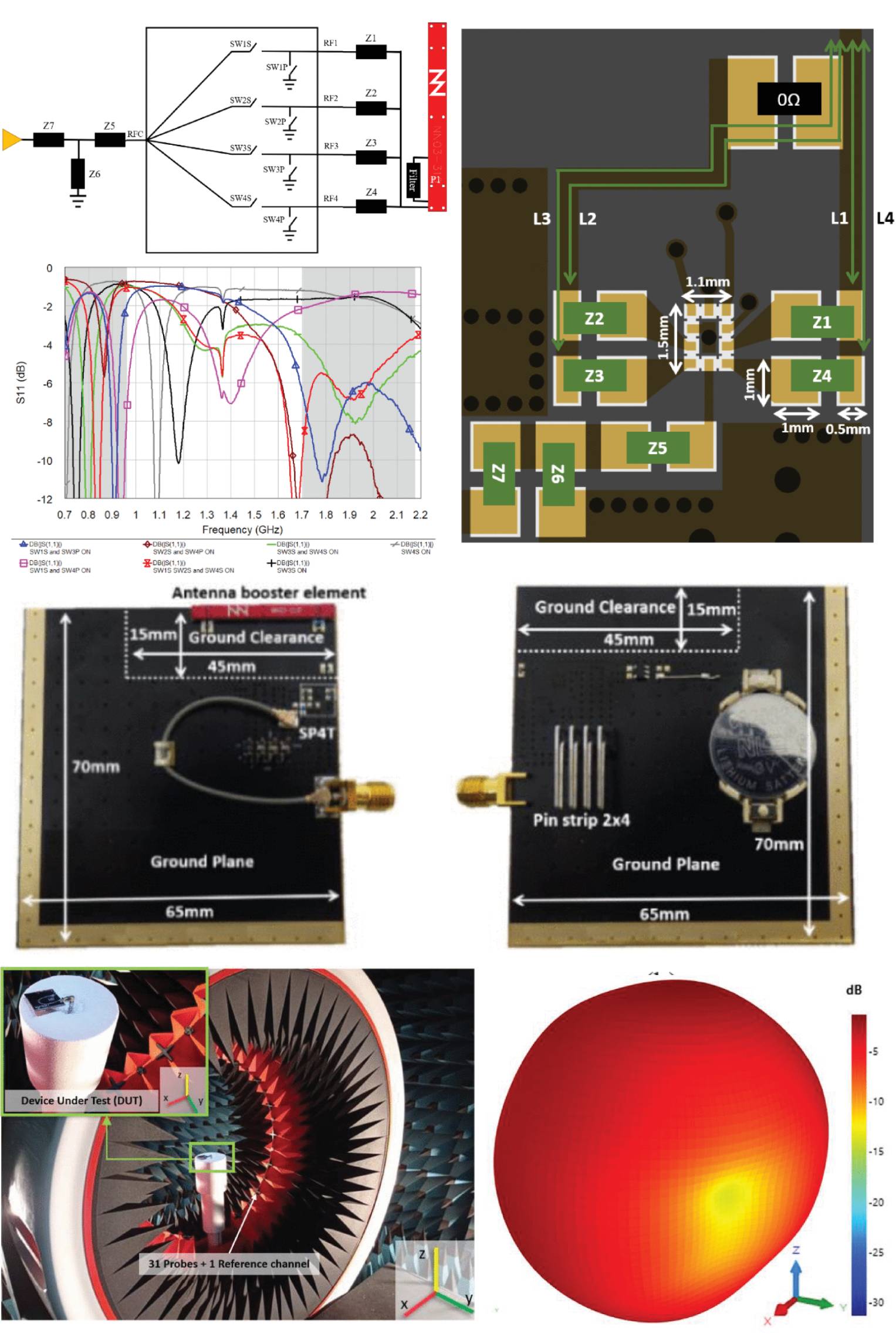
Reconfigurable Antenna Booster System for Multiband Operation in IoT Devices With an SP4T Switch
29 January 2024 Elena García, Aurora Andújar, Joan L. Pijoan, and Jaume Anguera propose, design, and build a reconfigurable architecture with a single SP4T (Single-Pole 4-Throw) operating at 698 MHz – 960 MHz and 1710 MHz – 2170 MHz embedding a 30 mm x 3 mm x 1 mm ( 0.07λ ) non-resonant element called an antenna booster element. This approach does not require antennas with complex geometric shapes to achieve multiband behavior. Instead, they rely on a multiband matching network to achieve efficient operation across multiple frequency bands. This design approach is easier, faster, and simpler than creating a new antenna for every device.
-

A Low-Profile Broadband Filtering Dielectric Resonator Antenna Based on SISL With the Improvement of Suppression Level
26 January 2024 Ningning Yan, Cong Wang, Yu Luo and Kaixue Ma present a substrate integrated suspended line (SISL) based broadband filtering dielectric resonator antenna (DRA) with the improvement of suppression level to achieve a low-profile, wide-bandwidth, and highly selective design. The dielectric resonator is cylindrical and fed from the bottom by a microstrip-coupled slot. The dual head structure with the designed open stub can provide two radiation nulls on both sides of the passband for the filtering function and can excite three resonant modes (HEM 11δ, HEM 11δ, and TE131 mode) at different resonant frequencies to enlarge the impedance bandwidth of the proposed antenna.
-

Connected Antenna Arrays With Beamsteering Capability for On-Package Millimetre-Wave Applications
25 January 2024 Md Rasheduzzaman Al-Amin, Reza Shamsaee Malfajani, Elham Baladi and Mohammad S. Sharawi design, fabricate and measure on-package, beamsteerable, slot-based connected antenna arrays (CAA), namely a single slot connected antenna array (SSCAA) and a double slot connected antenna array (DSCAA) for millimeter-wave (mm-wave) applications. Both structures are designed in a multi-layer stack-up fashion considering the package environment. The proposed SSCAA and DSCAA show 12.3% (centered at 27.55 GHz) and 16.5% (centered at 30.2 GHz) of measured bandwidths (−10 dB return loss) in their respective operating frequency bands. The measured realized gains of the SSCAA and DSCAA are 9.89 dBi and 12.5 dBi at broadside, demonstrating efficiencies of 89% and 78% respectively.
-

Mm-Wave Building Penetration Losses: A Measurement-Based Critical Analysis
18 January 2024 Silvi Kodra, Marina Barbiroli, Enrico Maria Vitucci, Franco Fuschini and Vittorio Degli-Esposti carry out a measurement campaign at 27 and 38 GHz to investigate the coverage and interference assessment issues of mm-wave radio links in in-building applications, and in particular, analyse the outdoor-to-indoor and through-floor attenuation. It is observed that in-building losses heavily depend on the building type, and that modern construction techniques make through-floor penetration almost impossible.
-

Ultra-Wideband Antennas for Wireless Capsule Endoscope System: A Review
17 January 2024 Ben Li, Yifan Wang, Junchi Zhao and Jingjing Shi present a comprehensive review of different ultra-wideband UWB antenna designs for wireless capsule endoscopy (WCE) system. In-body and on-body UWB antennas are classified according to the radiative performances and structure. Particular attention is also paid to the models used in simulation and experiment, as well as some key performance parameters and technologies in the process of antenna design. This extensive summary of UWB antennas for WCE systems will help to understand the prospects and challenges in this field.
-

Compact Dielectric Resonator Antenna With Improved Bandwidth via Loading of Metal Ring
16 January 2024 Hui Gu and Lei Ge propose a novel dielectric resonator antenna (DRA) characterized by a compact size and wide bandwidth. The achievement of wideband performance involves the introduction of a metallic ring structure inside the dielectric resonator, ensuring that the antenna’s volume remains compact. Fundamental and higher-order modes, TM01δ, TM021+δ of the cylinder DRA are first investigated by using E-field distribution analysis, and it is found that these two modes are hard to resonate in proximity to each other. Therefore, a thin metal ring, acting as a perturbation structure is inserted into the DR to perturb the E-field of the higher-order mode and reduce its resonant frequency.
-

A Dual-Beam Filtering Antenna Based on Dual-Mode Patch Loaded With π-Shaped Vias
15 January 2024 Lingyan Zhang, Tiannan Ni, Jin Shi, Gu Liu and Kai Xu utilize a dual-beam filtering patch antenna is proposed, wherein a symmetrical π-shaped metal vias-loaded dual-mode patch and a cross-shaped metal strip. The dual-mode patch resonator is realized through the loading of metal vias in the weak field region of mode TM21, which effectively moves mode TM01 closer to TM21. Using a cross-shaped metal strip to excite the dual-mode patch resonator not only provides a reflection zero and broadens the bandwidth, but also generates two radiation nulls through zero coupling, thus improving the frequency selectivity.
-

Aperture Efficiency of Non-Uniform Antenna Arrays With Controlled Sidelobe Level
15 January 2024 Ahmed Alieldin and Yi Huang presents a comprehensive study and proposes accurate mathematical modelling of the aperture efficiency of an antenna array which is divided into two components: power-loss efficiency (which dominates total aperture efficiency) and power-distribution efficiency to gain a better understanding. The paper also shows how the sidelobe level of an antenna array is linked to these efficiencies and how they can be improved. It is proved that the aperture efficiency exponentially decays when lowering the sidelobe level. However, it converges to a certain value when the sidelobes vanish.
-

Calderón Strategies for the Convolution Quadrature Time-Domain Electric Field Integral Equation
15 January 2024 Pierrick Cordel, Alexandre Dély, Adrien Merlini and Francesco P. Andriulli introduce new integral formulations based on the convolution quadrature method for the time-domain modeling of perfectly electrically conducting scatterers that overcome some of the most critical issues of the standard schemes based on the electric field integral equation (EFIE). The standard time-domain EFIE-based approaches typically yield matrices that become increasingly ill-conditioned as the time-step or the mesh discretization density increase and suffer from the well-known DC instability. This work presents solutions to these issues that are based both on new Calderón strategies and quasi-Helmholtz projectors regularizations.
-

An Integrated DRA-Based Large Frequency Ratio Antenna System Consisting of a MM-Wave Array and a MIMO Antenna for 5G Applications
03 January 2024 Awab Muhammad, Muhammad U. Khan, Reza Shamsaee Malfajani, Mohammad S. Sharawi and Moath Alathbah present a large frequency ratio antenna that covers the widely separated 5G bands. The proposed antenna consists of a 2-element rectangular DRA (rDRA)-based MIMO antenna for the sub-6 GHz band, with an embedded 1×4 cylindrical DRA (cDRA) array covering the mmW band. The rDRAs are fabricated through a cost and time-efficient 3D printing process, whereas small dimensions of cDRAs are precisely machined through a CNC. The proposed antenna has a measured impedance bandwidth of 31.63% at 4.9 GHz and 21.5% at 28 GHz. The antenna has a peak gain of 6.6 dBi at the sub-6 GHz and 12 dBi at the mmW bands.
-

4×4 UWB Phased Array Antenna With >51° Far-Field Scanning Range for Wireless Power Transfer Application
02 January 2024 Adnan Basir Patwary and Ifana Mahbub design a single unit antenna to achieve ultrawideband (UWB) operation while maintaining high gain and unidirectional radiation pattern. It determines the array element spacing based on the theoretical modeling and simulation and measurement based validation to achieve the highest gain, minimum coupling coefficient, and lower side lobe level (SLL). In order to achieve beam steering, each 2×2 subarray is considered as a single quadrant thus dividing the 4×4 phased array antenna into four quadrants where all 16 single elements are individually fed. The far-field radiation beam is steered by controlling the phase difference between each quadrant.
-

Analytical Equations for Designing Meander Line Antennas
01 January 2024 Ngu War Hlaing, Kamilia Kamardin, Yoshihide Yamada, Takuji Arima, Masaharu Takahashi and Naobumi Michishita note that the prior self-resonant equations in Meander Line Antenna (MLA) design included only inductive reactance (XC), neglecting the capacitive reactance (XD) equation. They address the gap by introducing new design equations, presenting a newly derived XD equation and an improved Q factor expression. The inadequacies of the existing Q factor equation, reliant on the radius of a sphere encompassing the antenna, are addressed by proposing a more fitting expression that incorporates antenna structural parameters using the ratio of reactance to resistance. The overview of existing design equations sets the stage for the introduction of these newly developed equations.
-

Wideband/Dual-Band Dielectric Filtering Inverted-L Antenna With Reflective and Quasi-Reflectionless Radiation Nulls
29 December 2023 Wen Zheng, Shiyan Wang, Yin Li, Zai-Cheng Guo, Gang Zhang, Li Yang, and Roberto Gómez-García propose a class of dielectric filtering inverted-L antenna with reflective- and quasi-reflectionless-type radiation nulls to achieve wideband or dual-band operation. To this aim, a dual-function dissipative branch is exploited, which is in-parallel loaded at the feedline of the microstrip-fed dielectric inverted-L antenna. This absorptive branch, which is terminated in a grounded resistor, exhibits a quasi-complementary frequency response with regard to the one of the antenna. In this manner, it can mostly absorb the out-of-band RF-signal power not radiated by the antenna, hence creating quasi-reflectionless-type radiation nulls.
-

True-Time-Delay Metasurface Assisted Broadband and Planarized Resonant Cavity Antenna
29 December 2023 Tayyab A. Khan and Alex M. H. Wong planarize a recently proposed resonant cavity antennas (RCA), which achieved a broad 3dB bandwidth of over 20% using a spherically modified ground (SMG), by replacing the SMG with a true-time-delay metasurface (TTD-MS) that mimics the both reflection phase shift and time-delay of the SMG over antenna’s entire operation bandwidth. They verify the proposed method through full-wave simulations and experimental measurements that demonstrate an impedance bandwidth (S11≤−10dB) of 32% and a 3dB-gain bandwidth of 21.3% (from 11.95 GHz to 14.8 GHz), with a peak gain of 17.5 dBi.
-

Nyström-Type Technique for Electromagnetic Wave Scattering in Inhomogeneous Material, Plasma and Metamaterial Slabs
28 December 2023 John L. Tsalamengas present a simple, stable, and spectrally-accurate quasi-analytical method for studying the reflection, transmission, and radiation of EM waves in the presence of single-layer or multilayer material, plasma, or metamaterial slabs that are inhomogeneous along the normal to the slab interfaces. Our approach formulates the problem as a linear Volterra integral equation of the second kind, discretized using an entire-domain Nyström method with a high-order Gauss-type quadrature.
-

Physical Optics Applied to Parallel-Plate Lens Antennas
26 December 2023 Francisco Mesa, Mingzheng Chen, Pilar Castillo-Tapia and Oscar Quevedo-Teruel use the Physical Optics (PO) method to derive simplified expressions to compute the radiation electric fields of planar graded-index and geodesic lenses based on a parallel-plate waveguide (PPW) implementation. If the PO method is combined with ray-tracing (RT) techniques, the resulting RT-PO procedure is capable of computing radiation patterns and gain of the PPW-based lens antennas when their apertures have a general shape and the electric field is vertically polarized. The RT-PO method is validated by comparing it with the full-wave simulation results of the commercial software ANSYS HFSS for three application cases.
-

A Dual-Polarized and Wideband Switchable Absorption/Transmission Frequency Selective Surface With Multispectral Functionality
25 December 2023 Huangyan Li, Youyi Feng, Minxin Zhao, Xiang Wang, Danilo Brizi, Xiaoxing Fang, Jun Hu, Boyu Sima, Zhiyuan Zong, Wen Wu and Agostino Monorchio develop a microwave absorption/transmission switchable frequency selective surface (A/T-SFSS) with enhanced multispectral functionality in the visible and infrared spectra. By controlling the flowing liquid medium (pure water in this work), efficient manipulation of two opposite states, absorption and transmission, can be achieved in the microwave frequency band with a wide switchable bandwidth. When functioning as a wideband absorber, the proposed A/T-SFSS exhibits an absorption rate over 90% from 6.50 GHz to 10.48 GHz.
-

SIW Sub-Array Antenna With High Isolation Offering Dual-Polarized Monopulse Patterns
25 December 2023 Maksim Kuznetcov, Symon K. Podilchak and Mathini Sellathurai present a high isolation antenna which offers dual-polarization monopulse beam patterns, making the design suitable for polarization diverse or full-duplex (FD) systems. The single-layer structure is defined by a network of 2-D sub-arrays oriented in a cross-shape configuration using series-fed slots in substrate integrated waveguide (SIW) technology. Also, the proposed design exploits dual-differential feeding to achieve a −10 dB impedance matching bandwidth (BW) from 23.2 GHz to 25.4 GHz, and measured isolation values are more than 70 dB (peaking to about 90 dB) over this same operating range.
-

Low-SAR and High-FBR Patch Antenna With Small Ground Size for Wearable Devices
14 December 2023 Shu-Wei Yu, Xiao Zhang, Qiong-Sen Wu, Lei Zhu, Tao Yuan and Qing-Hua Jiang propose a high front-to-back ratio (FBR) microstrip patch antenna with small ground plane size in this article. In order to suppress the serious back lobe brought by such a small ground, a hybrid loading technique consisting of coupled branch (CB) and resistor-loaded ground slot (RLGS) is introduced. Through the hybrid loading, extra magnetic currents on the ground are excited, by which the backward radiation of the original patch could be cancelled.
-

Cusp Phased Metasurfaces for Wideband RCS Reduction Under Broad Angles of Incidence
15 December 2023 Mustafa K. Taher Al-Nuaimi, William G. Whittow, Guan-Long Huang and Rui-Sen Chen presents an efficient and effective design approach of the phase distribution calculation across metasurface for significant radar cross section (RCS) reduction of a circular polarization (CP) and liner polarization (LP) radar waves. The RCS reduction using the proposed design approach is achieved by imposing a novel cusp phase mask (which is usually used to generate 3D self-accelerating and self-healing cusp beams) at each geometric phased anisotropic unit cell composing the proposed cusp phased metasurface.
-

Seamless Integration Technology for Filtenna Toward 5G/6G Wireless Communications
13 December 2023 Wei Hong, Zi-Jun Guo and Zhang-Cheng Hao review the design methodologies, operational principles, and implementation strategies of filtennas with illustrated examples in this paper. Whether in the context of 5G or 6G networks, base transceiver stations (BTS) require a substantial number of radio frequency (RF) transceiver chains and antenna array, particularly in mmWave frequency bands. It is known that bandpass RF filters between antenna elements and transceivers are key components for suppressing out-of-band spurs and interference. The single board seamless integration of transceivers and antennas has become a growing trend. It means there is no extra room for a large number of filters at mmWave bands, leading to the emergence of integrated designs that combine filtering circuitry with antennas, known as filtenna or filtering antenna.
-

A Design of Dual-Polarized Composite Patch-Monopole Antenna With Reconfigurable Radiation Pattern
13 December 2023 Thanh Tung Phung, Son Xuat Ta, Khac Kiem Nguyen and Nghia Nguyen-Trong describe a design of dual-polarized composite patch-monopole antenna with reconfigurable radiation pattern. The design consists of a double differential-feed patch loaded with four vertical monopoles symmetrically. The monopoles are connected to or disconnected from the ground plane (GND) by changing the ON/OFF states of p-i-n diodes. By adjusting the connections between the monopoles and GND, the pattern reconfigurability (i.e., one widebeam and three narrow-beam modes) can be achieved for each polarization. The proposed antenna can switch the beam in two dimensions separately (xz− and yz− plane). The proposed antenna is characterized computationally and validated experimentally.
-

An X-Band Linear-to-Circular Polarizer With High Refractive-Index Metamaterials
13 December 2023 Yat Sing To, Xue Ren, Quan-Wei Lin and Hang Wong present a novel wideband low-profile linear-to-circular polarizer based on high refractive-index metamaterials in the X band. The proposed design is a multilayer structure that is built from two kinds of metamaterial unit cells consisting of 4-H-shaped strips and 1-H-shaped strips. Combining the two unit cells realizes the flexible and independent control of the refractive index difference between two orthogonal E-field components and thus achieves a consistent 90-degree phase delay over a wide bandwidth.
-

Compact Omnidirectional Circularly Polarized Antenna via Alford Loop and Wire-Patch Structure Combination
08 December 2023 Francesco Positano, Luca Santamaria, Robert Staraj and Leonardo Lizzi present a compact single-fed omnidirectional circularly polarized (OCP) antenna. The circular polarization is obtained by combining an Alford Loop (AL) and a Wire-Patch (WP) radiating structures, which are used to generate two orthogonal E-field components. The antenna exhibits a clear right-handed circular polarization (RHCP) with a dipole-like omnidirectional radiation pattern. A prototype has been realized using two FR-4 printed circuit boards (PCBs) and experimentally tested.
-

The Path Reduction Factor for the Prediction of Rain Attenuation Affecting Short EHF Terrestrial Links
08 December 2023 Francesco Capelletti, Carlo Riva, Giuseppe Roveda and Lorenzo Luini Investigate the path reduction factor (PRF), a key element of semi-empirical rain attenuation statistics prediction models, to shed some light on its value for links shorter than 1 km. PRF is here calculated from simulations underpinned by the use of the Enhanced Synthetic Storm Technique (E-SST) to take into account the rain rate spatial distribution along the path. This novel approach, in contrast with the more customary one of inferring a PRF model from measurements, offers the advantage of avoiding considering any unwanted additional attenuation not due to precipitation, but typically linked to system-induced effects.
-

High-Permittivity Dielectric Half-Loop Yagi-Uda Antenna With End-Fire Radiation
07 December 2023 Wen Zheng, Shiyan Wang, Mengjiao Tang, Gang Zhang, Wang Ren and Changzhou Hua propose a kind of half-loop Yagi-Uda antenna made of high-permittivity dielectric to realize end-fire radiation. As two typical materials with high permittivity, low-loss zirconia ceramic and liquid pure water are here employed for the proposed antenna to attain high radiation efficiency and support the characteristic of pattern reconfigurability, respectively. The thin dielectric waveguide with high permittivity is here used as the metal wire of conventional wire antennas, due to its traveling-wave radiation under TM01 mode. The different radiation characteristics of the electrically small loop and full-wave loop antennas are discussed.
-

Characteristic Modes Analysis for Circularly Polarized 1-Bit Dual-Layer Transmitarray Design
07 December 2023 Francesco Alessio Dicandia and Simone Genovesi present a novel approach for designing a circularly polarized (CP) transmitarray (TA) by resorting to the characteristic modes analysis (CMA) . Two miniaturized dual-layer polarization-insensitive unit cells are tailored to provide the two copolar transmission coefficient phase states that act as a 1-bit spatial phase shifter in the TA. The exploitation of a pair of characteristic modes (CMs), radiating either right-handed CP (RHCP) or left-handed CP (LHCP) scattered field, is at the basis of the TA operation.
-

Sparse Array Mutual Coupling Reduction
05 December 2023 C. Larmour, N. Buchanan, V. Fusco and M. Ali Babar Abbasi provide a concise overview of recent developments in sparse antenna arrays, with a specific focus on techniques for reducing mutual coupling in this article. It explores the concept and definitions of sparse arrays in different applications, highlighting their historical significance in antenna theory. The paper addresses the mutual coupling problem and presents reduced coupling geometrical configurations through illustrative examples. Various mutual coupling compensation techniques are discussed. The paper conducts a comprehensive comparison of multiple array design optimisation techniques, including genetic algorithm, covariance matrix adaptation evolution strategy, particle swarm optimisation, trust-region framework, Nelder-Mead simplex algorithm, interpolated Quasi-Newton, and classic Powell.
-

Linearly Scanning Spoof Surface Plasmon Polaritons Leaky-Wave Antenna With High Scanning Rate
3 December 2023 Yue Wang, Shengying Liu, Chunsheng Guan, Hao Yu, Jinxiang Wang, Qun Wu, Changfei Zhou and Xumin Ding propose a wide-angle linearly scanning leaky-wave antenna (LWA) based on spoof surface plasmon polaritons (SSPPs) with a very high scanning rate. A sine curve period is introduced to construct the SSPPs transmission line in the form of a sine curve, which can transform the dispersion curve to the fast wave region to realize the desired dispersion properties for linearly high scanning rate LWA. The simulated results show that the proposed LWA achieves a scanning angle range of 109° over a narrow operation bandwidth of 7.73–8.13 GHz, implying high linearity, and a high scanning rate.
-

Dual-Linearly Polarized Magneto-Electric Dipole Antenna for In-Band Full-Duplex Applications
01 December 2023 Qian Tan and Kwai-Man Luk propose a dual-linearly polarized (DLP) magneto-electric (ME) dipole antenna for the in-band full-duplex (IBFD) application. It is formed by ME dipoles with a shared central part, giving a compact and symmetrical antenna structure. It has four isolated channels, two for dual-LP transmitting (TX) and the other two for dual-LP receiving (RX). Due to the symmetrical structure, it can provide similar radiation patterns for both the TX and RX ports. Good isolation between any two of all four ports is obtained over a wide frequency range by modifying the antenna structure without introducing any additional complex feeding structures.
-

A Step-by-Step Design Methodology for Broadband Tunable Microwave Metasurface Absorbers Using Theory of Characteristic Modes
29 November 2023 Zihao Ning, Mengmeng Li, Dazhi Ding, Xia Ai, Jiaqi Liu and Chao-Fu Wang develop a characteristic mode (CM)-based design methodology for the reconfigurable microwave metasurface absorbers (MMA) with using commercially available substrates. Theoretical intrinsic connection between modal behaviors and absorption properties is first formulated for the design of the structures. As a proof of the method, a broadband MMA consisting of butterfly elements is step-by-step designed. The positions and values of the impedance loading are determined based on the modal significances and modal currents for broadband operation. The absorption performance is evaluated by the formulated theoretical model and verified by full-wave simulation.
-

User Effects on Mobile Phone Antennas: Review and Potential Future Solutions
29 November 2023 Igor Syrytsin, Gert Frølund Pedersen and Shuai Zhang explore the significant impact of human proximity on antenna design evolution in mobile communication from GSM to LTE and future 5G technologies. The paper offers a comprehensive view of the challenges posed by human interactions in current antenna designs, alongside modern solutions to mitigate these issues.
-

Design of a Dual-Branch Resonator End-Launcher for Low-Loss WBAN Communications Using Wearable Waveguide Surfaces
28 November 2023 Maria El Bacha, Fabien Ferrero and Leonardo Lizzi propose a compact 30 mm x 30 mm dual-branch resonator end-launcher to enable communication through a waveguide surface manufactured with textile-compatible material at 2.4GHz. A 25 mm x 25 mm clearance zone area is respected for electronic component integration. The end-launcher topology uses a balanced dual-branch configuration to maximize electromagnetic coupling with the flexible waveguide surface. A design methodology is proposed to co-design the end-launcher and the waveguide surface.
-

Compact Multi-Beamforming Networks Based on Generalized Joined Coupler Matrix With Flexible Beam Angles and Low Sidelobe Levels
27 November 2023 Yang Xu, He Zhu and Y. Jay Guo propose a design of generalized joined coupler (GJC) matrix as a multibeam feeding network using planar circuits and is verified experimentally. The GJC matrix design is built based on a mixture of one-section and two-section branch-line couplers, which are able to realize a wide range of coupling coefficients. A thorough investigation from theoretical analysis to electromagnetic modeling is conducted on one-section and two-section branch-line couplers, and a general design guideline is given for choosing the appropriate type and dimensions for each coupler in a GJC matrix. Then, two types of BFN using microstrip line working at 5 GHz and stripline working at 12 GHz are designed, fabricated and measured, respectively.
-

Wideband and Wide Beam Scanning Dual-Polarized Phased Array Antenna-in-Package Design for 5G Applications
27 November 2023 Haoran Zhang and Atif Shamim utilize multiple design strategies, such as employing stacked patch topology, electromagnetic band gap (EBG) structures, and the rotation of elements to obtain a true wideband performance. The single element of the phased array was a dual linear polarized stacked patch antenna with notched corners. Compared to a standard patch antenna, the bandwidth was enhanced by 15.3%. The undesired mutual coupling between elements was minimized by rotating nearby elements and introducing EBG structures between the adjacent elements.
-

Compact Amplitude-Monopulse Antenna for Joint Two-Dimensional Direction Finding and Sectorized Communications in the 2.4 GHz ISM Band
23 November 2023 Miguel Poveda-García, José Antonio López-Pastor, María Campo-Valera, Alejandro Gil-Martínez, David Cañete-Rebenaque and José Luis Gómez-Tornero propose a compact antenna design to synthesize two-dimensional amplitude monopulse radiation patterns, with application to integrated sensing and communications in the ISM 2.4 GHz band. The antenna makes use of two air-filled leaky waveguides to generate four diagonally scanned beams without the need of complex feeding networks. The design demonstrates the generation of monopulse patterns in the two perpendicular planes of the antenna, covering an angular field of view of 40° X 60° where the Direction of Arrival can be estimated. The simple structure and compactness of this antenna makes it very suitable for low-cost multi-functional joint radar-communications using commercial wireless networks.
-

Bandwidth Enhancement of H-Plane MIMO Patch Antennas in Integrated Sensing and Communication Applications
20 November 2023 Lina Ma, Zijian Shao, Jun Lai, Changzhan Gu and Junfa Mao propose a low-cost compact decoupled bandwidth enhancement technique to address the high mutual coupling issue between wideband closely-spaced multiple-input and multiple-out (MIMO) patch antennas. The wideband decoupling property is realized by combining two decoupling circuits introduced by defected ground structure (DGS) and coplanar decoupling structure, respectively. An equivalent circuit is given to clarify the decoupling mechanism and provide physical insight. To validate the feasibility of the proposed design scheme, two prototypes of decoupled wideband patch arrays based on coplanar-fed and probe-fed schemes are simulated, fabricated, and measured in the 5.8 GHz ISM band, respectively.
-

A Compact, Circularly-Polarized, Substrate-Integrated Waveguide, Millimeter-Wave Beamsteering System for 5G Mobile Terminals
17 November 2023 Khaled Al-Amoodi, Rashid Mirzavand, Mohammad Mahdi Honari, Jordan Melzer, Duncan G. Elliott and Pedram Mousavi propose a compact, circularly-polarized (CP), end-fire, 4×1 continuous beamsteering antenna array implemented using substrate-integrated waveguides for 5G mobile terminals. The purpose of this system is to complement the radiation patterns of planar phased arrays on the faces of a typical mobile terminal. The proposed system seamlessly integrates previously-presented antennas and polarizers, with adjustable phase shifters and a feeding network in a multi-layered, single stack, printed circuit board (PCB) for continuous beamsteering in a compact package.
-

Dual-Band Shared-Aperture Base-Station Antenna Array With Dual Polarization Using Filtering Magnetoelectric Dipole Antenna
17 November 2023 Zhi Jing Xiao, Yun Fei Cao, Jia Sheng Lin, Yu Lan and Quan Xue present a dual-band shared-aperture antenna array using a filtering magnetoelectric (ME) dipole antenna for the application of mobile-communication base station. It is realized by interleaving a lower-band (LB) filtering ME dipole antenna operating from 1.7 to 2.8 GHz and four higher-band (HB) patch antennas in the band of 3.3-3.9 GHz. The filtering performance of the proposed ME dipole antenna is realized by U-shaped slots etched on the radiating arms and a cross-shaped microstrip line inside the aperture of the magnetic dipole, and used to realize a high cross-band isolation.
-

Modeling and Characterization of Electrically Small Ultrawideband Antenna for Headstage-Based Wireless Neural Signal Recording System
16 November 2023 Adnan Basir Patwary, Nishanth Virushabadoss, Rashaunda Henderson and Ifana Mahbub use microsystems that record neural signals collected simultaneously after neural simulation in the diagnosis of neural diseases. They propose a 15× 15 mm2 slot antenna with a 50 Ω microstrip excitation line. The slot antenna is created by the addition of slots in the ground plane which is a common miniaturization method as it results in ultrawideband operating frequency. A lumped component-based model along with a 3D EM model of the modified SMA connector used for the measurement and headstage model is also developed to observe the effect on the antenna performance.
-

A Slot-Connected Cavity Design With Corresponding Equivalent Circuit Model Analysis for Fully Metallic 3-D Vivaldi Antenna for Wireless Power Telemetry Applications
16 November 2023 Sunanda Roy, Karthik Kakaraparty and Ifana Mahbub present the design of fully metallic 3D Vivaldi antenna that can be used for wireless power transmission applications. The 3D antenna consists of 1) a tapered profile, 2) a rectangular cavity, and 3) a horizontal slot cut that is used as a transition between the cavity and the tapered profile. The proposed antenna design is fabricated using two distinct approaches, the first of which is a 3D metal additive manufacturing (AM scheme) with a sequential material layer addition technique. The second version is based on the CNC milling (CNCM) technique implemented by selectively removing material in a controlled way.
-

On Performance Characterization of Harmonic Transponders
15 November 2023 Milan Polivka and Jeff Frolik show that harmonic transponders’ conversion loss is dependent jointly on interrogation power, interrogation frequency, and interrogation angle. This coupled nature of the device’s behavior necessitates performance metrics that capture these characteristics. They present a methodology to generically test these devices and propose metrics that capture the noted dependencies.
-

Dual-Polarized Magneto-Electric Dipole for 5G 28-GHz Phased Array Applications
15 November 2023 Giuseppe Scalise, Emilio Arnieri, Giandomenico Amendola, Mohadig W. Rousstia, Sergio Pires and Luigi Boccia report a low-profile dual-polarized magneto electric (ME) dipole antenna configuration implemented on standard multilayer PCB technology. The proposed radiator is conceived for dual-polarized 28 GHz 5G phased array applications. Wideband operation is achieved by applying several low-frequency techniques which allow to fulfil the 5G requirements without increasing the dielectric core thickness. A 4×8 ME-dipole phased array is then designed, fabricated, and tested. The measured beam scanning range without the blindness in the E-plane is ±55° for the vertical polarization. Stable radiation patterns and a gain of up to 22 dBi are also achieved.
-

A Lightweight Spherical Generalized Luneburg Lens Antenna With Low Cross-Polarization Over a Wide Range in Azimuth and Elevation
14 November 2023 Maral Ansari, Oskar Zetterstrom, Nelson J. G. Fonseca, Oscar Quevedo-Teruel and Y. Jay Guo present a novel dual-slant polarized three-dimensional (3D) periodic Luneburg lens with a diameter of 390 mm (4.6λ0 at 3.55 GHz). Copper-plated cubes with truncated corners are placed in a body-centered cubic (BCC) lattice and held together with layers of Rohacell foam. The sizes of the cubes are varied to realize the gradient refractive index (GRIN) profile of a generalized Luneburg lens at a low cost, with a low weight and loss.
-

Enhancing Gain Through Optimal Antenna Element Distribution in a Thinned Array Configuration
08 November 2023 Michael Ortiz, Md Nazim Uddin, Marisol Roman Guerra and Elias A. Alwan present an array thinning approach for a 25-element antenna array arranged in a 5×5 grid at 5.4 GHz. Our goal is to eliminate a maximum number of antenna elements with minor gain loss and hence reduce the array size, weight, cost, and power requirements. Consequently, the space saved by the thinned array configuration presents opportunities to integrate additional antennas and hardware, allowing for a low-profile antenna-in-package. Our study showed that a 64% array reduction (from 25 to 9 probe-fed patch antennas) achieved an array gain comparable to a full array configuration.
-

Dispersion Characteristics and Applications of Higher Order Isosceles Triangular Meshes in the Finite Element Method
08 November 2023 Yuhua Niu, Jinbo Liu, Wen Luo, Zengrui Li and Jiming Song proposed research shows that under the same order, the equilateral triangular meshes have the most uniform dispersion distribution. The isosceles triangles with equal base and height have more uniform dispersion error than the square meshes, while the maximum phase error is similar. Taking the rectangular waveguide as an example, the relative errors in the cut-off frequency are analyzed based on different meshes.
-

Accurate Determination of Antenna Gain in the 300-GHz Band Using Amplitude Center Estimated From Electrooptic Near-Field Measurements
07 November 2023 Yuta Hayashi, Yu Katsuue, Yusuke Tanaka and Shintaro Hisatake propose and demonstrate an accurate antenna-gain determination method using the distance between the amplitude centers (ACs) of the antennas determined from the spatial phase distribution of the near field measured based on an electrooptic technique. Employing a WR-3.4 horn antenna, we show that at 286 GHz, the proposed method determines antenna gain with the same level of error even when the antenna separation distance is 1/5 shorter than that obtained using the conventional method that employs the physical distance between the antenna apertures in the Friis equation.
-

Application of Coherently Radiating Periodic Structures for Feeding Subarrays in Limited-Scan Arrays
07 November 2023 Elizvan Juarez, Marco A. Panduro, David H. Covarrubias, Alberto Reyna and Carlos Del Rio present a new design technique to improve the reduction of phase shifters using sub-arrays and CORPS (coherently radiating periodic structures) technology. The CORPS network generates the values of cophasal excitation with reduced input ports. These values feed an optimal sub-arrays structure. Furthermore, fixed and variable amplifiers allow a low SLL (side lobe level) by using a raised cosine amplitude distribution along sub-arrays inputs. The theoretical model of CORPS-Subarrays, numerical and experimental results of several design cases are presented. The proposed design achieves a ±14° scanning range with a higher reduction of phase shifters than other techniques presented previously in the state of art.
-

Efficient Calibration of Colocated MIMO Radar
06 November 2023 Ricard L. Grove and Jørgen Dall present a calibration technique that reduces the number of measurements required to obtain adequate calibration coefficients, compensating for all system imperfections that can be described in matrix form. This includes channel imbalance and mutual coupling under the assumption of minimum scattering antennas. The proposed technique estimates the calibration matrix for the transmit and receive array separately, by canceling out the element radiation pattern and effects from the other array through normalization.
-

UTD-Type Solution of Physical Optics Approximation for Reconfigurable Intelligent Surface Modeled by a Continuous Planar Surface
02 November 2023 Xin Du, Chechia Kang and Jun-Ichi Takada propose a UTD-type solution of the physical optics approximation (PO) for RIS modeled by a continuous planar surface in a two-dimensional environment. The authors validate the proposal under different scenarios in an indoor environment (0.1−20 m) at the terahertz bands (100−300 GHz), by comparing them with those computed using the Fresnel approximation, the Fraunhofer approximation, PO, and the full-wave approach based on the method of moment (MoM). The simulated results show that compared to MoM, the proposal and PO achieve good accuracy with a smaller error of less than 1 dB, while the Fresnel and Fraunhofer approximations present imperfect accuracy with an error of larger than 1 dB in the near-field region.
-

Increasing the Bandwidth of Wideband Antennas Using the Frequency Pulling Technique
02 November 2023 Anastasios G. Koutinos, Constantinos L. Zekios and Stavros V. Georgakopoulos address the limitation of frequency pulling technique (FPT) by (1) extending FPT to wideband designs, (2) using feeding points located at different planes, and (3) designing feeding networks as unequal power dividers. The networks not only simplify the design complexities associated with the traditional approach but also offer the capability to apply FPT to non-planar designs (e.g., 3D antenna configurations). To demonstrate the latter, they engineer a triangular tapered slot antenna, feeding it with a coupled microstrip line. As a result, the bandwidth of our modeled antenna increases from 34.51% to 78.25%, demonstrating excellent agreement between simulated and measured results.
-

Electromagnetic Imaging System Calibration With 2-Port Error Models
01 November 2023 Seth Cathers, Joe LoVetri, Ian Jeffrey and Colin Gilmore introduce a novel approach to calibration that models the antennas and field propagation as 2-port networks (rather than scalars or a comprehensive model), for which common network theory and de-embedding techniques can be applied. The accuracy of the proposed 2-port method is experimentally tested against the scalar calibration technique on a 2D imaging system. The use of both metallic and dielectric calibration objects is tested, and the inversion performance is compared for the calibration techniques.
-

Tuning-Range Extension Strategies for Varactor-Based Frequency-Reconfigurable Antennas
01 November 2023 Quoc Hung Dang, Nghia Nguyen-Trong, Christophe Fumeaux and Shengjian Jammy Chen present tuning range extension strategies for varactor-based frequency-reconfigurable planar patch antennas. The three tuning range optimization methods described in the paper include co-optimization of antenna dimensions and varactor properties, exploitation of multiple radiation modes, and reduction of parasitic capacitance. The first two strategies are emphasized by briefly reviewing two previously reported wide tuning range frequency-agile planar antennas.
-

Decoupling for Millimeter-Wave Array Antennas Using Near-Field Shrinking Dielectric Superstrate
31 October 2023 Shengyuan Luo, Yiming Zhang, Peng Mei, Gert Frølund Pedersen, and Shuai Zhan propose a decoupling concept of near-field shrinking dielectric superstrate (NFSDS) for large-scale, wideband, and dual-polarized mm-wave arrays. An NFSDS with a thickness of 4 mm ( 0.32λ0 at 24 GHz) is mounted seamlessly above the array, which shrinks the near field of the array elements to reduce the space wave coupling while slightly increasing the surface wave coupling of the arrays. By loading a superstrate with a certain thickness and low permittivity, the total coupling of the mm-wave arrays is reduced significantly.
-

2 × 2 Lens Array Antenna Using Square-Bottom Concave-Convex Lens in 300-GHz Band
17 October 2023 Bazilah Baharom, Yoshiki Sugimoto, Bakar Rohani, Kunio Sakakibara, Nobuyoshi Kikuma, Yoshihide Yamada and Nurul Huda Abd Rahman proposes a 2×2 lens array antenna composed of square-bottom lenses with a concave-convex lens shaping design to improve the uniformity and aperture efficiency. The measured results of the proposed 2×2 square-bottom concave-convex lens array antenna with a lens height of 9.74 mm achieved a boresight gain of 34.9 dBi, and the lowest sidelobe level observed was greater than −12 dB in the 300-GHz band.
-

Synthesis of Plane-Wave Generator in 3-D Sphere Quiet Zone for Advanced Antenna Measurement by Hybridizing LSM and GA
11 October 2023 Haidong Chen, Weijun Zhong, Mu Tan, Zhaoling He, Ting Li, Quan Xue and Wenquan Che hybridize the Least Square Method (LSM) and Genetic Algorithm (GA) to efficiently synthesize the linear and planar array Plane Wave Generator (PWG) to create a 3-D Quiet Zone (QZ) with high performance for the antenna pattern measurement in a chamber with limited space. Based on the PWG with an 8-element linear array, the amplitude and phase deviations of 0.89 dB and 14.50° are obtained in a circular QZ with a diameter of 7λ , and that with an 8×8 -element plane array achieves 1.09 dB and 14.89° deviations in a 3-D sphere QZ.
-

New Analysis and Design Techniques for Arbitrary Reactance Trap Dipoles
05 October 2023 Paul R. Winniford, Adrian L. Bauer, Hjalti H. Sigmarsson and Jessica E. Ruyle present a significantly revised analysis of a classic resonator loaded antenna– the trap dipole. The authors demonstrate in calculation, simulation, and measurement that trap dipoles antennas are not matched or resonant at the same frequency as the trap load resonance. The new analysis unites traditional high impedance trap loads with a wide variety of resonant and reactive loads to achieve multiband antenna performance with quasi-first order field distributions at the operating frequencies.
-

Impact of 3-D Antenna Radiation Pattern in UAV Air-to-Ground Path Loss Modeling and RSRP-Based Localization in Rural Area
05 October 2023 Sung Joon Maeng, Hyeokjun Kwon, Ozgur Ozdemir and İsmail Güvenç investigate the impact of 3D antenna patterns on a UAV air-to-ground path loss model, utilizing datasets obtained from a measurement campaign. They conducted UAV experiments in a rural area at various fixed heights, while also characterizing the 3D antenna radiation pattern by using an anechoic chamber facility. By analyzing reference signal received power (RSRP) using path loss models that account for antenna patterns, the team observed that the measurement results, obtained at different UAV heights, aligned well with the two-ray path loss model when incorporating the measured antenna pattern.
-

Low Sidelobe Pattern Synthesis of Array Antennas With a Triangular or Skew Lattice Using the IFT Method
05 October 2023 Will P. M. N. Keizer describes how the present 2D FFTs, direct and inverse, only applicable for rectangular lattices, can be modified in a simple way to make them suitable for the processing signals arranged along a triangular or skew grid. These two modified FFTs are subsequently implemented in the IFT method. The IFT method, updated in this way, is then very suited for the low sidelobe pattern synthesis of array antennas with a triangular lattice or skew lattice.
-

A Global Optimization Method for Wideband and Small Supergain Arrays Design Using Artificial Neural Network
04 October 2023 Abdellah Touhami, Sylvain Collardey and Ala Sharaiha introduce an efficient approach for compact, wideband and supergain arrays design using artificial neural network (ANN) based optimization. The proposed method optimize at the same time the distance inter-elements of the array antenna, its input impedance as well as its directivity. Such global optimization considerably improves the performances of superdirective arrays in terms of gain, bandwidth and efficiency. The proposed method is used afterwards to synthesize a three-elements array using two different unit elements.
-

Compact and Broadband Substrate Integrated Dielectric Resonator Antenna Suitable for 5G Millimeter-Wave Communications
27 September 2023 Jie-Er Zhang, Qinfang Zhang, Wei Qin, Wen-Wen Yang and Jian-Xin Chen proposes a compact and broadband substrate-integrated dielectric resonator antenna (SIDRA) suitable for 5G millimeter-wave band applications. Four operating modes from three resonators, including TE111 and TE131 modes from the DR, slot mode from the H-shaped feeding slot, and patch mode from the inserted ring patch, are excited to achieve a bandwidth of 61.9% (24-45.5 GHz) with a compact size of 0.37λ00×0.37λ0×0.125λ0. The proposed DRA can be extended to an array with ∼0.5λ0 element interval to obtain wide-angle beam scanning capability.
-

Equivalent Circuit to Overcome Thévenin Limit for Receiving Lossy Dipole Antennas Motivated by the Poynting Streamline Analysis
27 September 2023 Junming Diao and Lu Liu propose to overcome the limitation of the Thévenin equivalent circuit in determining the loss and scattered powers when dealing with a lossy antenna that is near a large load impedance. They model and analyze the antenna directly as a receiver and visualize the flow of field energy around the antenna through generating streamlines of the Poynting vector field. Motivated by the Poynting streamline analysis, a new equivalent circuit for receiving lossy electric and magnetic dipole antennas is introduced in response to an incident plane wave, which addresses the shortcomings of the traditional Thévenin equivalent circuits.
-

Compact and Broadband Substrate Integrated Dielectric Resonator Antenna Suitable for 5G Millimeter-Wave Communications
27 September 2023 Jie-Er Zhang, Qinfang Zhang, Wei Qin, Wen-Wen Yang and Jian-Xin Chen propose a compact and broadband substrate-integrated dielectric resonator antenna (SIDRA) suitable for 5G millimeter-wave band applications. Four operating modes from three resonators, including TE111 and TE131 modes from the DR, slot mode from the H-shaped feeding slot, and patch mode from the inserted ring patch, are excited to achieve a bandwidth of 61.9% (24-45.5 GHz) with a compact size of 0.37λ0×0.37λ0×0.125λ0.
-

Excitation Diversity in Adaptively Thinned Arrays for Microwave Sensing Applications
26 September 2023 Sandra Costanzo and Giovanni Buonanno propose an excitation diversity technique included in thinned arrays design to overcome the unacceptable discrepancy between the actual radiation pattern and the desired one, especially for small to medium-sized arrays, after reducing the complexity of the feeding network. Data distributions achieved with the above approach are averaged to obtain potential high-quality final images. Moreover, the proposed methodology can be easily implemented in real-time adaptive arrays.
-

Design of Compact and High Isolation Dual-Polarized Antenna Array via Plasmonic Meta-Structure
20 September 2023 Zhang Wen Cheng, Shimeng Wang, Yue Teng Chen, Ji Ran Chen, Jing Cheng Liang, Feng Gao, Shuai Luan, Xin Liu, Hui Feng Ma and Tie Jun Cui propose a compact and high isolation dual-polarized antenna array based on plasmonic meta-structure operating at 2.58 GHz. The compact principle of the dual-polarized antenna is mainly based on spoof surface plasmon polariton (SSPP) radiation patch to support SSPP modes, which is fed by spatially coupled excitation. The cross-polarization coupling between two polarization ports can be improved to below −32 dB, showing high isolation characteristics.
-

A Quad-Polarization and Beam Agile Array Antenna Using Rat-Race Coupler and Switched-Line Phase Shifter
18 September 2023 Maodudul Hasan, Eisuke Nishiyama and Ichihiko Toyoda propose a quad-polarized microstrip array antenna with beam steering capability. The proposed antenna consists of two patch elements, one rat-race coupler, and two 90° switchable phase shifters. With the aid of just four PIN diodes, the two 90° phase shifters can provide four different diode arrangements for each port of the rat-race coupler. The array elements are excited by using orthogonal feed lines. Due to the combination of the rat-race coupler and phase shifters, different phase conditions are generated between the patch elements or orthogonal modes of the patches.
-

A Multi-Port Pattern Diversity Antenna With High Isolation
18 September 2023 Nghia Nguyen-Trong and Christophe Fumeaux propose a pattern-diversity antenna with 7 ports for multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) applications. Orthogonal modes are utilized to achieve high isolation among all 7 ports in a relatively compact shared volume. As distinguishing feature from previous works, the concept of tripolarization is generalized, allowing to design antennas with a large number of orthogonal patterns in a single multi-port device.
-

Ultra-Wideband Tightly Coupled Dipole Array Fed by a Tapering Meandered Balun
15 September 2023 Matthew W. Nichols, Michail O. Anastasiadis, Malcolm E. Taaffe, Elias A. Alwan and John L. Volakis present an ultra-wideband (UWB) phased array operating from UHF to C-bands (0.14 to 5.85 GHz). This design employs an integrated, compact tapered spline balun in conjunction with a triple-layer semi-resistive frequency selective surface (FSS) network. Notably, the integration of the meandered balun within a dual-polarized tightly-coupled dipole array (TCDA) allowed for a contiguous bandwidth of 40:1 with VSWR < 2.5 at broadside.
-

Broadband Multi-Shaped Metasurface Circularly Polarized Antenna With Suppressed Non-CP Radiation Modes
13 September 2023 Nathapat Supreeyatitikul, Titipong Lertwiriyaprapa, Nonchanutt Chudpooti, Monai Krairiksh and Chuwong Phongcharoenpanich propose a multi-shaped metasurface broadband circularly polarized (CP) patch antenna with parasitic elements for 5G new radio (NR) applications. The proposed metasurface CP patch antenna comprises triple-layered substrates without air gap. The upper layer sits with multi-shaped metasurface elements and parasitic patches. The middle layer consists of an L-shaped slot functioning as the ground plane, and the lower layer contains a microstrip and a fan-shaped stub functioning as the feed line. The proposed metasurface CP patch antenna with parasitic elements is evaluated using characteristic mode analysis (CMA).
-

Synthesis of Symmetric, Two-Element Biomimetic Antenna Arrays Using Singular Value Decomposition
04 September 2023 Son Vu, Saeid Jamilan, Barry D. Van Veen, Hung Luyen and Nader Behdad present a method for determining the four-port S-matrix of the external coupling network (ECN) for symmetric, two-element biomimetic antenna arrays (BMAAs) by employing singular value decomposition (SVD). The presented approach greatly facilitates the synthesis procedure of symmetric, two-element BMAAs and allows all possible scattering matrices of a four-port network realizing the ECN to be easily determined.
-

Efficient Optimization Design of Large Circular Phased Arrays With Low Sidelobes for Beam Scanning
04 September 2023 Yi-Xuan Zhang, Tian-Ye Gao, Li Zhang, Yong-Chang Jiao and Tao Ni propose an efficient optimization design method for large circular phased arrays with low sidelobes for beam scanning. Based on the differential evolution algorithm (DE), each layer’s radius and element number are optimized to obtain the required element arrangement. If the main beam scans from the Z-axis, it is difficult for designers to find the maximum sidelobe.
-

Low-Cost Hybrid Implementation of an Efficient E-Band Array Based on Stepped and Ridged Slots
01 September 2023 Sherif R. Zahran, Emilio Arnieri, Stefano Moscato, Matteo Oldoni, Dario Tresoldi, Giandomenico Amendola and Luigi Boccia present an 8×8 waveguide antenna array composed of stepped and slotted radiators for E-band applications. The proposed array architecture, including the feeding network, can be realized through the integration of a single metallic block adhered with an additional top photo-etched sheet. This approach effectively reduces manufacturing complexity, resulting in a low-cost solution that can be easily fabricated using standard market-ready technologies.
-

Multi-Mode Antennas for Ultra-Wide-Angle Scanning Millimeter-Wave Arrays
28 August 2023 Gabriele Federico, Zhe Song, Guilherme Theis, Diego Caratelli and A. Bart Smolders present a novel multi-mode millimeter-wave antenna array with enhanced scan range and reduced scan losses. The individual array element consists of a differentially fed microstrip patch on top of which a cylindrical dielectric resonator is integrated. The radiation pattern of the antenna element can be reconfigured by changing the phase offset between the feeding ports of the patch and the dielectric resonator to excite two distinct radiating modes.
-

A Dual-Band Dual-Polarized Base Station Antenna Array With Isolation Enhancement
28 August 2023 Lei Ge, Yinhui Wang, Mingye Du, Weiyang Liu and Yue Zhao design a dual-band dual-polarized antenna with isolation enhancement. The proposed antenna operates in the frequency range of 3.4–3.6 GHz and 4.8-5 GHz, where the center frequency of the high band (HB) is 1.4 times that of the low band (LB). Two radiating patches are placed in different layers to create the two distinct resonances and the bottom patch which is shorted to the ground by four metal posts acts as the ground for the top patch antenna. A metal wall is introduced between LB feeding probes to enhance the polarization isolation to more than 25 dB. Complementary split-ring resonator (CSRR) structures are etched on the feedlines to improve the cross-band isolation to over 25 dB.
-

Near-Field Calibration Methods for Integrated Analog Beamforming Arrays and Focal Plane Array Feeds
11 August 2023 Roel X. F. Budé, Kevin A. P. Van Hastenberg, Ulf Johannsen and A. Bart Smolders propose a near-field calibration method for millimeter-wave analog beamforming array antennas and focal plane array antennas. Nonidealities of the beamformer integrated circuits with vector modulators are taken into consideration, and a way to reduce the measurement set for vector modulators with high resolution is proposed. This method is both practical and achieves a good calibration as evidenced by measurements of the radiation patterns, and it is suitable for use in an automated factory calibration setup.
-

Coupled Array of Diverse Elements for Wideband High Spherical Coverage
10 August 2023 Quangang Chen, Veli-Pekka Kutinlahti, Jaakko Haarla, Anu Lehtovuori and Ville Viikari propose a flexible cluster array concept utilizing diverse antenna elements and the mutual coupling among them to improve the spherical coverage. This innovative approach can not only enhance the impedance matching but also improve the beamforming performance across a wide frequency band by adjusting excitation amplitudes and phases. Equations are derived to achieve specific objectives such as minimizing the total active reflection coefficient or maximizing the realized gain of an antenna array.
-

Analysis and Experimental Demonstration of Reflectarray Antennas in Quasi-Regular Lattices
09 August 2023 Borja Imaz-Lueje, Juan Córcoles, Marcos R. Pino and Manuel Arrebola present investigations on reflectarray antennas using non-periodic element distributions. The study involves the analysis and design of two reflectarrays based on quasi-periodic lattices with rectangular and pentagonal profiles, whose performance is compared with equivalent reflectarrays comprised of regular grids of elements. The characterization of these antennas is performed using a tailored analysis technique for reflectarrays with periodical and quasi-periodical grids. The proposed technique uses the Method of Moments under local periodicity conditions (MoM-LP) to compute the field on the surface of each cell and then the far field radiated by the aperture.
-

Shared Impedance Noise Coupling in Radio Receivers
08 August 2023 Yihong Qi and Yunlong Luo elucidates a shared impedance noise coupling mechanism, which sheds light on how passive antennas can introduce excess noise into the wireless system. This article introduces the general theory of antenna noise temperature, providing an explanation for the mechanism of noise coupling through a shared impedance path. Additionally, a mathematical expression for radiated sensitivity is presented.
-

Uncertainty Analysis Methodology for Measurements of Dynamic Millimeter-Wave Channels
01 August 2023 Robbert Schulpen, A. Bart Smolders, Ulf Johannsen, and L. A. Bronckers present a novel uncertainty analysis methodology to quantify uncertainties of condensed parameters in measurements of dynamic millimeter-wave channels. The bandwidth limitation and multipath threshold are identified as important impairments. Therefore, the methodology provides three uncertainty metrics for condensed parameters, namely a standard uncertainty to quantify the impact of random variations; a bias due to the multipath threshold; and a total bias including the impact of the bandwidth limitation.
-

End-to-End Channel Modeling and Generation Software Based on Statistical mmWave Channel Model
28 July 2023 Yusuke Koda, Ruiting Ouyang and Hiroshi Harada develop an end-to-end software to automatically perform channel modeling and simulation with statistical validity just by inputting measured power profiles. The developed software involves comprehensive algorithms to reach channel parameter extraction, such as multi-path component (MPC) extraction, MPC clustering, and maximum-likelihood estimations for respective parameters. They highlight that channel parameters reported by the IEEE 802.15.3c task group (TG) do not necessarily fit the original power profiles, highlighting the need to examine the validity of the existing parameters by leveraging the developed software.
-

Design of a Compact 4-Element GNSS Antenna Array With High Isolation Using a Defected Ground Structure (DGS) and a Microwave Absorber
25 July 2023 Abdullah Madni, and Wasif Tanveer Khan presents a compact (125 mm diameter) wideband 4-element antenna array with a high isolation level for global navigation satellite system (GNSS) applications. The array consists of four right hand circularly polarized (RHCP) single feed rectangular patch antennas that can cover BeiDou B1 band (1561.098 MHz), GPS L1 band (1575.42 MHz), Galileo E1 band (1575.42 MHz) and GLONASS G1 band (1602 MHz) of the GNSS upper L-band (1559 - 1610 MHz). The proposed array has a wide frequency bandwidth of 80 MHz with an axial ratio of less than 3 dB. The patch elements are designed on a substrate which has a high dielectric constant to achieve a compact size.
-

A Study on mm-Wave Propagation in and Around Buildings
20 July 2023 Leonardo Possenti, Marina Barbiroli, Enrico M. Vitucci, Franco Fuschini, Mattia Fosci, and Vittorio Degli-Esposti analyze in depth the peculiar characteristics of mm-wave propagation, joint measurement and simulation campaigns in indoor and outdoor microcellular environments. The investigation highlights that the assumption that mm-wave NLoS connectivity is hardly feasible is not necessarily true as significant reflections, scattering and even transmission mechanisms can provide good NLoS coverage in the considered indoor and outdoor scenarios. This is also reflected in the limited angle-spread differences between LoS and NLoS locations in some cases.
-

Dual-Port RHCP Compact Antenna at 868 MHz Using a 120° Hybrid Coupler
19 July 2023 Fabien Ferrero, and Le Huy Trinh present the design of a compact dual-port circularly polarized antenna based on the new coupler topology. The antenna can radiate a right-hand circular polarization (RHCP) in two opposite directions depending on the input port. In the proposed structure, the radiating system has three inverted F antennas connected to a 120° hybrid coupler. The modeling and design of the 5-ports hybrid coupler are described and experimentally validated.
-

Wide-Angle Beam Scanning Phased Array Antennas: A Review
18 July 2023 Ming Li, Shu-Lin Chen, Yanhui Liu and Y. Jay Guo investigate and discuss several challenges that hinder wide-angle beam scanning (WABS) for conventional phased array antennas (PAAs), including the strong mutual coupling, narrow beamwidth of the element antenna, etc. We then review and summarize a variety of innovative techniques to overcome these challenges. Subsequently, we discuss and analyze potential research gaps of WABS PAAs for future emerging applications.
-

Compact U6G Massive MIMO Antenna Arrays With Double-Layer Partial Reflective Decoupling Layers for Mutual Coupling Suppression
18 July 2023 Ting Liu, Jiayue Jiang, Luyu Zhao, Ge Zhao, Huiqing Zhai, Yuan-Ming Cai, Teyan Chen, and Wenwei Xu utilize a systematic decoupling strategy of two partial reflective decoupling layers (PRDLs) and dummy decoupling probes (DDPs) to suppress the complicated couplings in a ±45° dual-polarized, compact antenna array operating at Upper 6 GHz (U6G, 6425–7125 MHz) bands. Finely engineered neutralization electromagnetic waves are introduced by two PRDLs to counteract the original couplings. Two layers of PRDLs are placed above the antenna array in a step-by-step manner to gradually cancel out several major couplings while DDPs are placed around the antenna elements to reduce the remaining couplings.
-

Wide-Angle Beam Scanning Phased Array Antennas: A Review
18 July 2023 Ming Li, Shu-Lin Chen, Yanhui Liu, and Y. Jay Guo investigate and discuss several challenges that hinder wide-angle beam scanning (WABS) for conventional phased array antennas (PAAs), including the strong mutual coupling, narrow beamwidth of the element antenna, etc. in this review. They then review and summarize a variety of innovative techniques to overcome these challenges, and analyze potential research gaps of WABS PAAs for future emerging applications.
-

A 3-D Printed Ultra-Wideband Achromatic Metalens Antenna
17 July 2023 Yu-Xuan Xie, Geng-Bo Wu, Wen-Qiang Deng, Shu-Yan Zhu and Chi Hou Chan propose a millimeter-wave achromatic metalens antenna using three-dimensional (3D) printing technology to reduce the dispersion effect and enlarge its bandwidth. The proposed ultra-wideband achromatic metalens antenna consists of a convex-liked metalens (VLM) and a concave-liked metalens (CLM) integrated as a metalens group. The VLM is designed on the basis of dielectric posts with different heights. The calculated transmission phase (from 0 to 2π ) of VLM can be realized by changing the height of dielectric posts.
-

Airborne Reflector-Based Ground Penetrating Radar for Environmental and Archaeological Studies
17 July 2023 Zayed Mohammad, and Andrew M. Chrysler design and propose a wideband airborne reflector-based ground penetrating radar (GPR). It consists of 15 discrete panels, each panel supported by a single multi-rotor unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV). A lightweight, wideband Vivaldi antenna was developed as the feed structure. The antenna operates within the frequency range of 100–500 MHz and has a bandwidth of 387 MHz. The proposed antenna will possess a penetration depth of 2 m.
-

Feed Integration and Packaging of a Millimeter-Wave Antenna Array
17 July 2023 Matthew W. Nichols, Stavros Koulouridis, Satheesh B. Venkatakrishnan, Elias A. Alwan, and John L. Volakis present and demonstrat a novel approach for integrating a wideband vertically fed antenna array at Millimeter-Wave (mm-Wave) frequencies. Specifically, a novel cost-effective Antenna-In-Package (AiP) fabrication approach is presented, then a prototype operating from 55 GHz to 64 GHz is built while predicted performance is verified via measurements. This approach relies on separating fabrication into- the array and
- the back-end feeding board.
-

A 3-D Printed Ultra-Wideband Achromatic Metalens Antenna
17 July 2023 Yu-Xuan Xie, Geng-Bo Wu, Wen-Qiang Deng, Shu-Yan Zhu, and Chi Hou Chan propose a millimeter-wave achromatic metalens antenna using three-dimensional (3D) printing technology to reduce the dispersion effect and enlarge its bandwidth. The proposed ultra-wideband achromatic metalens antenna consists of a convex-liked metalens (VLM) and a concave-liked metalens (CLM) integrated as a metalens group.
-

A Technique to Realize Aperture Coupled Microstrip Patch as a Truly Low Cross-Polar Antenna by Mitigating the Major Issues Over its Skewed Radiation Planes
14 July 2023 Sk Rafidul, Chandrakanta Kumar, and Debatosh Guha address and resolve the limitation of the low cross-polarized (XP) radiations of aperture-fed microstrip patch by introducing a pair of additional printed loops adjacent to the radiating patch.Detailed investigations leading to the design insight have been presented. A C-band rectangular patch promises as much as 7 dB suppression in the diagonal plane XP level keeping the overall performance across the principal radiation planes unchanged.
-

Antenna Design for the Arctic Weather Satellite Microwave Sounder
14 July 2023 Roland Albers, Anders Emrich, and Axel Murk propose an antenna design for the Arctic Weather Satellite (AWS), a prototype mission for an operational constellation of microwave sounders, complimenting existing meteorological sounders. The AWS is a microsatellite with a single cross-track scanning radiometer operating in the 54, 89, 183 and 325 GHz bands. Due to the small platform size, the core design focus of the radiometer’s quasi-optics is less complexity and a more compact setup than comparable spaceborne microwave sounders. The main challenge for instrument performance is that only one of the four horns can be located in the focus of the scanning reflector. Consequently, scan angle dependent spillover variations and beam asymmetries can occur. This paper details the simulation and optimisation efforts of the quasi-optics to minimise the aforementioned effects.
-

Tuning the Angular Characteristics of Biomimetic Antenna Arrays
11 July 2023 Ines Dorsch Dominik Schwarz, Sarah Forster, and Christian Waldschmidt present the concept and the design process of a tunable Biomimetic Antenna Arrays (BMAA). By electronically tuning varactor diodes, such an array can adapt its angular characteristics depending on the direction-of-arrival (DoA) and signal strength of a radar target. The theoretical requirements for the desired task are examined with general S-parameter simulations. Extensive circuit simulations of a proposed architecture unveil a variety of achievable designs of tunable BMAAs. Radar measurements of different implementations in the 77 GHz range and the theoretical analysis are in good agreement.
-

Receive Mode Time-Modulated Antenna Array Incorporating Subsampling—Theoretical Concept and Laboratory Investigation
07 July 2023 Edward A. Ball, Sumin David Joseph and Alan Tennant present an eight element Subsampling Time Modulated Array (STMA) operating in receive mode with a carrier at 2.4 GHz using bespoke Radio Frequency (RF) hardware. Each STMA cell incorporates subsampling functionality, with the sampling frequency significantly below the carrier frequency and requiring minimal additional hardware. By using this concept, the hardware required for a receiver incorporating an antenna array can be reduced and costs saved. STMA design equations and architecture strategies are presented, and a prototype hardware demonstrator is introduced.
-

A Dual Wide-Band Mushroom-Shaped Dielectric Antenna for 5G Sub-6-GHz and mm-Wave Bands
05 July 2023 Reza Shamsaee Malfajani, Hamed Niknam, Sampada Bodkhe, Daniel Therriault, Jean-Jacques Laurin and Mohammad S. Sharawi present the design and implementation of a dual wide-band mushroom-shaped antenna. The antenna consists of a cylindrical dielectric resonator (cDRA), a cylindrical dielectric rod as a waveguide (cDR), and a dielectric lens (DL). The cDRA in conjunction with the DL acts as a sub-6-GHz antenna. At the mm-wave band, the small cDR acts as a waveguide, which transfers the wave from the feed toward the larger cDRA and the DL in order to produce a high gain.
-

A Diffusion Model for Multi-Layered Metasurface Unit Cell Synthesis
04 July 2023 Chen Niu, Mario Phaneuf, and Puyan Mojabi propose a deep learning approach based on a diffusion model to yield metasurface unit cell designs. This method takes desired two-port scattering parameters along with the frequency of operation in an attempt to synthesize three-layered metasurface unit cells. The core of this approach lies in casting the three-layered unit cell synthesis process as conditional three-channel binary image synthesis. The conditions are governed by the desired scattering parameters at a given frequency whereas the binary nature implies the presence and absence of metallic traces.
-

A Deep Learning-Based Approach to Design Metasurfaces From Desired Far-Field Specifications
04 July 2023 Chen Niu, Mario Phaneuf, Tianke Qiu and Puyan Mojabi develop a deep learning neural network model in conjunction with a method to incorporate auxiliary surface waves for the macroscopic design of transmitting metasurfaces. The main input to the neural network model is the user-defined desired far-field specifications. This network is used to calculate the required tangential electromagnetic fields on the metasurface. These fields will then be augmented by incorporating auxiliary surface waves along the metasurface for power redistribution to satisfy the requirement for having lossless and passive metasurfaces.
-

Statistical Evaluation of the Role of GNSS Signal Propagation Orientation in Low-Latitude Amplitude Scintillation Severity
30 June 2023 Alison Moraes, Jonas Sousasantos, Bruno J. Affonso, Paulo R. P. Silva, Eurico R. De Paula and João F. G. Monico perform an analysis considering aspects of the orientation of the propagation of the radio signals through the plasma bubbles structures to evaluate how this geometry can affect the scintillation profile. The dataset covers five months of records from three stations over the Brazilian region during the last solar cycle maximum. The initial results indicate that propagation paths fully aligned are consistently related to larger values of S4 and more severe scintillation.
-

Physics-Based Coherent Modeling of Long-Range Millimeter-Wave Propagation and Scattering in Rain
12 June 2023 Behzad Yektakhah and Kamal Sarabandi present a fast and accurate numerical method for phase coherent modeling of wave propagation and scattering in random media, like rain. In this approach, the random medium is divided into sufficiently large finite slabs and each slab is modeled as a network with multiple input/output ports where ports represent rays with different polarizations propagating in different directions entering and leaving the slabs. The proposed method considers multiple scattering among all scatterers and thus the entire physics of wave-particle interactions is accounted for.
-

Bandwidth Enhancement of Low-Profile Metasurface Antenna Using Nonuniform Geometries
08 June 2023 Hayden A. Banting and Carlos E. Saavedra investigate artificial magnetic conductor metasurface antennas using a robust, surrogate-assisted, differential evolution optimization technique. Using a uniform metasurface array configuration as a starting point, multiple array configurations are parameterized and the differential evolution optimizer yields nonuniform array geometries exhibiting wideband performance. Two prototypes are fabricated and characterized to experimentally confirm the advantages of proposed designs.
-

Post-Fabrication Technique to Manage Material Variations in 3-D Printed Microstrip Antenna Substrates
08 June 2023 Zere Iman, Zubair Akhter, Yiyang Yu and Atif Shamim present a post-fabrication technique capable of compensating for variations in the εr of 3D printed substrates, focusing on microstrip patch antennas (MPAs). The proposed technique, suitable for correcting the fr of a single microstrip patch antenna, uses either a single blind via or an array of vias in the 3D-printed substrate. Two MPAs were fabricated on a 3D-printed substrate and it is shown that their fr values can be shifted upward or downward by following the proposed guidelines.
-

3D Printed Hemispherically Radiating Antenna for Broadband Millimeter Wave Applications
23 May 2023 Lukas Engel, Danti Khouri, Konstantin Lomakin, Andreas Hofmann, Micha Kleinlein, Ingrid Ullmann, Martin Vossiek, and Gerald Gold present a 3D printed monolithic antenna for millimeter wave-sensing applications with a full hemispherical coverage. The antenna is designed as an ensemble of a waveguide horn antenna and a differentially fed dipole antenna. The slotted waveguide approach was utilized to improve the manufacturing quality on the waveguide inside.
-

Reflectarray Feeds Augmented With Size-Reducing GRIN Lenses for Improved Power Handling and Aperture Efficiency
19 May 2023 Eric B. Whiting, Galestan Mackertich-Sengerdy, Ryan J. Chaky, Colin A. Mussman, Sawyer D. Campbell, Pingjuan L. Werner, and Douglas H. Werner demonstrate highly effective approaches for optimizing GRIN lenses to achieve different design objectives including high gain radiation with a compact feed as well as improved aperture efficiency and power handling. Additive manufacturing is employed to fabricate the lenses, and measured results agree well with simulations.
-

Analytic Approximation of In-Body Path Loss for Implanted Antennas
15 May 2023 Mingxiang Gao, Zvonimir Sipus, and Anja K. Skrivervik present a simplified model of an implanted antenna that provides closed-form approximate expressions to estimate EM radiation from the implant. In particular, they extend the expressions for the reactive near-field losses to both deep and shallow implants, by taking into account the implantation depth.n The proposed approximate method is verified by comparing the results obtained with the full-wave simulations in the case of a miniature implanted antenna, and with both simulated and measured results from two practical examples found in the literature.
-

3-D Printable Synthetic Metasurface to Realize 2-D Beam-Steering Antenna
10 May 2023 Foez Ahmed, Touseef Hayat, Muhammad U. Afzal, Shiyu Zhang, Karu P. Esselle, and William G. Whittow present highly radio-frequency (RF) transparent phase gradient synthetic metasurfaces made of sub-wavelength-sized 3D printable meta-atoms with tailored permittivity that cannot be achieved with off-the-shelf, commercially available materials. The synthesized meta-atoms design uses one dielectric block of PREPERM ® ABS 1000 material with air and metallic inclusions to make low- and high-permittivity materials. The inclusions’ size and height are varied to achieve a complete phase range from 0 to 360°, while maintaining transmission magnitudes greater than −3.0 dB.
-

A 3D-Printed Encapsulated Dual Wide-Band Dielectric Resonator Antenna With Beam Switching Capability
09 May 2023 Reza Shamsaee Malfajani, Hamed Niknam, Sampada Bodkhe, Daniel Therriault, Jean-Jacques Laurin, and Mohammad S. Sharawi present the concept of encapsulated dielectric resonator antennas (E-DRAs). In E-DRAs, smaller-sized DRAs with a specific permittivity is embedded inside a larger DRA with a lower permittivity allowing for simultaneous efficient radiation at two widely separated and widely covered frequency bands. The proposed E-DRAs cover both the sub-6-GHz band (with a large size DRA) and mm-wave band (with smaller sized DRAs) for 5G and beyond applications.
-

3-D Printed All-Dielectric GRIN Lens Antenna With an Integrated Feeder
05 May 2023 Anastasios Paraskevopoulos, Francesca Maggiorelli, Ilir Gas Hi, Cristian Della Giovampaola, Matteo Albani, Stefano Maci present the design, fabrication, and experimental verification of a new type of Graded-index (GRIN) lens antenna with an integrated feeder. The continuously varying refractive index distribution is chosen appropriately to offer the rays collimation at the lens aperture. It is practically implemented by varying the material density in a host medium, thus realizing a new type of all-dielectric high gain antenna, entirely using 3D printing. This solution can find application to high gain wireless communication and measurement systems.
-

Fully Printed 3-D Antennas With Wideband Radiation Isotropy Based on Annular Currents Models
02 May 2023 Ruiqi Wang, Kirill Klionovski and Atif Shamim propose a theoretical model based on annular ring currents to synthesize quasi-isotropic antenna radiation patterns. The theoretical model shows that wideband radiation isotropy can be achieved by optimizing the combination of azimuthal currents. We subsequently present spherical and cubical ESA designs that achieve measured wide impedance and radiation isotropy bandwidths exceeding 10% for the GSM900 band.
-

Circularly-Polarized Patch Antennas With Enhanced Bandwidth Based on Capacitively Coupled Orthogonal Patch Radiators
02 May 2023 Qiong-Sen Wu, Xiao-Yu Tang, Xiao Zhang, Lei Zhu, Gary Zhang and Chun-Bing Guo propose circularly-polarized (CP) patch antennas with enhanced bandwidth based on capacitively coupled orthogonal patch radiators Several patch radiators are alternately arranged one by one along the x - and y -direction, producing orthogonal currents and far fields. The adjacent patch radiators are coupled to each other and the coupling structure not only contributes to power distribution but also introduces 90° phase shift for circularly-polarized radiation.
-

A Concept of Advanced Design Governed by Theoretically Predicted Current Distributions on the Ground Plane Beneath an Aperture-Fed Microstrip Antenna
02 May 2023 Debi Dutta, Debatosh Guha and Chandrakanta Kumar explore a way of mitigating near field issues based on theoretical analysis and propose a simple strategic approach to reform the same for a rectangular patch. A representative design, theoretical justification, and experimental studies with an S-band prototype have been presented. XP suppression by 11dB has been experimentally achieved in the diagonal (D-) plane with no considerable changes in its H- or E-plane. That eventually attains an overall XP discrimination by nearly 27dB from the perspective of 3D radiation scenario.
-

Uniform Analysis of Multipath Components From Various Scenarios With Time-Domain Channel Sounding at 300GHz
02 May 2023 Johannes M. Eckhardt, Alper Schultze, Ramez Askar, Tobias Doeker, Michael Peter, Wilhelm Keusgen, and Thomas Kürner present a uniform and collaborative data evaluation of measurement sets from two different time-domain channel sounders. The channels show a great variety of characteristics depending on the scenario, the line-of-sight condition and the signal-to-noise ratio requirements of the prospective communication system. The extracted multipath components are published as research data for future analytical studies and simulations in relevant scenarios for the sixth generation of mobile systems.
-

Planar Array Subarray Division Method in Microwave Wireless Power Transmission Based on PSO&K-Means Algorithm
27 April 2023 Qian He Zhang and Zhao Yang Shen propose a clustering algorithm based on a combination of the particle swarm algorithm and the K-means algorithm for the subarray partitioning of planar arrays to address the problem of maximizing beam collection efficiency in microwave wireless power transmission. The effectiveness of the proposed method is evaluated by integrating the beam collection efficiency with parameters such as the receiving area and the size of the planar array.
-

Indirect Applications of Additive Manufacturing for Antennas
10 April 2023 Jonathan D. Lundquist, Lauren Linkous, Umar Hasni, and Erdem Topsakal report the fabrication methodology of stereolithography (SLA) printed molds for metal and resin cast antennas. In the first method, a conical horn created using metal cast molds printed from a glass-filled resin utilizes a casting technique allowing for low-cost 3D printing to fabricate metal antennas. The second casting method demonstrates the interchangeability between creating parts via SLA printing with a glass-filled resin and using the same resin cast into a reusable Polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) mold.
-

3-D-Printed Spiral Leaky Wave Antenna With Circular Polarization
05 April 2023 Tomás Lira-Valdés, Eva Rajo-Iglesias, and Francisco Pizarro present the design, manufacturing and measurement of a fully dielectric leaky wave antenna operating at 18 GHz. The antenna is composed of a grounded dielectric substrate with a top dielectric Archimedean spiral corrugation, which allows obtaining a directive pencil-beam in broadside direction with circular polarization depending on the turning sense of the spiral.
-

3-D Printed Dually Symmetric Orthomode Transducer and Horn Antenna at X-Band
03 April 2023 Ian Goode, and Carlos E. Saavedra present a dually symmetric orthomode transducer (OMT) and horn antenna for both single port linearly polarized operation and dual port circular polarization use. The feed uses two waveguide splitters and a feed bend to feed a four-port horn antenna that has the two groups of ports orthogonal to each other to produce a symmetric radiation pattern. The feed is printed from 316L stainless steel while the horn is printed from a plastic polymer and metallized using aluminum tape.
-

Practical Correlation-Matrix Approaches for Standardized Testing of Wireless Devices in Reverberation Chambers
30 March 2023 Kate A. Remley, Sara Catteau, Ahmed Hussain, Carnot L. Nogueira, Mats Kristoffersen, John Kvarnstrand, Brett Horrocks, Jonas Fridén, Robert D. Horansky, and Dylan F. Williams extend the autocorrelation-based approaches currently used in standards to full correlation-matrix-based approaches in order to identify correlation between both spatially adjacent and non-adjacent samples in reverberation-chamber measurements. They employ a scalar metric that allows users to identify the number of effectively uncorrelated samples in new types of stirring sequences.
-

Systematic Design Method for Mutual Coupling Reduction in Closely Spaced Patch Antennas
28 March 2023 Hui Deng, Lei Zhu, and Zhao-An Ouyang present a systematic design approach to reduce the mutual coupling between a pair of closely spaced microstrip patch antennas (MPAs). This method can effectively overcome the main drawback of previous two-path cancellation methods, i.e., lack a systematic design guideline and heavily rely on the time-expensive trial-and-error procedure to mitigate mutual coupling in a best-effort manner. They propose the concept and workflow of the systematic design method, and introduce the circuit-level modeling upon the proposed two coupling routes.
-

Angle-Dependent Synthesis Method for Holographic Multi-Feed Antennas
27 March 2023 Thomas Frey, Maximilian Döring, Nico Riese, Christian Waldschmidt, and Tobias Chaloun present a novel synthesis method for holographic multi-feed antennas to combine all sub-holograms into an angle-dependent shared holographic aperture. In order to find the global error minimum between the shared holographic aperture and all ideal sub-holograms, a non-pixel-based genetic optimization is used. For a more accurately implementation of the analytical impedance tensor an eigenvector approach taking all tensor components into account is introduced.
-

Additive Manufacturing of Linear Continuous Permittivity Profiles and Their Application to Cylindrical Dielectric Resonator Antennas
16 March 2023 Simon P. Hehenberger, Stefano Caizzone, and Alexander G. Yarovoy consider the utilization of additive manufacturing (AM) to engineer the permittivity profile of dielectric resonator antennas (DRAs). The capabilities of AM are exploited to create continuously swept permittivity profiles and applied to cylindrical DRAs. The spatial variant lattices (SVL) synthesis algorithm is implemented to create the desired permittivity profiles from a single material, and resulting geometries are manufactured using a high-permittivity material in a fused deposition modeling AM process.
-

Additively-Manufactured All-Dielectric Microwave Polarization Converters Using Ceramic Stereolithography
15 March 2023 Steve M. Young, Mark Kauf, Jeffrey Kutsch, and Anthony Grbic report a class of all-dielectric, additively-manufactured polarization converters with tailored temporal frequency responses within the Ku and Ka microwave bands (15– 40 GHz). These multi-layer devices consist of cascaded, subwavelength, high-contrast gratings with different fill fractions and orientations, providing control over the effective anisotropic properties of each layer. Three example devices based on alumina/air gratings have been monolithically fabricated using ceramic stereolithography: a broadband reflective half-wave plate, a broadband isotropic polarization rotator, and a dual-band linear-to-circular polarization converter.
-

Highly Efficient Calibration of Antenna Arrays by Active Targets in the Near-Field
08 March 2023 Matthias Linder, Benedikt Meinecke, Enes Halici, Dominik Schwarz, and Christian Waldschmidt propose a calibration setup employing active calibration targets (ACT) to reduce the calibration effort, hereby defined as the number of required measurements. The setup allows the storage of a multitude of data points within a single measurement. It is placed in the near-field of the array to relax the requirements on the size of the anechoic chamber. Employing multiple targets makes it challenging to compensate for the near-field effects.
Menu
- Home
- About
- Awards
- Membership
- Publications
- Conferences
- Education